
The citric acid cycle—also known as the Krebs cycle, Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of biochemical reactions to release the energy stored in nutrients through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The chemical energy released is available under the form of ATP. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized.

Oxidative phosphorylation or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation is the metabolic pathway in which cells use enzymes to oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis.
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane.
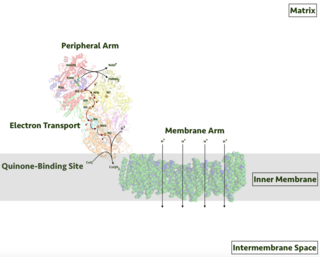
Respiratory complex I, EC 7.1.1.2 is the first large protein complex of the respiratory chains of many organisms from bacteria to humans. It catalyzes the transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and translocates protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane of bacteria.

Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other, nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD+ and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively.

Glutamate dehydrogenase is an enzyme observed in both prokaryotes and eukaryotic mitochondria. The aforementioned reaction also yields ammonia, which in eukaryotes is canonically processed as a substrate in the urea cycle. Typically, the α-ketoglutarate to glutamate reaction does not occur in mammals, as glutamate dehydrogenase equilibrium favours the production of ammonia and α-ketoglutarate. Glutamate dehydrogenase also has a very low affinity for ammonia, and therefore toxic levels of ammonia would have to be present in the body for the reverse reaction to proceed. However, in brain, the NAD+/NADH ratio in brain mitochondria encourages oxidative deamination. In bacteria, the ammonia is assimilated to amino acids via glutamate and aminotransferases. In plants, the enzyme can work in either direction depending on environment and stress. Transgenic plants expressing microbial GLDHs are improved in tolerance to herbicide, water deficit, and pathogen infections. They are more nutritionally valuable.

Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes that occur in animals. It takes part in gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, the glyoxylate cycle, amino acid synthesis, fatty acid synthesis and the citric acid cycle.

Malate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.37) (MDH) is an enzyme that reversibly catalyzes the oxidation of malate to oxaloacetate using the reduction of NAD+ to NADH. This reaction is part of many metabolic pathways, including the citric acid cycle. Other malate dehydrogenases, which have other EC numbers and catalyze other reactions oxidizing malate, have qualified names like malate dehydrogenase (NADP+).

Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) (EC 1.1.1.42) and (EC 1.1.1.41) is an enzyme that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate, producing alpha-ketoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) and CO2. This is a two-step process, which involves oxidation of isocitrate (a secondary alcohol) to oxalosuccinate (a ketone), followed by the decarboxylation of the carboxyl group beta to the ketone, forming alpha-ketoglutarate. In humans, IDH exists in three isoforms: IDH3 catalyzes the third step of the citric acid cycle while converting NAD+ to NADH in the mitochondria. The isoforms IDH1 and IDH2 catalyze the same reaction outside the context of the citric acid cycle and use NADP+ as a cofactor instead of NAD+. They localize to the cytosol as well as the mitochondrion and peroxisome.
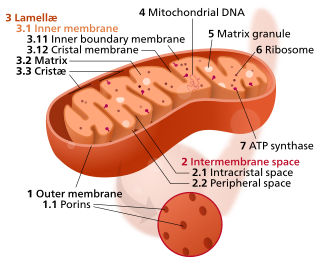
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions.[1] The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
The oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (OGDC) or α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex is an enzyme complex, most commonly known for its role in the citric acid cycle.
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-4 isomerase (3β-HSD) is an enzyme that catalyzes the biosynthesis of the steroid progesterone from pregnenolone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone from 17α-hydroxypregnenolone, and androstenedione from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in the adrenal gland. It is the only enzyme in the adrenal pathway of corticosteroid synthesis that is not a member of the cytochrome P450 family. It is also present in other steroid-producing tissues, including the ovary, testis and placenta. In humans, there are two 3β-HSD isozymes encoded by the HSD3B1 and HSD3B2 genes.
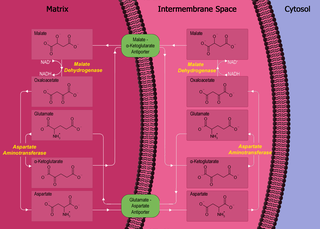
The malate–aspartate shuttle is a biochemical system for translocating electrons produced during glycolysis across the semipermeable inner membrane of the mitochondrion for oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotes. These electrons enter the electron transport chain of the mitochondria via reduction equivalents to generate ATP. The shuttle system is required because the mitochondrial inner membrane is impermeable to NADH, the primary reducing equivalent of the electron transport chain. To circumvent this, malate carries the reducing equivalents across the membrane.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase is a kinase enzyme which acts to inactivate the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase by phosphorylating it using ATP.

In enzymology, a homoserine dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Malate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.39) or NAD-malic enzyme (NAD-ME) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic) (EC 1.6.5.9, NDH-2, ubiquinone reductase, coenzyme Q reductase, dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-ubiquinone reductase, NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, NADH-coenzyme Q reductase, NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase, NADH-CoQ reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
NADH dehydrogenase is an enzyme that converts nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) from its reduced form (NADH) to its oxidized form (NAD+). Members of the NADH dehydrogenase family and analogues are commonly systematically named using the format NADH:acceptor oxidoreductase. The chemical reaction these enzymes catalyze is generally represented with the following equation:
Pseudohypoxia refers to a condition that mimics hypoxia, by having sufficient oxygen yet impaired mitochondrial respiration due to a deficiency of necessary co-enzymes, such as NAD+ and TPP. The increased cytosolic ratio of free NADH/NAD+ in cells (more NADH than NAD+) can be caused by diabetic hyperglycemia and by excessive alcohol consumption. Low levels of TPP results from thiamine deficiency.















