
Carl Borivoj Presl was a Czech botanist. The standard author abbreviation C.Presl is used to indicate this person as the author when citing a botanical name.

Dryopteris expansa, the alpine buckler fern, northern buckler-fern or spreading wood fern, is a species of perennial fern native to cool temperate and subarctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere, south at high altitudes in mountains to Spain and Greece in southern Europe, to Japan in eastern Asia, and to central California in North America. It prefers cool, moist mixed or evergreen forests and rock crevices on alpine slopes, often growing on rotting logs and tree stumps and rocky slopes. It is characteristically riparian in nature, and is especially associated with stream banks.

Luis Née was a French-born Spanish botanist and prolific collector of plant specimens who accompanied the Malaspina Expedition on its five-year scientific exploration of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands. In addition to his botanical work he was a pharmacist with a keen interest in medicinal plants and their applications.
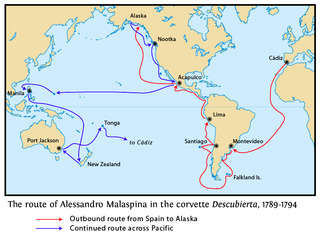
The Malaspina Expedition (1789–1794) was a five-year maritime scientific exploration commanded by Alejandro Malaspina and José de Bustamante y Guerra. Although the expedition receives its name from Malaspina, he always insisted on giving Bustamante an equal share of command. Bustamante had, however, acknowledged Malaspina as the "head of the expedition" since the beginning.

Nikolai Stepanovich Turczaninow was a Russian botanist and plant collector who first identified several genera, and many species, of plants.

Edward Lee Greene was an American botanist known for his numerous publications including the two-part Landmarks of Botanical History and the describing of over 4,400 species of plants in the American West.

Thaddeus Xaverius Peregrinus Haenke was a botanist who participated in the Malaspina Expedition, exploring a significant portion of the Pacific basin including the coasts of North and South America, Australia, the Philippines, New Zealand, and the Marianas. His collections of botanical specimens were the basis for the initial scientific descriptions of many plants in these regions, particularly South America and the Philippines. His extensive botanical work and far-ranging travel have prompted some to liken him to a "Bohemian Humboldt", named after Alexander von Humboldt, who made himself familiar with some of Haenke's findings before embarking on his journey to the Americas in 1799.

Alloteropsis is a genus of Old World plants in the grass family.

Antonio Pineda was a Spanish naturalist and military officer. He participated in the Malaspina Expedition as leader of the natural history team which included Thaddäus Haenke and Luis Née. His scientific exploration and collecting covered a significant portion of the Pacific basin including the coast of South America, Mexico, and the Philippines. Before his untimely death in the Philippines, Pineda had amassed a huge volume of documents including scientific reports, diaries, and logbooks as well as a significant collection of natural history specimens.

Philipp (Filip) Maximilian Opiz was a Czech-German forester and botanist.
Leptosolena is a genus of plants in the Zingiberaceae. It has only one known species, Leptosolena haenkei, endemic to the island of Luzon in the Philippines.

Bikkia tetrandra is an herbaceous member of the family Rubiaceae, distinguished by its white square-shaped flowers. It is native to Papuasia and islands of the western Pacific, including the Caroline Islands, Fiji, Mariana Islands, New Caledonia, New Guinea, Niue, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Vanuatu, and Wallis-Futuna Islands. The stems ignite easily and can be used to make torches or candles.

Myriopteris aurea, the golden lip fern or Bonaire lip fern, is a moderately-sized fern native to the Americas, a member of the family Pteridaceae. Unlike many members of its genus, its leaf is only modestly dissected into lobed leaflets (pinnae), which are hairy both above and below. One of the cheilanthoid ferns, until 2013 it was classified in the genus Cheilanthes as Cheilanthes bonariensis, when the genus Myriopteris was again recognized as separate from Cheilanthes. It typically grows on dry, rocky slopes, and ranges from Mexico, where it is common and widespread, and the southwestern United States south and east through Central and South America as far as Chile and Argentina.
Argyrochosma incana, the hairy false cloak fern, is a fern known from the southwestern United States through Mexico to Guatemala, and from a disjunct population in the Dominican Republic. It grows on rocky slopes and steep banks, often in forests. Like many of the false cloak ferns, it bears white powder on the underside of its leaves. First described as a species in 1825, it was transferred to the new genus Argyrochosma in 1987, recognizing their distinctness from the "cloak ferns".

Josef Karl Maly (1797–1866) was a physician botanist closely associated with the town of Graz, Austria. He published multiple works on Austrian flora, with a particular focus on medicinal and economic botany.

Piper hederaceum, also known as the giant pepper vine, is a vine in the pepper family Piperaceae. It is endemic to eastern Australia, growing in rainforests from Lockhart River, Queensland to Bermagui, New South Wales.

Piper interruptum is a vine in the pepper family Piperaceae, native to the eastern parts of Southeast Asia and to Melanesia and Queensland.

Piper guahamense, the Guam pepper, is a plant in the family Piperaceae, and is endemic to the Mariana Islands.

Callicarpa lamii is a plant in the mint family that is endemic to the Mariana Islands. It is one of two Callicarpa plants endemic to the Mariana Islands, the other being Callicarpa candicans var. paucinervia.

Peperomia tuberosa is a species of flowering plant from the genus Peperomia. It was first described by Philipp Maximilian Opiz and published in the book "Reliquiae Haenkeanae 1(3): 164. 1828 ". It primarily grows on wet tropical biomes. It may a synonym of Peperomia lanceolatopeltata. It grows primarily in the seasonally dry tropical biome.


















