
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes, which are Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario and are in general on or near the Canada–United States border. Hydrologically, lakes Michigan and Huron are a single body joined at the Straits of Mackinac. The Great Lakes Waterway enables modern travel and shipping by water among the lakes.

Salmon is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic and North Pacific basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, char, grayling, whitefish, lenok and taimen.

The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third largest river in the world by discharge volume, following the Amazon and the Ganges rivers. It is also the world's deepest recorded river, with measured depths of around 219.5 m (720 ft). The Congo-Lualaba-Chambeshi River system has an overall length of 4,700 km (2,920 mi), which makes it the world's ninth-longest river. The Chambeshi is a tributary of the Lualaba River, and Lualaba is the name of the Congo River upstream of Boyoma Falls, extending for 1,800 km (1,120 mi).

Henry Walter Bates was an English naturalist and explorer who gave the first scientific account of mimicry in animals. He was most famous for his expedition to the rainforests of the Amazon with Alfred Russel Wallace, starting in 1848. Wallace returned in 1852, but lost his collection on the return voyage when his ship caught fire. When Bates arrived home in 1859 after a full eleven years, he had sent back over 14,712 species of which 8,000 were new to science. Bates wrote up his findings in his best-known work, The Naturalist on the River Amazons.

The Chao Phraya is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.

A piranha or piraña is one of a number of freshwater fish in the family Serrasalmidae, or the subfamily Serrasalminae within the tetra family, Characidae in order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, floodplains, lakes and reservoirs. Although often described as extremely predatory and mainly feeding on fish, their dietary habits vary extensively, and they will also take plant material, leading to their classification as omnivorous.

The brown trout is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, Salmo trutta morpha fario, a lacustrine ecotype, S. trutta morpha lacustris, also called the lake trout, and anadromous forms known as the sea trout, S. trutta morpha trutta. The latter migrates to the oceans for much of its life and returns to fresh water only to spawn. Sea trout in Ireland and Great Britain have many regional names: sewin in Wales, finnock in Scotland, peal in the West Country, mort in North West England, and white trout in Ireland.

Osbert Salvin FRS was an English naturalist, ornithologist, and herpetologist best known for co-authoring Biologia Centrali-Americana (1879–1915) with Frederick DuCane Godman. This was a 52 volume encyclopedia on the natural history of Central America.
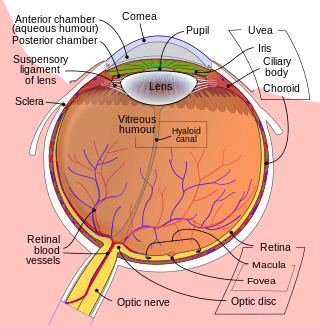
The fovea centralis is a small, central pit composed of closely packed cones in the eye. It is located in the center of the macula lutea of the retina.

A salmon run is an annual fish migration event where many salmonid species, which are typically hatched in fresh water and live most of the adult life downstream in the ocean, swim back against the stream to the upper reaches of rivers to spawn on the gravel beds of small creeks. After spawning, all species of Pacific salmon and most Atlantic salmon die, and the salmon life cycle starts over again with the new generation of hatchlings.

The Chinook salmon is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus Oncorhynchus. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other vernacular names for the species include king salmon, Quinnat salmon, Tsumen, spring salmon, chrome hog, Blackmouth, and Tyee salmon. The scientific species name is based on the Russian common name chavycha (чавыча).

William Lucas Distant was an English entomologist.
The Central East African lampeye is a species of fish in the family Poeciliidae. It is found in Tanzania and Uganda. Its natural habitats are swamps, freshwater lakes, freshwater marshes, intermittent freshwater marshes, and inland deltas. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Craterocephalus is a genus of small and slender brackish or freshwater silversides from Australia and New Guinea. It is the most diverse genus in the family Atherinidae, containing 25 of the 71 species.
The Finke River hardyhead is a species of fish in the family Atherinidae. It is endemic to the Finke River system in the Northern Territory, where it is widespread in open water or around aquatic vegetation. They occur in a wide range of salinity and pH and in Summer seek refuge in semi-permanent water holes. They are omnivores and feed on small crustaceans, insects, gastropods, polychaete worms, algae and fish eggs. This species shows a wide tolerance to temperature and salinity and is omnivore, probably spawning during warmer months. It was previously mis-identified as Craterocephalus eyresii.

Synodontis centralis is a species of upside-down catfish that is endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it occurs in the middle Congo Basin. It was first described by Max Poll in 1971. The original specimens were obtained in Ndwa village, Kunungu, Zaire. The species name centralis refers to its habitat in the central Congo Basin.

The Biologia Centrali-Americana is an encyclopedia of the natural history of Mexico and Central America, privately issued in 215 parts from 1879 to 1915 by the editors Frederick DuCane Godman and Osbert Salvin, of the British Museum in London. It was begun by Alfred Maudslay publishing his first long-form description of the Archaeology at Chichen Itza.
Hardyhead refers to a number of species of fish in the family Atherinidae, including:

The North American jaguar is a jaguar population in North America, ranging from the Southwestern United States to Central America. They are most associated to Central and South America. This population has declined over decades and was almost extirpated from the United States by 1960.

Craterocephalus eyresii, the Lake Eyre hardyhead, is a species of freshwater silverside from the family Atherinidae which is endemic to the Lake Eyre basin in Australia.















