The original inhabitants of Mauritania were the Bafour, presumably a Mande ethnic group, connected to the contemporary Arabized minor social group of Imraguen ("fishermen") on the Atlantic coast.
The music of Mauritania comes predominantly from the country's largest ethnic group: the Moors. In Moorish society musicians occupy the lowest caste, iggawin. Musicians from this caste used song to praise successful warriors as well as their patrons. Iggawin also had the traditional role of messengers, spreading news between villages. In modern Mauritania, professional musicians are paid by anybody to perform; affluent patrons sometimes record the entertainment, rather than the musicians themselves, and are then considered to own the recording.
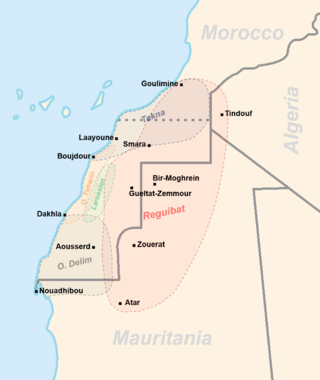
The Sahrawis, or Sahrawi people, are an ethnic group native to the western part of the Sahara desert, which includes the Western Sahara, southern Morocco, much of Mauritania, and along the southwestern border of Algeria. They are of mixed Hassani Arab and Sanhaji Berber descent, as well as West African and other indigenous populations.

Chinguetti is a ksar and a medieval trading center in northern Mauritania, located on the Adrar Plateau east of Atar. Chinguetti had a population of 4,800 as of 2013.

Atar is a town in northwestern Mauritania, the capital of the Adrar Region and the main settlement on the Adrar Plateau. Situated on the oued Seguellil, it is home to an airport, a museum and a historic mosque, constructed in 1674.

Kaédi is the largest city and administrative center of the Gorgol Region of Southern Mauritania, located on the border with Senegal. It is approximately 435 km from Mauritania's capital, Nouakchott.
Arab Islamic Front of Azawad was a militant rebel group in northern Mali. It was headed by Ahmed Ould Sidi Mohamed.

Mortagne is a commune in the Vosges department in Grand Est in northeastern France.

Tiris al-Gharbiyya was the name for the area of Western Sahara under Mauritanian control between 1975 and 1979.

The African Liberation Forces of Mauritania is an illegal and exiled paramilitary organization for Black natives and inhabitants of Mauritania.
The Hassane is a name for the traditionally dominant warrior tribes of the Sahrawi-Moorish areas of present-day Mauritania, southern Morocco and Western Sahara. Although lines were blurred by intermarriage and tribal re-affiliation, the Hassane were considered descendants of the Arab Maqil tribe Beni Hassan. They held power over Sanhadja Berber-descended zawiya (religious) and znaga (servant) tribes, extracting from these the horma tax in exchange for armed protection.

The Emirate of Trarza was a precolonial state in what is today southwest Mauritania. It has survived as a traditional confederation of semi-nomadic people to the present day. Its name is shared with the modern Region of Trarza. The population, a mixture of Berber tribes, had been there for a long time before being conquered in the 11th century by Hassaniya Arabic speakers from the north. Europeans later called these people Moors/Maures, and thus have titled this group "the Trarza Moors".

Issues impacting Women in Mauritanian society include female genital mutilation, child marriage, and polygamy.
Ahmad ibn al-Amin al-Shinqiti is one of Mauritania's most famous writers. He is the author of the geographical, literary and historical compendium Al-Wasit fi tarájim udaba al-Shinqit, ed. Fuad Sayyid, Cairo 1958. The survey is the only major Arabic-language work about Mauritania published by a Mauritanian author.

Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a sovereign country in Northwest Africa. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Western Sahara to the north and northwest, Algeria to the northeast, Mali to the east and southeast, and Senegal to the southwest. By land area Mauritania is the 11th-largest country in Africa and 28th-largest in the world; 90% of its territory is in the Sahara. Most of its population of some 4.3 million lives in the temperate south of the country, with roughly a third concentrated in the capital and largest city, Nouakchott, on the Atlantic coast.
El Mina is a suburb of Nouakchott and urban commune in western Mauritania. It has a population of 95,011.

The Mauritanian passport is an official travel document issued by the Agence Nationale Du Registre Des Populations Et Des Titres Sécurisés .. That grants citizens of Mauritania for international travel in accordance with visa requirements. It serves to provide identification and citizenship verification, allowing holders to travel worldwide and seek entry into other countries.
T'heydinn or T'heydinne is a Moorish epic ensemble of Mauritania. It is an important literary and artistic manifestation of the Hassaniya language and was, in 2011, added to the UNESCO's Intangible Cultural Heritage List.

Elections to the French National Assembly were held in Mauritania on 10 November 1946. Previously Mauritania had elected MPs in a single joint constituency with neighbouring Senegal, but the new 1946 constitution had separated the two territories politically, giving Mauritania one seat in the Assembly. The result was a victory for Horma Ould Babana, a member of the French Section of the Workers' International. His opponents were Yvon Razac, a member of the MRP and the candidate favored by the French government and traditional Moorish leaders, and Souleymane Diop, an independent.

Noura Mint Seymali is a Mauritanian griot, singer, songwriter, and instrumentalist.













