Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognised union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between them and their in-laws. It is nearly a cultural universal, but the definition of marriage varies between cultures and religions, and over time. Typically, it is an institution in which interpersonal relationships, usually sexual, are acknowledged or sanctioned. In some cultures, marriage is recommended or considered to be compulsory before pursuing sexual activity. A marriage ceremony is called a wedding, while a private marriage is sometimes called an elopement.

Polygyny is a form of polygamy entailing the marriage of a man to several women. The term polygyny is from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (polugunía); from Ancient Greek πολύ (polú) 'many' and γυνή (gunḗ) 'woman, wife'.
Polygamy is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more than one husband at the same time, it is called polyandry. In sociobiology and zoology, researchers use polygamy in a broad sense to mean any form of multiple mating.

A spouse is a significant other in a marriage. The word 'spouse' can only ever be used when a couple is married legally or by common law. A male spouse is called a husband while a female spouse is called a wife.

A wife is a woman in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until their marriage is legally dissolved with a divorce judgment; or until death, depending on the kind of marriage. On the death of her partner, a wife is referred to as a widow. The rights and obligations of a wife to her partner and her status in the community and law vary between cultures and have varied over time.
Conflict of marriage laws is the conflict of laws with respect to marriage in different jurisdictions. When marriage-related issues arise between couples with diverse backgrounds, questions as to which legal systems and norms should be applied to the relationship naturally follow with various potentially applicable systems frequently conflicting with one another.
Lobolo or lobola in Zulu, Xhosa, Swazi, Silozi, and northern and southern Ndebele roora in [ChiShona}, sometimes referred to as "bride wealth" or "bride price" is a property in livestock or kind, which a prospective husband, or head of his family, undertakes to give to the head of a prospective wife's family in gratitude of letting the husband marry their daughter and for the brides family for raising her.

Marriage law is the body of legal specifications and requirements and other laws that regulate the initiation, continuation, and validity of marriages, an aspect of family law, that determine the validity of a marriage, and which vary considerably among countries in terms of what can and cannot be legally recognized by the state.

Traditional Sunni and Shia Islamic marital jurisprudence allows Muslim men to be married to multiple women. Men can have up to four wives at a time according to the islamic jurisprudence.
Criticisms of marriage are arguments against the practical or moral value of the institution of marriage or particular forms of matrimony. These have included the effects that marriage has on individual liberty, equality between the sexes, the relationship between marriage and violence, philosophical questions about how much control can a government have over its population, the amount of control a person has over another, the financial risk when measured against alternatives and divorce, and questioning of the necessity to have a relationship sanctioned by government or religious authorities.
Akin to Uganda, Republic of the Congo and the Central African Republic, Zambia is one of the few Christian nations that allows polygamous unions to be legally formed. Under Zambian law, polygamous unions may be contracted and they have been reported to be extremely widespread in the nation. Similar to most countries that provide polygamy as a form of marriage, the first wife must consent to the practice of polygamy before she marries her husband. If she declines, her husband will not be allowed to marry another woman while married to his current wife. According to a 2003 survey, 16% of marriages in Zambia are polygamous. While frequently more common in rural areas, the practice can also be found in more urban settings.

The legal status of polygamy varies widely around the world. Polygamy is legal in 58 out of nearly 200 sovereign states, the vast majority of them being Muslim-majority countries. Some countries that permit polygamy have restrictions, such as requiring the first wife to give her consent.

Marriage in China has undergone change during the country's economic reform period, especially as a result of new legal policies such as the New Marriage Law of 1950 and the family planning policy in place from 1979 to 2015. The major transformation in the twentieth century is characterized by the change from traditional structures for Chinese marriage, such as arranged marriage, to one where the freedom to choose one’s partner is generally respected. However, both parental and cultural pressures are still placed on many individuals, especially women, to choose socially and economically advantageous marriage partners. In 2024, China was on track to record fewer marriages since records began in 1980. In 2010, the 1.96 million couples applying for divorce in 2010 represented a rate 14% higher than the year before and doubled from ten years ago. Despite the rising divorce rate, marriage is still thought of as a natural part of the life course and as a responsibility of good citizenship in China.
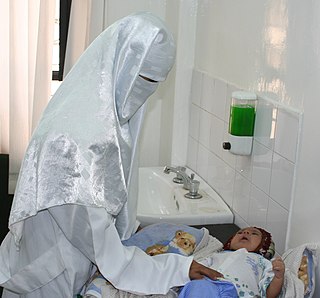
Women in Yemen suffer from gender-based discrimination due to the highly patriarchal character of Yemeni society. Although the government of Yemen has made efforts to improve the rights of women, many cultural and religious norms stand in the way of equal rights for women. Poor enforcement of the legislation by the Yemeni government exacerbates the problem.

Women in Madagascar generally live longer than men, whom they outnumber. Marrying young, they are traditionally subservient to their husbands. Roughly a third have their first child before the age of 19, and those who wish to delay having children may not have access to contraceptives. Although it is illegal with no exceptions, abortion is common, with an estimated 24 percent of women having had one. While they are constitutionally equal to men, they have unequal property rights and employment opportunities in certain areas.

Women in South Sudan are women who live in and are from South Sudan. Since the Independence of South Sudan on 9 July 2011, these women have gained more power but still face issues of inequality. Many women in this area do not have adequate access to health resources and education. While these women often face inequality, there has been progress since South Sudan's official declaration of independence. In recent years, this inequality has gained national attention and people have become more interested in the issue of child marriage that this area faces. Along with this, there has started to be a focus on the very high level of maternal mortality in South Sudan. With a maternal mortality rate of 789 deaths per 100,000 live births, South Sudan has one of the highest rates in the world.

Women in Belgium are European women who live in or are from Belgium. Generation after generation, Belgian women are able to close the "occupational gender gap". In younger generations, this is due to the increasing availability of "part-time jobs in services" for women. In 1999, the average earnings of a Belgian woman was 91 percent of the salary of a Belgian man. When not doing part-time jobs, Belgian women still "do more of the domestic work", depending on the agreement between female and male partners.
A marry-your-rapist law, marry-the-rapist law, or rape-marriage law is a rule of rape law in a jurisdiction under which a man who commits rape, sexual assault, statutory rape, abduction or other similar act is exonerated if he marries his female victim, or in some jurisdictions at least offers to marry her. The "marry-your-rapist" law is a legal way for the accused to avoid prosecution or punishment.
Even in the modern era, gender inequality remains an issue in Japan. In 2015, the country had a per-capita income of US$38,883, ranking 22nd of the 188 countries, and No. 18 in the Human Development Index. In the 2019 Gender Inequality Index report, it was ranked 17th out of the participating 162 countries, ahead of Germany, the UK and the US, performing especially well on the reproductive health and higher education attainment indices. Despite this, gender inequality still exists in Japan due to the persistence of gender norms in Japanese society rooted in traditional religious values and government reforms. Gender-based inequality manifests in various aspects from the family, or ie, to political representation, to education, playing particular roles in employment opportunities and income, and occurs largely as a result of defined roles in traditional and modern Japanese society. Inequality also lies within divorce of heterosexual couples and the marriage of same sex couples due to both a lack of protective divorce laws and the presence of restrictive marriage laws. In consequence to these traditional gender roles, self-rated health surveys show variances in reported poor health, population decline, reinforced gendered education and social expectations, and inequalities in the LGBTQ+ community.
Child marriage in the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the eighteenth highest in the world. In a child marriage, one or both parties are under the age of eighteen years old. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), 37% of girls are married before they turn eighteen, and 10% of girls are married before age fifteen. Though significantly less than the rate of child marriage for girls, 6% of boys in the DRC are married before age eighteen.












