
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae, a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth except glaciers. The world's richest diversity of orchid genera and species is found in the tropics.

In the botanical classification of plants, Aeridinae Pfitzer is a subtribe of the tribe Vandeae whose representatives all have a monopodial growth habit and do not possess pseudobulbs.

The taxonomy of the Orchidaceae (orchid family) has evolved slowly during the last 250 years, starting with Carl Linnaeus who in 1753 recognized eight genera. De Jussieu recognized the Orchidaceae as a separate family in his Genera Plantarum in 1789. Olof Swartz recognized 25 genera in 1800. Louis Claude Richard provided us in 1817 with the descriptive terminology of the orchids. (See External links below). The next step was taken in 1830-1840 by John Lindley, who recognized four subfamilies. He is generally recognized as the father of orchid taxonomy. The next important step was taken by George Bentham with a new classification, recognizing subtribes for the first time. This classification was first presented in a paper that Bentham read to the Royal Society in 1881. Then it was published in 1883 in the final volume of Genera Plantarum. The next great contributors were Pfitzer (1887), Schlechter (1926), Mansfeld (1937), Dressler and Dodson (1960), Garay (1960, 1972), Vermeulen (1966), again Dressler (1981). and Burns-Balogh and Funk (1986). Dressler's 1993 book had considerable influence on later work.

Adrorhizinae is an orchid subtribe in the tribe Vandeae.

Disperis is a genus of plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It has about 78 species. Most of the species are from tropical and southern Africa, as well as Indian Ocean islands. A few are native to the tropical or the warmer subtropical regions of Asia and Malesia.

Dendrophylax is a genus of leafless neotropical orchids native to Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and Florida. The name is from Greek δένδρον ("tree") and φύλαξ. One species, Dendrophylax lindenii, featured heavily in the book The Orchid Thief.

Rhynchostylis is a genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), closely allied to the genus Vanda and comprising four currently accepted species native to the Indian Subcontinent, China, Indochina, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines.

The Vandeae is a large monophyletic tribe within the family of orchids.
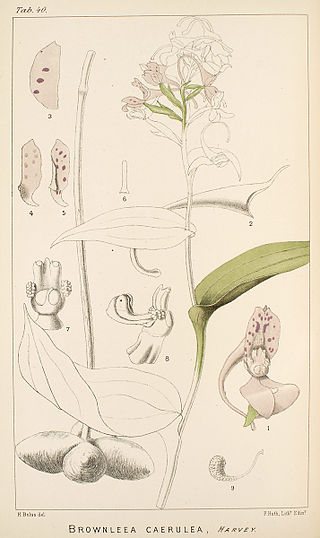
Brownleea is a genus of flowering plants from the family Orchidaceae native to Africa and Madagascar. Eight species are known.
- Brownleea coeruleaHarv. ex Lindl.
- Brownleea galpiniiBolus
- Brownleea graminicolaMcMurtry
- Brownleea macrocerasSond.
- Brownleea maculataP.J.Cribb
- Brownleea mulanjiensisH.P.Linder
- Brownleea parvifloraHarv. ex Lindl.
- Brownleea recurvataSond.

Cyrtorchis is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family Orchidaceae native to Africa.
Triceratorhynchus is a genus of flowering plants of the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to central Africa: Cameroon, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, and Kenya.

Polystachya neobenthamia is a species of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is terrestrial, lithophilic and grows among leaf litter and other detritus on rock faces. It is endemic to Tanzania.

Pachites is a genus of flowering plants in the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It contains two known species, both endemic to South Africa. One of these, Pachites appressus, is very rare.

Angraecinae is a subtribe in the family Orchidaceae. The subtribe consists of approximately 47 genera. The type genus is Angraecum. Most of the genera are endemic to Africa, Madagascar and other Indian Ocean Islands, a few genera can also be found in the Americas.

Aerangidinae is classified as a subtribe within the tribe Vandeae in the family Orchidaceae. However, it is likely to soon become a synonym of Angraecinae with the genera below re-allocated to this sub-tribe. As traditionally circumscribed, it consists of 36 genera and about 300 species. The type genus of this subtribe is Aerangis. Members of this group are epiphytic orchids having a monopodial habit and are endemic to tropical Africa and Madagascar. They are distinguished from the other subtribes in Vandeae by having an elongate rostellum, an elongate spur, and two pollinia. Most genera in the group indicate pollination by moths, however leaf beetles are reported as frequent visitors, but it is unknown whether they are vectors for pollination.

The Eriinae form a subtribe of Podochileae, a tribe of the orchid family (Orchidaceae). The name is derived from the genus Eria.

Dendrobieae is a tribe in the subfamily Epidendroideae, in the family Orchidaceae. The Dendrobieae are mostly tropical, epiphytic orchids which contain pseudobulbs.

Diseae is an orchid tribe in the subfamily Orchidoideae. It was recognized in Genera Orchidacearum volume 2, which was published in 2001. It consisted of 12 genera in five subtribes. In molecular phylogenetic studies that were published after 1999, it was shown that Diseae is paraphyletic over the tribe Orchideae. In a classification of orchids that was published in 2015, Diseae was not recognized, but was instead placed in synonymy under Orchideae.

Coryciinae is a subtribe of orchids that has been differently defined and placed in the two classification systems that are currently in use for orchids. Genera Orchidacearum, which is currently the definitive work on orchid taxonomy, delimits Coryciinae as consisting of five genera: Disperis, Evotella, Ceratandra, Pterygodium, and Corycium, and it places Coryciinae in the mostly African tribe Diseae, along with four other subtribes: Brownleeinae, Huttonaeinae, Disinae, and Satyriinae. The genera of Coryciinae are small to medium in size and the number of species in each genus is as follows: Disperis (78), Pterygodium (19), Corycium (15), Ceratandra (6), and Evotella (1).

Zygopetalinae is an orchid subtribe in the tribe Cymbidieae with 418 species.


















