Related Research Articles
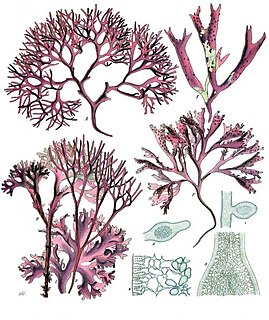
Chondrus crispus—commonly called Irish moss or carrageen moss —is a species of red algae which grows abundantly along the rocky parts of the Atlantic coast of Europe and North America. In its fresh condition this protist is soft and cartilaginous, varying in color from a greenish-yellow, through red, to a dark purple or purplish-brown. The principal constituent is a mucilaginous body, made of the polysaccharide carrageenan, which constitutes 55% of its dry weight. The organism also consists of nearly 10% dry weight protein and about 15% dry weight mineral matter, and is rich in iodine and sulfur. When softened in water it has a sea-like odour and because of the abundant cell wall polysaccharides it will form a jelly when boiled, containing from 20 to 100 times its weight of water.
Pyropia columbina, Southern laver or karengo in the Māori language, is a species of edible seaweed traditionally harvested by South Island Māori. It is closely related to Japanese Nori and Welsh laverbread.

Porphyra is a coldwater seaweed that grows in cold, shallow seawater. More specifically, it belongs to red algae phylum of laver species, comprising approximately 70 species. It grows in the intertidal zone, typically between the upper intertidal zone and the splash zone in cold waters of temperate oceans. In East Asia, it is used to produce the sea vegetable products nori and gim. There are considered to be 60 to 70 species of Porphyra worldwide and seven around Britain and Ireland where it has been traditionally used to produce edible sea vegetables on the Irish Sea coast. Porphyra is a chief source of plant-based vitamin B12.
The history of phycology is the history of the scientific study of algae. Human interest in plants as food goes back into the origins of the species and knowledge of algae can be traced back more than two thousand years. However, only in the last three hundred years has that knowledge evolved into a rapidly developing science.

Ectocarpales is a very large order in the brown algae. The order includes families with pseudoparenchymatous (Splachnidiaceae) or true parenchymatous (Scytosiphonaceae) tissue. Pseudoparenchymatous refers to a filamentous alga with cells packed very close together to give an appearance of parenchymatous tissue, the latter being composed of cells which can truly divide in three dimensions, unusual among the algae. Filamentous algae are composed of cells that divide along a single plane, allowing only elongation to form filaments of one or more rows of cells. Algae that can divide in two planes can form sheet-like thalli or bodies. Cells that can divide in a third plane potentially allow for the organism to develop a more complex body plan, and diversification of body plans into an erect thallus of some sort and a holdfast for attaching the upright portion to the substrate.

Durvillaea is a genus of brown algae in the monotypic family Durvillaeaceae. All members of the genus are found in the southern hemisphere, including Australia, New Zealand, South America, and various subantarctic islands.

Conceptacles are specialized cavities of marine and freshwater algae that contain the reproductive organs. They are situated in the receptacle and open by a small ostiole. Conceptacles are present in Corallinaceae, and Hildenbrandiales, as well as the brown Fucales. In the Fucales there is no haploid phase in the reproductive cycle and therefore no alternation of generations. The thallus is a sporophyte. The diploid plants produce male (antheridia) and female (oogonia) gametangia by meiosis. The gametes are released into the surrounding water; after fusion, the zygote settles and begins growth.

Red algae, or Rhodophyta, are one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta also comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 currently recognized species with taxonomic revisions ongoing. The majority of species (6,793) are found in the Florideophyceae (class), and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats but are relatively rare in freshwaters. Approximately 5% of the red algae occur in freshwater environments with greater concentrations found in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, there are no terrestrial species, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck where the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.
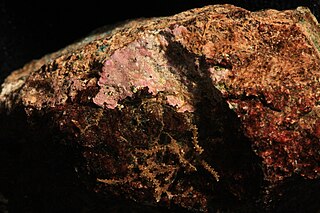
Hildenbrandia is a genus of thalloid red alga comprising 26 species. The slow-growing, non-mineralized thalli take a crustose form. Hildenbrandia reproduces by means of conceptacles and produces tetraspores.

Apophlaea is a genus of thalloid algae that is endemic to New Zealand. This genus has two species, both from the high intertidal zone on New Zealand's coasts. Specimens can reach around 15 cm in size. The thalli take a crustose form, but also contain upright, branching frond-like protrusions that reach 5–8 cm in height. Secondary pit connections and secondary pit connectionsare present in the organisms. Apophlaea reproduces by means of conceptacles; it produces tetraspores.

Pyropia tenera, also known as gim or nori, is a red algal species in the genus Pyropia. The specific name, tenera, means "delicate" and alludes to its small size. It typically grows to lengths between 20 and 50 cm. It is most typically found in the western Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean.
Kallymenia ercegovicii a red algae species first discovered in the Mediterranean Sea, in the coast of Croatia.

Clymene coleana, formerly known as Porphyra cinnamomea, is a red alga species in the genus Clymene. This species is endemic to New Zealand.
Pyropia rakiura, formerly known as Porphyra rakiura, is a red alga species in the genus Pyropia, known from New Zealand. It is monostromatic, monoecious, and grows in the intertidal zone, predominantly on rock substrata. With P. cinnamomea, P. coleana and P. virididentata, they can be distinguished by morphology, as well as geographical, ecological and seasonal distribution patterns, and importantly, chromosome numbers, which in this species n = 2. Finally, these four species are distinguished by a particular nucleotide sequence at the 18S rDNA locus.
Pyropia virididentata, formerly known as Porphyra virididentata, is a red alga species in the genus Pyropia. It is endemic to New Zealand. It is monostromatic, monoecious, and grows in the intertidal zone, predominantly on rock substrata. With Porphyra cinnamomea, Pyropia rakiura and Clymene coleana, they can be distinguished by morphology, as well as geographical, ecological and seasonal distribution patterns, and importantly, chromosome numbers, which in this species n = 3. Finally, these four species are distinguished by a particular nucleotide sequence at the 18S rDNA locus.

Pyropia is a genus of red alga [seaweed] in the family Bangiaceae. It is found around the world in intertidal zones and shallow water. The genus has folding frond-like blades which are either red, brown or green. Some Pyropia species are used to create nori, and are thus important subjects for aquaculture.

Batrachospermaceae is a family of fresh water red algae (Rhodophyta). Genera within the Batrachospermaceae generally have a "Lemanea-type" life history with carpospores germinating to produce chantransia. Sporophyte phase with meiosis occurs in an apical cell to produce the gametophyte stage. Pit connections have two pit plug cap layers with the other layer enlarged. This family of freshwater red algae is uniaxial, meaning each filament with a single apical cell. The genera included within Batrachospermaceae are listed in the table below.
Pythium porphyrae, is a parasitic species of oomycete in the family Pythiaceae. It is the cause of red rot disease or red wasting disease, also called akagusare (赤ぐされ) in Japanese. The specific epithet porphyrae (πορφυρα) stems from the genus of one of its common hosts, Porphyra, and the purple-red color of the lesions on the thallus of the host. However, many of its hosts have been moved from the genus Porphyra to Pyropia.

Timothy John Entwisle, is an Australian botanist, much of whose research work is in phycology (algae). See for example the articles. He was awarded a Ph.D. from La Trobe University in 1986 for work on the taxonomy of Vaucheria.

Pyrophyllon subtumens is an obligate red algal epiphyte of Durvillaea southern bull-kelp, and is endemic to New Zealand.
References
- ↑ Nelson, W (2001). "Four new species of Porphyra (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) from the New Zealand region described using traditional characters and 18S rDNA sequence data". Cryptogamie Algologie. 22 (3): 263–284. doi:10.1016/S0181-1568(01)01060-1. ISSN 0181-1568.