
Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

Chondrus crispus—commonly called Irish moss or carrageenan moss —is a species of red algae which grows abundantly along the rocky parts of the Atlantic coasts of Europe and North America. In its fresh condition it is soft and cartilaginous, varying in color from a greenish-yellow, through red, to a dark purple or purplish-brown. The principal constituent is a mucilaginous body, made of the polysaccharide carrageenan, which constitutes 55% of its dry weight. The organism also consists of nearly 10% dry weight protein and about 15% dry weight mineral matter, and is rich in iodine and sulfur. When softened in water it has a sea-like odour. Because of the abundant cell wall polysaccharides, it will form a jelly when boiled, containing from 20 to 100 times its weight of water.

Coralline algae are red algae in the order Corallinales. They are characterized by a thallus that is hard because of calcareous deposits contained within the cell walls. The colors of these algae are most typically pink, or some other shade of red, but some species can be purple, yellow, blue, white, or gray-green. Coralline algae play an important role in the ecology of coral reefs. Sea urchins, parrot fish, and limpets and chitons feed on coralline algae. In the temperate Mediterranean Sea, coralline algae are the main builders of a typical algal reef, the Coralligène ("coralligenous"). Many are typically encrusting and rock-like, found in marine waters all over the world. Only one species lives in freshwater. Unattached specimens may form relatively smooth compact balls to warty or fruticose thalli.

Florideophyceae is a class of exclusively multicellular red algae. They were once thought to be the only algae to bear pit connections, but these have since been found in the filamentous stage of the Bangiaceae. They were also thought only to exhibit apical growth, but there are genera known to grow by intercalary growth. Most, but not all, genera have three phases to the life cycle. In the subclass Nemaliophycidae there are three orders, Balbianiales, Batrachospermales, and Thoreales, which lives exclusively in freshwater.

The Santa Cruz cypress is a species of North American tree within the cypress family. The species is endemic to the Santa Cruz Mountains within the Santa Cruz and San Mateo counties of west-central California. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service listed the species on the Endangered Species Act in 1987 due to increasing threats from habitat loss and disruption of natural forest fire regimes. In 2016, the conservation status of the Santa Cruz cypress changed to Threatened. The cited reasoning was a decrease in threats against their habitat.

Ochrophytes, also known as heterokontophytes or stramenochromes, are a group of algae. They are the photosynthetic stramenopiles, a group of eukaryotes, organisms with a cell nucleus, characterized by the presence of two unequal flagella, one of which has tripartite hairs called mastigonemes. In particular, they are characterized by photosynthetic organelles or plastids enclosed by four membranes, with membrane-bound compartments called thylakoids organized in piles of three, chlorophyll a and c as their photosynthetic pigments, and additional pigments such as β-carotene and xanthophylls. Ochrophytes are one of the most diverse lineages of eukaryotes, containing ecologically important algae such as brown algae and diatoms. They are classified either as phylum Ochrophyta or Heterokontophyta, or as subphylum Ochrophytina within phylum Gyrista. Their plastids are of red algal origin.

Peyssonnelia is a genus of thalloid red alga, named after naturalist Jean-André Peyssonnel (1694–1759) It includes the algae commonly known as rumoi-iwanokawa, mayoi-iwanokawa and akase-iwanokawa. Specimens can reach around 20 cm in size. Peyssonnelia produces tetraspores.
The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms.

Red algae, or Rhodophyta, make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 genera amidst ongoing taxonomic revisions. The majority of species (6,793) are Florideophyceae, and mostly consist of multicellular, marine algae, including many notable seaweeds. Red algae are abundant in marine habitats. Approximately 5% of red algae species occur in freshwater environments, with greater concentrations in warmer areas. Except for two coastal cave dwelling species in the asexual class Cyanidiophyceae, no terrestrial species exist, which may be due to an evolutionary bottleneck in which the last common ancestor lost about 25% of its core genes and much of its evolutionary plasticity.
Goniotrichum is a disputed genus of red algae in the monotypic order Goniotrichales and class Bangiophyceae.

Plocamium is a genus of red algae in the family Plocamiaceae. It contains around 40 species and has a cosmopolitan distribution in temperate seas, although it is most diverse in the southern hemisphere. It is widely distributed in tropical and also warm-temperate and cold-temperate seas, such as northern Europe, the northern Arabian Sea and western Australia. They are also found in the Antarctic regions of Admiralty Bay and Terra Nova Bay.
Saltwater fish, also called marine fish or sea fish, are fish that live in seawater. Saltwater fish can swim and live alone or in a large group called a school.

Atya lanipes is a freshwater amphidromous shrimp of the Atyidae family in the Decapoda order. It is found widely in the Caribbean and is common in the Toro Negro State Forest in central Puerto Rico. It is also known as jonga and in some places people refer to it as "guábara” or “chágara”.
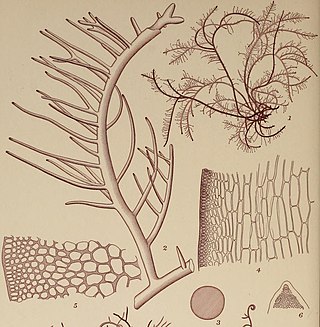
Hypnea is a genus of red algae, and a well known carrageenophyte.

Cyanidiophytina is a subdivision of red algae.

Palmariales is an order of marine algae. It includes the edible seaweed dulse.

Naccariaceae is a family of red algae in the order Bonnemaisoniales, with 3 monotypic genera that are found in both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.

Halymeniales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae.

Peyssonneliales is a monotypic order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae. It contains only 1 known family, PeyssonneliaceaeDenizot, M., 1968.














