The Mesozoic Era is the era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about 252 to 66 million years ago, comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of gymnosperms and of archosaurian reptiles, such as the dinosaurs; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic.

The Permian is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period 298.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia.
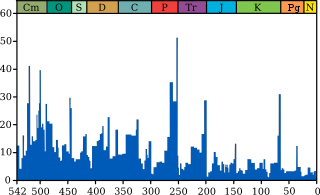
Approximately 251.9 million years ago, the Permian–Triassicextinction event forms the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, and with them the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras. It is Earth's most severe known extinction event, with the extinction of 57% of biological families, 83% of genera, 81% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species. It is also the greatest known mass extinction of insects. It is the greatest of the "Big Five" mass extinctions of the Phanerozoic. There is evidence for one to three distinct pulses, or phases, of extinction.

The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic.

Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male or female. Cycads vary in size from having trunks only a few centimeters to several meters tall. They typically grow slowly and have long lifespans. Because of their superficial resemblance to palms or ferns, they are sometimes mistaken for them, but they are not closely related to either group. Cycads are gymnosperms (naked-seeded), meaning their unfertilized seeds are open to the air to be directly fertilized by pollination, as contrasted with angiosperms, which have enclosed seeds with more complex fertilization arrangements. Cycads have very specialized pollinators, usually a specific species of beetle. Both male and female cycads bear cones (strobili), somewhat similar to conifer cones.

Gnetophyta is a division of plants, grouped within the gymnosperms, that consists of some 70 species across the three relict genera: Gnetum, Welwitschia, and Ephedra. The earliest unambiguous records of the group date to the Jurassic, and they achieved their highest diversity during the Early Cretaceous. The primary difference between gnetophytes and other gymnosperms is the presence of vessel elements, a system of small tubes (xylem) that transport water within the plant, similar to those found in flowering plants. Because of this, gnetophytes were once thought to be the closest gymnosperm relatives to flowering plants, but more recent molecular studies have brought this hypothesis into question, with many recent phylogenies finding them to be nested within the conifers.

Lepidodendron is an extinct genus of primitive lycopodian vascular plants belonging the order Lepidodendrales. It is well preserved and common in the fossil record. Like other Lepidodendrales, species of Lepidodendron grew as large-tree-like plants in wetland coal forest environments. They sometimes reached heights of 50 metres, and the trunks were often over 1 m in diameter. They are often known as "scale trees", due to their bark having been covered in diamond shaped leaf-bases, from which leaves grew during earlier stages of growth. However, they are correctly defined as arborescent lycophytes. They thrived during the Carboniferous Period, and persisted until the end of the Permian around 252 million years ago. Sometimes erroneously called "giant club mosses", the genus was actually more closely related to modern quillworts than to modern club mosses. In the form classification system used in paleobotany, Lepidodendron is both used for the whole plant as well as specifically the stems and leaves.

Glossopteris is the largest and best-known genus of the extinct Permian order of seed plants known as Glossopteridales. The name Glossopteris refers only to leaves, within the framework of form genera used in paleobotany.

Pteridospermatophyta, also called "pteridosperms" or "seed ferns" are a polyphyletic grouping of extinct seed-producing plants. The earliest fossil evidence for plants of this type are the lyginopterids of late Devonian age. They flourished particularly during the Carboniferous and Permian periods. Pteridosperms declined during the Mesozoic Era and had mostly disappeared by the end of the Cretaceous Period, though Komlopteris seem to have survived into Eocene times, based on fossil finds in Tasmania.

Bennettitales is an extinct order of seed plants that first appeared in the Permian period and became extinct in most areas toward the end of the Cretaceous. Bennettitales were amongst the most common seed plants of the Mesozoic, and had morphologies including shrub and cycad-like forms. The foliage of bennettitaleans is superficially nearly indistinguishable from that of cycads, but they are distinguished from cycads by their more complex flower-like reproductive organs, at least some of which were likely pollinated by insects.

The Lopingian is the uppermost series/last epoch of the Permian. It is the last epoch of the Paleozoic. The Lopingian was preceded by the Guadalupian and followed by the Early Triassic.
Gigantopterids (Gigantopteridales) is an extinct, possibly polyphyletic group of seed plants known from the Permian period. Gigantopterids were among the most advanced land plants of the Paleozoic Era and disappeared around the Permian–Triassic extinction event around 252 million years ago. Though some lineages of these plants managed to persist initially, they either disappeared entirely or adapted radically, evolving into undetermined descendants, as surviving life prospered again in much-altered ecosystems. One hypothesis proposes that at least some "gigantopterids" became the ancestors of angiosperms and/or Bennettitales and/or Caytoniales.

Gondwana was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia, Zealandia, Arabia, and the Indian Subcontinent.

A seed plant or spermatophyte, also known as a phanerogam or a phaenogam, is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte that includes most of the familiar land plants, including the flowering plants and the gymnosperms, but not ferns, mosses, or algae.

Dicroidium is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed plants. It is the archetypal genus of the corystosperms, an extinct group of seed plants, often called "seed ferns", assigned to the order Corystospermales or Umkomasiales. Species of Dicroidium were widely distributed and dominant over Gondwana during the Triassic. Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica.

Lepidopteris is a form genus for leaves of Peltaspermaceae, an extinct family of seed plants, which lived from around 260 to 190 million years ago, from the Late Permian to Early Jurassic. Fossils of the genus have been found across both hemispheres. Nine species are currently recognized.Lepidopteris was a common and widespread seed fern, which survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event but was largely wiped out by the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris callipteroides is especially common between the first two episodes of the Permian-Triassic extinction event, and L. ottonis forms a comparable acme zone immediately before the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris would persist into the Early Jurassic in Patagonia, represented by the species Lepidopteris scassoi.

Cartorhynchus is an extinct genus of early ichthyosauriform marine reptile that lived during the Early Triassic epoch, about 248 million years ago. The genus contains a single species, Cartorhynchus lenticarpus, named in 2014 by Ryosuke Motani and colleagues from a single nearly-complete skeleton found near Chaohu, Anhui Province, China. Along with its close relative Sclerocormus, Cartorhynchus was part of a diversification of marine reptiles that occurred suddenly during the Spathian substage, soon after the devastating Permian-Triassic extinction event, but they were subsequently driven to extinction by volcanism and sea level changes by the Middle Triassic.

The Peltaspermales are an extinct order of seed plants, often considered "seed ferns". They span from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Jurassic or the Jurassic-Cretaceous Boundary. It includes at least one valid family, Peltaspermaceae, which spans from the Permian to Early Jurassic, which is typified by a group of plants with Lepidopteris leaves, Antevsia pollen-organs, and Peltaspermum ovulate organs, though the family now also includes other genera like Peltaspermopsis, Meyenopteris and Scytophyllum. Along with these, two informal groups of uncertain taxonomic affinities exist, each centered around a specific genus ; Supaia and Comia, known from the Early Permian of the Northern Hemisphere, especially of North America. Both the "Comioids" and the "Supaioids" are associated with the peltaspermacean ovulate organ Autunia. The Late Triassic-Middle Jurassic genus Pachydermophyllum may also have affinities to the peltasperms.

Corystosperms are a group of extinct seed plants belonging to the family Corystospermaceae assigned to the order Corystospermales or Umkomasiales. They were first described based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa. Corystosperms are typified by a group of plants that bore forked Dicroidium leaves, Umkomasia cupulate ovulate structures and Pteruchus pollen organs, which grew as trees that were widespread over Gondwana during the Middle and Late Triassic. Other fossil Mesozoic seed plants with similar leaf and/or reproductive structures have also sometimes been included within the "corystosperm" concept sensu lato, such as the "doyleoids" from the Early Cretaceous of North America and Asia. A potential corystosperm sensu lato, the leaf genus Komlopteris, is known from the Eocene of Tasmania, around 53-50 million years old, over 10 million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
Pentoxylales is an extinct order of seed plants known from the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of East Gondwana.


















