
Defamation is a communication that injures a third party's reputation and causes a legally redressable injury. The precise legal definition of defamation varies from country to country. It is not necessarily restricted to making assertions that are falsifiable, and can extend to concepts that are more abstract than reputation – like dignity and honour. In the English-speaking world, the law of defamation traditionally distinguishes between libel and slander. It is treated as a civil wrong, as a criminal offence, or both.

Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplomats, or its secret services for a hostile and foreign power, or attempting to kill its head of state. A person who commits treason is known in law as a traitor.
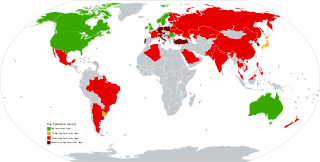
Flag desecration is the desecration of a flag, violation of flag protocol, or various acts that intentionally destroy, damage, or mutilate a flag in public. In the case of a national flag, such action is often intended to make a political point against a country or its policies. Some countries have laws against methods of destruction or forbidding particular uses ; such laws may distinguish between the desecration of the country's own national flag and the desecration of flags of other countries. Some countries have also banned the desecration of all types of flags from inside the country to other country flags.

Lèse-majesté or lese-majesty is an offence or defamation against the dignity of a ruling head of state or of the state itself. The English name for this crime is a modernised borrowing from the medieval French, where the phrase meant 'a crime against the Crown'. In classical Latin, laesa māiestās meant "hurt or violated majesty".

The Offences against the Person Act 1861 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. It consolidated provisions related to offences against the person from a number of earlier statutes into a single Act. For the most part these provisions were, according to the draftsman of the Act, incorporated with little or no variation in their phraseology. It is one of a group of Acts sometimes referred to as the Criminal Law Consolidation Acts 1861. It was passed with the object of simplifying the law. It is essentially a revised version of an earlier consolidation act, the Offences Against the Person Act 1828, incorporating subsequent statutes.
Resisting arrest, or simply resisting, is an illegal act of a suspected criminal either fleeing, threatening, assaulting, or providing a fake ID to a police officer during arrest. In most cases, the person responsible for resisting arrest is criminally charged or taken to court.

Between 1941 and 1945, the government of Nazi Germany perpetrated the Holocaust: a large-scale industrialised genocide in which approximately six million Jews were systematically murdered throughout German-occupied Europe. Since World War II, several countries have criminalised Holocaust denial—the assertion by antisemites that the genocide was fabricated or has been exaggerated. Currently, 17 European countries, along with Israel and Canada, have laws in place that cover Holocaust denial as a punishable offence. Many countries also have broader laws that criminalise genocide denial as a whole, including that of the Holocaust. Among the countries that have banned Holocaust denial, Russia, Austria, Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania have also banned Nazi symbols. Additionally, any expression of genocide justification is also a criminal offence in several countries, as is any attempt to portray Nazism in a positive light.

The Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to combat corruption in government agencies and public sector businesses in India.
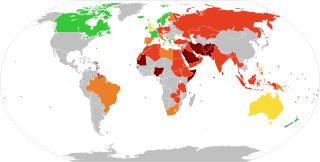
A blasphemy law is a law prohibiting blasphemy, which is the act of insulting or showing contempt or lack of reverence to a deity, or sacred objects, or toward something considered sacred or inviolable. According to Pew Research Center, about a quarter of the world's countries and territories (26%) had anti-blasphemy laws or policies as of 2014.

The Code of Criminal Procedure, commonly called Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC), was the main legislation on procedure for administration of substantive criminal law in India. It was enacted in 1973 and came into force on 1 April 1974. It provides the machinery for the investigation of crime, apprehension of suspected criminals, collection of evidence, determination of guilt or innocence of the accused person and the determination of punishment of the guilty. It also deals with public nuisance, prevention of offences and maintenance of wife, child and parents.

The Passports Act is an act of the Parliament of India "for the issue of passports and travel documents, to regulate the departure from India of citizens of India and for other persons and for matters incidental or ancillary thereto." The Act applies to whole of India extending to citizens of India living outside the country. The Act replaced the Indian Passport Ordinance 1967 and was enacted by Act 15 of 1967 with retrospective effect from 5 May 1967. The act describes the procedures in getting an Indian passport, which replaced the British Indian passport and The Passport Act of 1920.
The Section 326 B in the Indian Penal Code lays down the punishment for attempted acid attacks. The minimum punishment is 5 years' imprisonment. It can extend up to 7 years' imprisonment with fine. A separate law to punish offenders in such cases was passed along with amendment of law on sexual offences. Such a legislation in line with the laws in other countries like Bangladesh was demanded by various sections of the society for a long time.
The Section 326 A in the Indian Penal Code lays down the punishment for acid attacks. The minimum punishment is 10 years' imprisonment. It can extend up to life imprisonment with fine. A separate law to punish offenders in such cases was passed along with amendment of law on sexual offences. Such a legislation in line with the laws in other countries like Bangladesh was demanded by various sections of the society for a long time.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Northern Nigeria face unique legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Federal law prohibits all forms of homosexual activities and prescribes up to 14 years imprisonment for those found culpable. While the Maliki form of Shari'a law applied in 12 states have lesser penalty for unmarried persons, it prescribes the death penalty for married individuals.
Adultery was a criminal offence under Chapter XX of the Indian Penal Code until it was quashed by the Supreme Court of India on 27 September 2018 as unconstitutional. The law dated from 1860. Under Section 497 of the Indian Penal Code, which was the section dealing with adultery, a man who had consensual sexual intercourse with the wife of another man without that husband's consent or connivance could have been punished for this offence with up to five years imprisonment, a fine or both. As such, the concept of adultery targeted the act of sexual intercourse occurring between a married woman and a man other than her husband, in which case the man would be guilty whereas the wife was exempt from punishment. When a married man had sexual intercourse with an unmarried woman, no party was punishable; while if a married man had sexual intercourse with a married woman other than his wife, the married man's crime was against the husband of that married woman, not against the man's own wife towards whom he had been unfaithful. Adultery was only prosecutable upon the complaint of the aggrieved husband.

The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 an Act of the Parliament of India to provide for the conservation of forests and for matters connected therewith or ancillary or incidental thereto. It was further amended in 1988. This law extends to the whole of India. It was enacted by Parliament of India to control further deforestation of Forest Areas in India. The act came into force on 25 October 1980. It has five sections.
Article 365 of the Sri Lankan Penal Code criminalizes "carnal intercourse against the order of nature" and provides for a penalty of up to ten years in prison.
Section 124A of the Indian Penal Code lays down the punishment for sedition. The Indian Penal Code was enacted in 1860, under the British Raj. Section 124A forms part of Chapter VI of the Code which deals with offences against the state. Chapter VI comprises sections from 121 to 130, wherein sections 121A and 124A were introduced in 1870. The then British government of India feared that the Khilafat movement on the Indian subcontinent would wage a war against them. Particularly after the successful suppression of Wahabi/Waliullah Movement, the need was felt for such a law. Throughout the Raj, the section was used to suppress political dissent in favour of independence, including Lokmanya Tilak and Mahatma Gandhi, both of whom were found guilty and imprisoned.
Hate speech is public speech that expresses hate or encourages violence towards a person or group based on something such as race, religion, sex, or sexual orientation. Hate speech is "usually thought to include communications of animosity or disparagement of an individual or a group on account of a group characteristic such as race, colour, national origin, sex, disability, religion, or sexual orientation".
The Section 228A of the Indian Penal Code was inserted into the Indian Penal Code 1860 by the Criminal Law amendment Act 1983 by the Parliament of India to prevent social victimization or ostracism of the victim of a sexual offence. The law provides for up to two years imprisonment with or without fine for those who reveal the identity of victims of sexual abuse in public. The law has been amended subsequently to add more sections of the Indian Penal Code under its purview.









