
The Carolina mantis is a species of praying mantis of the subfamily Stagmomantinae.

Hymenopodidae is a family of the order Mantodea (mantises), which contains six subfamilies. Some of the species in this family mimic flowers and are found camouflaged among them; these are called flower mantises. Their coloration is aggressive mimicry, luring prey to approach close enough to be seized and eaten.

Miomantis caffra is a species of praying mantis native to southern Africa. It appeared in New Zealand in 1978, and was found more recently in Portugal and Los Angeles, USA, likely spread through the exotic pet trade. Females are facultatively parthenogenetic and unmated females can produce viable offspring.

Extatosoma tiaratum, commonly known as the spiny leaf insect, the giant prickly stick insect, Macleay's spectre, or the Australian walking stick, is a large species of Australian stick insect endemic to Australia. The species has the Phasmid Study Group number PSG9.

Iris oratoria, known by the common name Mediterranean mantis, due to humans first studying it in lands around the Mediterranean Sea, is a species of praying mantis. Its range is expanding in the Middle East, Western Asia and the United States.

Flower mantises are those species of praying mantises that mimic flowers. Their coloration is an example of aggressive mimicry, a form of camouflage in which a predator's colours and patterns lure prey. The flower mantises are not a natural group with a single ancestor, but most of the species are in the family Hymenopodidae. Their behaviours vary, but typically involve climbing a plant, and then staying still until a prey insect comes within range. Many species of flower mantises are popular as pets.

Archimantis latistyla, commonly known as the large brown mantis is a species of mantid native to Australia. The large brown mantis has two subspecies, a widespread subspecies and the stick mantis ghost from Bundabergs Turtle Sands. The stick mantis ghosts are not as aggressive as the widespread species but have a defense display used to make the mantis appear larger by flinging its front legs into the air and putting its head down along with its antennae. Large brown mantids are light brown with short winged female and a long winged male. The subspecies from Bundaberg is a pale cream white with a yellow and black eye in between the arms. The large brown mantis female is short winged - her wings reach only half her abdomen and she is not able to fly—but the long winged male has wings that cover the entire abdomen. They have two pairs of wings - the top pair are the wing covers and the bottom wings enable the mantis to fly.

Phyllocrania paradoxa, common name ghost mantis, is a small species of mantis from Africa remarkable for its leaf-like body. It is one of the three species in the genus Phyllocrania. It is known for its distinct and exclusive camouflaged appearance of a dry weathered leaf.

Sphodromantis viridis is a species of praying mantis that is kept worldwide as a pet. Its common names include African mantis, giant African mantis, and bush mantis.

Stagmomantis californica, common name California mantis, is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae that is native to the western United States.

Blepharopsis mendica is a species of praying mantis found in North Africa, parts of the Mediterranean, Middle East and southern Asia, and on the Canary Islands. Devil's flower mantis, Egyptian flower mantis, thistle mantis, and Arab mantis are among its common names.
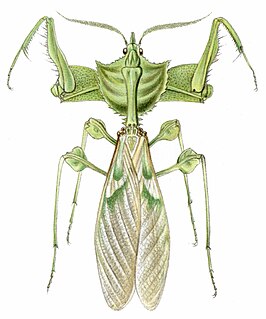
Idolomantis is a genus of praying mantises in the family Empusidae. It is represented by a single species, Idolomantis diabolica, commonly known as the devil's flower mantis or giant devil's flower mantis. It is one of the largest species of praying mantises, and is possibly the largest that mimics flowers

Stagmomantis limbata, common name bordered mantis, bosque mantis, Arizona mantis, or New Mexico praying mantis, is a species of praying mantis native to North America, most prevalent in the south-western United States. This beneficial insect is green or beige in color and grows up to around 3 inches long.

Pseudoharpax virescens, common name Gambian spotted-eye flower mantis, is a species of praying mantis native to western, central and eastern Africa. It takes its name from two eye spots on the dorsal side of the abdomen of adult females.
Acromantis formosana, known as the Taiwan flower mantis, is a species of mantis native to Taiwan.

Chloroharpax is a genus of praying mantis in the family Hymenopodidae. The genus is monotypic, being represented by a single species, Chloroharpax modesta, commonly called the Nigerian flower mantis, and is found across West Africa.

Empusa fasciata is a species of praying mantis in the genus Empusa in the order Mantodea.

Pseudocreobotra wahlbergii, or the spiny flower mantis, is a small flower mantis native to southern and eastern Africa.

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.

Pseudocreobotra is a genus of Sub-Saharan flower mantises. They are visually similar to Creobroter species of Asia, but belong to different subfamilies. Their forewings have prominent spiralled eyespots, which are flashed in a silent deimatic display, to startle would-be predators. The nymphs however, expand the raised abdomen in response to threats, to reveal a single dorsal eyespot. The species are easily reared in captivity.


















