Pseudomonas chlororaphis is a bacterium used as a soil inoculant in agriculture and horticulture. It can act as a biocontrol agent against certain fungal plant pathogens via production of phenazine-type antibiotics. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, similar species have been placed in its group.
Acidovorax facilis is an aerobic, chemoorganotrophic bacterium used as a soil inoculant in agriculture and horticulture.
Pseudomonas agarici is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that causes drippy gill in mushrooms. It was first isolated in New Zealand. P. agarici could not be grouped based on 16S rRNA analysis, so it is designated incertae sedis in the genus Pseudomonas.
Pseudomonas thivervalensis is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that infects the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, P. thivervalensis falls within the P. fluorescens group. It derives its name from the fact that it was first isolated in Thiverval, France.
Pseudomonas citronellolis is a Gram-negative, bacillus bacterium that is used to study the mechanisms of pyruvate carboxylase. It was first isolated from forest soil, under pine trees, in northern Virginia, United States.
Pseudomonas xanthomarina is a bacterium found in marine ascidians. Unlike many other members of the genus Pseudomonas, it is not fluorescent.
Pseudomonas rubescens is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that was originally isolated from the oil in a machine shop. The type strain is ATCC 12099.
Pseudomonas segitis is a Gram-negative, aerobic soil bacterium found in Korea. The type strain is IMSNU 14101.
Pseudomonas moraviensis is a Gram-negative soil bacterium. It is named after Moravia, the region of the Czech Republic where it was first isolated. The type strain is CCM 7280T.
Pseudomonas vranovensis is a Gram-negative soil bacterium.
Pseudomonas veronii is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, fluorescent, motile bacterium isolated from natural springs in France. It may be used for bioremediation of contaminated soils, as it has been shown to degrade a variety of simple aromatic organic compounds. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, P. veronii has been placed in the P. fluorescens group.
Pseudomonas jinjuensis is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, motile, single polar flagellated, yellow-white, rod bacterium isolated from soil in the Jinju Region of Korea. The type strain is LMG 21317.
Pseudomonas koreensis is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, motile, multiple polar flagellated, yellow-white, rod bacterium isolated from farming soil in Korea. The type strain is LMG 21318.
Pseudomonas umsongensis is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, motile, single polar-flagellated, yellow-white, rod-shaped bacterium isolated from the soil in the Umsong region of Korea. The type strain is LMG 21317.
Pseudomonas lini is a fluorescent, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium isolated from rhizospheric soil in France. The type strain is CFBP 5737, though there are also eight other strains known. This bacterium has also been isolated from endophytic tissues of lodgepole pine trees growing on gravel mining sites with potential to perform biological nitrogen fixation and plant growth promotion.
Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis is a Gram-negative, phenanthrene-degrading bacterium from a coal gasification site in Frederiksberg, Copenhagen, Denmark. It is able to catalyse the asymmetric oxidation of sulfides to give exclusively the R enantiomer. The type strain is DSM 13022.
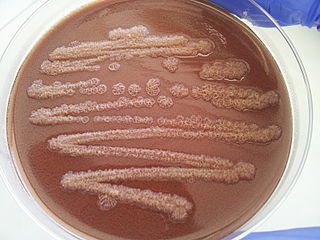
Pseudomonas stutzeri is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that is motile, has a single polar flagellum, and is classified as bacillus, or rod-shaped. While this bacterium was first isolated from human spinal fluid, it has since been found in many different environments due to its various characteristics and metabolic capabilities. P. stutzeri is an opportunistic pathogen in clinical settings, although infections are rare. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, this bacterium has been placed in the P. stutzeri group, to which it lends its name.
Pelomonas saccharophila is a Gram-negative soil bacterium. It was originally named Pseudomonas saccharophila in 1940, but was reclassified in 2005 to the newly created genus, Pelomonas. The original strain was isolated from mud.
Pseudomonas protegens are widespread Gram-negative, plant-protecting bacteria. Some of the strains of this novel bacterial species previously belonged to P. fluorescens. They were reclassified since they seem to cluster separately from other fluorescent Pseudomonas species. P. protegens is phylogenetically related to the Pseudomonas species complexes P. fluorescens, P. chlororaphis, and P. syringae. The bacterial species characteristically produces the antimicrobial compounds pyoluteorin and 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol (DAPG) which are active against various plant pathogens.
Comamonas terrae is a bacterium from the genus Comamonas, which was isolated from agricultural soil in Thailand. C. terrae has an arsenite-oxidizing ability.
