
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating habits that negatively affect a person's physical and/or mental health. They include binge eating disorder, where people eat a large amount in a short period of time; anorexia nervosa, where people eat very little due to a fear of gaining weight and thus have a low body weight; bulimia nervosa, where people eat a lot and then try to rid themselves of the food; pica, where people eat non-food items; rumination syndrome, where people regurgitate food; avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), where people have a reduced or selective food intake due to some psychological reasons ; and a group of other specified feeding or eating disorders. Anxiety disorders, depression and substance abuse are common among people with eating disorders. These disorders do not include obesity.

Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging. Binge eating refers to eating a large amount of food in a short amount of time. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at a normal weight. The forcing of vomiting may result in thickened skin on the knuckles and breakdown of the teeth. Bulimia is frequently associated with other mental disorders such as depression, anxiety, and problems with drugs or alcohol. There is also a higher risk of suicide and self-harm.
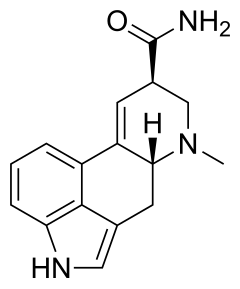
Ergine, also known as d-lysergic acid amide (LSA) and d-lysergamide, is an ergoline alkaloid that occurs in various species of vines of the Convolvulaceae and some species of fungi. The psychedelic properties in the seeds of ololiuhqui, Hawaiian baby woodrose and morning glories have been linked to ergine and/or isoergine, its epimer, as it is the dominant alkaloid present in the seeds.

Psychotria is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 1,582 species and is therefore one of the largest genera of flowering plants. The genus has a pantropical distribution and members of the genus are small understorey trees in tropical forests. Some species are endangered or facing extinction due to deforestation, especially species of central Africa and the Pacific.

Banksia alliacea is a species of shrub that is endemic to southwestern Western Australia. It grows to 2 m high and wide, with shaving brush-shaped inflorescences that smell of onions.
Pseuduvaria cerina is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is endemic to Peninsular Malaysia. James Sinclair, the Scottish botanist who first formally described the species, named it after its waxy yellow inner petals.
Pseuduvaria is a genus of the plant family Annonaceae. It contains the following species:
Pseuduvaria galeata is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is a tree endemic to Peninsular Malaysia.
Pseuduvaria prainii is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is endemic to the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Pseuduvaria taipingensis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is a tree endemic to Peninsular Malaysia.

The gorse tip moth is a smallish moth species of the family Depressariidae.

Liparis nervosa is a species of orchid found in the Tropics of Asia, Africa and America. It is a terrestrial species that grows in woodlands and grasslands.

Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder, characterized by low weight, food restriction, fear of gaining weight and a strong desire to be thin. Many people with anorexia see themselves as overweight even though they are, in fact, underweight. They often deny that they have a problem with low weight. They weigh themselves frequently, eat small amounts and only eat certain foods. Some exercise excessively, force themselves to vomit, or use laxatives to lose weight. Complications may include osteoporosis, infertility and heart damage, among others. Women will often stop having menstrual periods. In extreme cases, people with anorexia who continually refuse significant dietary intake and weight restoration interventions, and are declared incompetent to make decisions by a psychiatrist, may be fed by force under restraint via nasogastric tube after asking their parents or proxies to make the decision for them.

Gynacantha nervosa, the twilight darner, is a species of darner in the dragonfly family Aeshnidae. It is found in the Caribbean Sea, Central America, North America, and South America.
Pseuduvaria aurantiaca is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is endemic to New Guinea. Friedrich Anton Wilhelm Miquel, the Dutch botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Orophea aurantiaca, named it after its orange colored fruit.
Pseuduvaria beccarii is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is endemic to New Guinea. Rudolph Scheffer, the Dutch botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Orophea beccarii, named it after Odoardo Beccari, the Italian naturalist who collected the sample he examined.
Pseuduvaria borneensis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is endemic to Borneo. Yvonne Chuan Fang Su and Richard M.K. Saunders, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after the regions of Borneo where it is distributed including East Kalimantan, Sabah and Sarawak.
Pseuduvaria bruneiensis is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is endemic to Borneo. Yvonne Chuan Fang Su and Richard M.K. Saunders, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after Brunei where the specimens they examined were collected.
Pseuduvaria calliura is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is endemic to Borneo. Herbert Kenneth Airy Shaw, the English botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the long, beautiful tails, or tips, of its leaves.
Yvonne Chuan Fang Su is an evolutionary biologist who is notable for her co-discovery of Pseuduvaria bruneiensis and Pseuduvaria borneensis. Her doctoral work at the University of Hong Kong focused on the phylogeny of the flowering plant genus Pseuduvaria. Her work as a faculty member at Duke–NUS Medical School focuses on the evolution of viruses.









