
Pinus radiata, the Monterey pine, insignis pine or radiata pine, is a species of pine native to the Central Coast of California and Mexico. It is in the Pinaceae family.

Pinus sabiniana, with vernacular names including foothill pine, gray pine, and digger pine, is a pine endemic to California in the United States. Some sources discourage using the name "digger pine", considering it pejorative.

Pinus jeffreyi, also known as Jeffrey pine, Jeffrey's pine, yellow pine and black pine, is a North American pine tree. It is mainly found in California, but also in the westernmost part of Nevada, southwestern Oregon, and northern Baja California. It is named in honor of its botanist documenter John Jeffrey.

Pinus contorta, with the common names lodgepole pine and shore pine, and also known as twisted pine, and contorta pine, is a common tree in western North America. It is common near the ocean shore and in dry montane forests to the subalpine, but is rare in lowland rain forests. Like all pines, it is an evergreen conifer.

Pinus serotina, the pond pine, marsh pine or pocosin pine, is a pine tree found along the Southeastern portion of the Atlantic coastal plain of the United States, from southern New Jersey south to Florida and west to southern Alabama. This pine often has a crooked growth pattern and an irregular top and grows up to 21 metres (69 ft) high, rarely to 29 metres (95 ft).
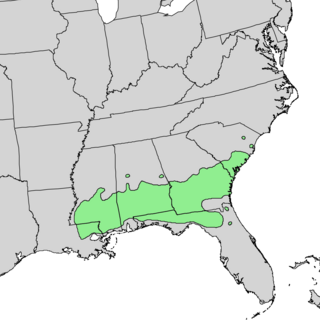
Pinus glabra, the spruce pine, is a tree found on the coastal plains of the southern United States, from southern South Carolina south to northern Florida and west to southern Louisiana. This pine is a straight-growing, medium-sized species, attaining heights of 20–40 m.

The Coulter pine or big-cone pine, Pinus coulteri, is a native of the coastal mountains of Southern California and northern Baja California (Mexico). Isolated groves are found as far north as Clearlake Ca on the flanks of Mt Konocti and Black Diamond Mines Regional Preserve. The species is named after Thomas Coulter, an Irish botanist and physician.

Pinus ponderosa, commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the most widely distributed pine species in North America.

Psidium is a genus of trees and shrubs in the family Myrtaceae. It is native to warmer parts of the Western Hemisphere.

Pinus ayacahuite, also called ayacahuite pine and Mexican white pine, is a species of pine native to the mountains of southern Mexico and western Central America, in the Sierra Madre del Sur and the eastern end of the Eje Volcánico Transversal, between 14° and 21°N latitude in the Mexican states of Guerrero, Oaxaca, Puebla, Veracruz and Chiapas, and in Guatemala, El Salvador and Honduras. It grows on relatively moist areas with summer rainfalls, however specimens from its eastern and southern distribution live under really wet conditions; it needs full sun and well drained soils. Its temperature needs fluctuate between 19 and 10 °C on average a year. This tree accepts from subtropical to cool climate.

Psidium cattleyanum , commonly known as Cattley guava, strawberry guava or cherry guava, is a small tree in the Myrtaceae (myrtle) family. The species is named in honour of English horticulturist William Cattley. Its genus name Psidium comes from the Latin psidion, or "armlet." The red-fruited variety, P. cattleyanum var. cattleyanum, is commonly known as purple guava, red cattley guava, red strawberry guava and red cherry guava. The yellow-fruited variety, P. cattleyanum var. littorale is variously known as yellow cattley guava, yellow strawberry guava, yellow cherry guava, lemon guava and in Hawaii as waiawī. Although P. cattleyanum has select economic uses, it is considered the most invasive plant in Hawaii.

Pinus oocarpa is a species of pine tree native to Mexico and Central America. It is the national tree of Honduras, where it is known as ocote. Common names include ocote chino, pino amarillo, pino avellano, Mexican yellow pine, egg-cone pine and hazelnut pine. It appears that it was the progenitor (original) species that served as the ancestor for some of the other pines of Mexico.

Pinus tecunumanii is a timber tree native to Mexico and Central America. It grows from the highlands of Chiapas and Oaxaca through Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, Honduras to Nicaragua. It occurs in two separated populations in their native habitats. High altitude group grows at 1500–2900 m and low altitude group from 500–1500 m.

Pinus montezumae, known as the Montezuma pine, is a species of conifer in the family Pinaceae.

The Central American pine-oak forests ecoregion, in the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests biome, is found in Central America and Chiapas state of southern Mexico.
Mexican conifers extend mainly across the main mountain ranges Sierra Madre Oriental, Sierra Madre Occidental and the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. Enclosed between these mountains there are dispersed groups of conifers in mid and high elevations valleys when rainfall conditions allow their growth. Mexican conifers grow in some places often associated with oaks.

Rhyacionia frustrana, the Nantucket pine tip moth, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in the United States from Massachusetts south to Florida, west to Missouri, Oklahoma, Texas and California. It is also found in the Dominican Republic, Cuba, Jamaica, Mexico (Oaxaca), Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua.

Psidium guineense is a species of guava.
Psidium amplexicaule, which is commonly known as mountain guava, is a species in the family Myrtaceae that is native to the Caribbean. It is rare in a moist limestone forest at 100–600 feet altitude on north coast of Puerto Rico. This plant can also be found on islands such as St. Thomas and St. John in the United States Virgin Islands and in Tortola and Virgin Gorda of the British Virgin Islands.

Psittacanthus schiedeanus G.Don is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Panamá, Costa Rica, Honduras and Mexico.

















