
Pachypodium brevicaule is a species of plant that belongs to the family Apocynaceae.
Amaranthus wrightii is a species of flowering plant. It goes by the common name of Wright's amaranth. It occurs from western Texas into southern Arizona and as far north as Colorado at elevations between 500–2,000 m (1,600–6,600 ft).

Nepenthes rigidifolia is a critically endangered tropical pitcher plant endemic to Sumatra, where it grows at elevations of 1000–1600 m above sea level.

Dypsis ambositrae is a species of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It is found only in Madagascar where it is threatened by habitat loss.
Bulbophyllum tokioi is a species of plant in the family Orchidaceae. It is endemic to Taiwan. It was described in 1935 by Noriaki Fukuyama.

Buddleja salviifolia, common names sage bush and sagewood, is endemic to much of southern and eastern Africa, from Kenya and Angola south, where it grows on rocky hillsides, along forest margins and watercourses. The species was described and named by Lamarck in 1792.

Epidendrum armeniacum is an epiphytic species of reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid that grows wild in Bolivia, Brazil, Ecuador, and Peru, at altitudes of 1–2 km.

Hypericum mutilum is a species of St. John's wort known by the common name dwarf St. John's wort. It is native to parts of North America and is present in other parts as an introduced species. It is an annual or perennial herb taking a multibranched erect form up to about 60 centimeters tall. The oval green leaves are one or two centimeters long and are covered in tiny glands. The inflorescence is a compound cyme of tiny flowers. H. mutilum subsp. mutilum and subsp. boreale have a diploid number of 16, and H. mutilum subsp. boreale can have a diploid number of 18.

Nepenthes andamana is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Phang Nga Province, Thailand, where it grows near sea level in coastal savannah and grassland. It is thought to be most closely related to N. suratensis.

Nepenthes chang is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Banthad Mountains of central Thailand, where it grows at elevations of 300–600 m above sea level. It is thought to be most closely related to N. kampotiana.

Nepenthes suratensis is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Surat Thani Province, Thailand, where it grows near sea level in coastal savannah and grassland. It is thought to be most closely related to N. andamana.

Boerhavia erecta, commonly known as the erect spiderling or the erect boerhavia, is one of more than 100 species in the genus Boerhavia L. Boerhavia erecta is native to the United States, Mexico, Central America and western South America, but now is cosmopolitan in tropical and subtropical regions. In Africa its distribution extends from West Africa, eastwards to Somalia and down to South Africa. It has recently been found in parts of Madagascar and Réunion. In Asia, it occurs in India, Java, Malaysia, the Philippines, China and the Ryukyu Islands.

Psittacanthus calyculatus,, is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, native to Colombia, Mexico, the Mexican Gulf, and Venezuela.
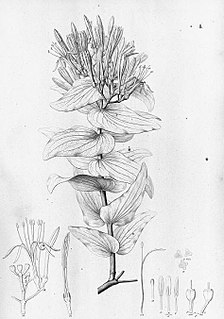
Psittacanthus cordatus is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Bolivia and Brazil.
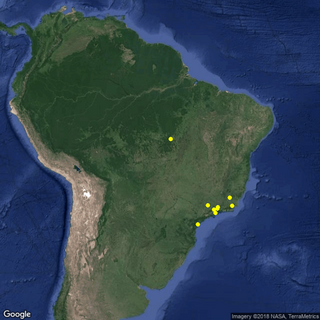
Psittacanthus brasiliensis is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is endemic to Brazil.

Psittacanthus schiedeanus G.Don is a species of Neotropical mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Panamá, Costa Rica, Honduras and Mexico.

Psittacanthus acinarius is a species of mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Peru, Venezuela, and French Guiana.
Psittacanthus biternatus is a species of mistletoe in the family Loranthaceae, which is native to Brazil, Venezuela, and Colombia.

Passiflora bogotensis is a climbing plant native to Colombia, in the genus Passiflora. It can also be found in Venezuela.

Protea pendula, also known as the nodding sugarbush or arid sugarbush, is a flowering plant of the genus Protea, in the family Proteaceae, which is only found growing in the wild in the Cape Region of South Africa. In the Afrikaans language it is known as knikkopsuikerbossie or ondersteboknopprotea.



















