
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Sources cite at least 118 identified "Egyptian" pyramids. Approximately 80 pyramids were built within the Kingdom of Kush, now located in the modern country of Sudan. Of those located in modern Egypt, most were built as tombs for the country's pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.

Huni was an ancient Egyptian king, the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Based on the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC.

The Giza pyramid complex in Egypt is home to the Great Pyramid, the Pyramid of Khafre, and the Pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx. All were built during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of ancient Egypt, between c. 2600 – c. 2500 BC. The site also includes several temples, cemeteries, and the remains of a workers' village.
Zawiya, Zawiyah, Zawia, Zaouia, Zaouiet and similar terms may refer to:

Khaba was a pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, active during the 3rd Dynasty of the Old Kingdom period. The exact time during which Khaba ruled is unknown but may have been around 2670 BC, and almost definitely towards the end of the dynasty.

Zawyet El Aryan is a town in the Giza Governorate, located between Giza and Abusir. To the west of the town, just in the desert area, is a necropolis, referred to by the same name. Almost directly east across the Nile is Memphis. In Zawyet El Aryan, there are two pyramid complexes and five mastaba cemeteries.

The Layer Pyramid is a ruined step pyramid dating to the 3rd Dynasty of Egypt and located in the necropolis of Zawyet El Aryan. Its ownership is uncertain and may be attributable to king Khaba. The pyramid architecture, however, is very similar to that of the Buried Pyramid of king Sekhemkhet and for this reason is firmly datable to the 3rd Dynasty.
Zawyet el-Maiyitin or Zawyet Sultan or Zawyet el-Amwat is a small village in Egypt, located in the Minya Governorate.

Minya Governorate is one of the governorates of Upper Egypt. Its capital city, Minya, is located on the left bank of the Nile River.
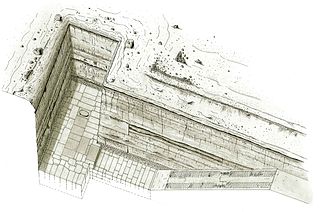
The Unfinished Northern Pyramid of Zawyet El Aryan, also known as Pyramid of Baka and Pyramid of Bikheris is the term archaeologists and Egyptologists use to describe a large shaft part of an unfinished pyramid at Zawyet El Aryan in Egypt. Archaeologists are generally of the opinion that it belongs to the early or the mid-4th Dynasty during the Old Kingdom period. The pyramid owner is not known for certain and most Egyptologists, such as Miroslav Verner, think it should be a king known under his hellenized name, Bikheris, perhaps from the Egyptian Baka. In contrast, Wolfgang Helck and other Egyptologists doubt this attribution.

Setka is the name of an ancient Egyptian crown prince. He is known for his statuette in the shape of a seated scribe. He is also the subject of a theory that claims he was pharaoh of Egypt for a very short time.
Baka was an ancient Egyptian prince. He is known for his destroyed statuette. He is also the subject of a theory that claims he was king of Egypt for a very short time. Thus, he might be identical to a scarcely known king named Bikheris.

The Oryx nome was one of the 42 nomoi in ancient Egypt. The Oryx nome was the 16th nome of Upper Egypt, and was named after the scimitar oryx. It was located, approximately, in the territories surrounding the modern city of Minya in Middle Egypt.

The pyramid of Athribis was a small mudbrick pyramid located at Athribis in the southern Nile Delta, northeast of the modern city of Banha. It was located the furthest north of all the pyramids in ancient Egypt and the only known pyramid to have been built in the Delta.
The pyramid of Elephantine is part of a group of seven very similar small step pyramids, along with the pyramids at Edfu South, el-Kula, Naqada, Zawyet el-Maiyitin, Seila, and Sinki. All of these were built far from the main centres of Egypt and are very poorly understood. The pyramid of Elephantine is located in the northwest part of the Old Kingdom city on the south end of the island of Elephantine in the Nile. The structure was discovered in 1907, but it could only be identified as a pyramid after excavations by the German Archaeological Institute in 1978–79.
The Edfu South pyramid is part of a group of seven very similar small step pyramids which were all built far from the main centres of Egypt and about which very little is known, along with the pyramids of Elephantine, el-Kula, Naqada, Zawyet el-Maiyitin, Sinki and Seila. It is located about five kilometres south of Edfu near Naga el-Ghoneimeya. It was first identified as a pyramid in 1979, when the German archaeologists Günter Dreyer and Werner Kaiser were leading a survey of Edfu after a tip off from the inspector. Further investigation and surveys of the surrounding area have been undertaken since 2010 by the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago.
The pyramid of Naqada, also called the pyramid of Ombos, is part of a group of seven very similar small step pyramids, which were all erected far from the major centres of Egypt and about which very little is known. It is located about 300 metres north of the ruins of the ancient site of Ombos, near the modern city of Naqada in Upper Egypt. The first excavation was undertaken in 1895 by Flinders Petrie and James Edward Quibell.

The pyramid of Seila is one of a group of seven small step pyramids which are very similar to one another, along with the Edfu South pyramid, the pyramid of Elephantine, the pyramid of El-Kula, the pyramid of Naqada, the pyramid of Zawyet el-Maiyitin, and the pyramid of Sinki. These pyramids were all built far from the major centres of Egypt and very little is known about them. The pyramid is located on an outcrop between the Faiyum Oasis and the Nile Valley, about 6 km north of the motorway from Wasta to Faiyum. Its builder may have been Snefru, the founder of the Fourth Dynasty. It was discovered in 1889/1890 by Flinders Petrie and revisited in 1898 by Ludwig Borchardt.

The Pyramid of el-Kula, along with the pyramids in Edfu-South, Elephantine, Ombos, Zawyet el-Maiyitin, Seila, and Sinki, belongs to a group of seven very similar small step pyramids that were all built far away from the major centers of Egypt and about which very little is known. It is located approximately six kilometers north of the ancient site of Hierakonpolis near the village of Naga el-Mamariya. Of all the pyramids mentioned above, it is in the best state of preservation. It was first described in 1837 by John Shae Perring and Richard William Howard Vyse, who called it el-Koofa. A thorough excavation and examination of the structure was carried out in 1949 under the direction of the Belgian Egyptologist Jean Capart.













