
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom bonded to two organyl groups. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C5H5N. It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group (=CH−) replaced by a nitrogen atom (=N−). It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide.
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.

Elias James Corey is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry "for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis", specifically retrosynthetic analysis.
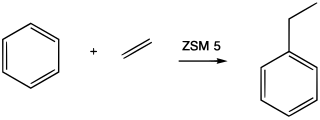
Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene. Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents.
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol may also be called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified. They are used as protecting groups of carbonyl groups, making them essential in synthesis of organic chemistry.
Dimethyl ether (DME; also known as methoxymethane) is the organic compound with the formula CH3OCH3, (sometimes ambiguously simplified to C2H6O as it is an isomer of ethanol). The simplest ether, it is a colorless gas that is a useful precursor to other organic compounds and an aerosol propellant that is currently being demonstrated for use in a variety of fuel applications.
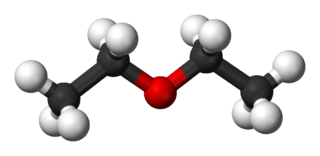
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3CH2)2O, sometimes abbreviated as Et2O. It is a colourless, highly volatile, sweet-smelling, extremely flammable liquid. It belongs to the ether class of organic compounds. It is a common solvent. It was formerly used as a general anesthetic.

Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a yellow-orange salt with the formula [C5H5NH]+[CrO3Cl]−. It is a reagent in organic synthesis used primarily for oxidation of alcohols to form carbonyls. A variety of related compounds are known with similar reactivity. PCC offers the advantage of the selective oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones, whereas many other reagents are less selective.
Adams' catalyst, also known as platinum dioxide, is usually represented as platinum(IV) oxide hydrate, PtO2•H2O. It is a catalyst for hydrogenation and hydrogenolysis in organic synthesis. This dark brown powder is commercially available. The oxide itself is not an active catalyst, but it becomes active after exposure to hydrogen whereupon it converts to platinum black, which is responsible for reactions.
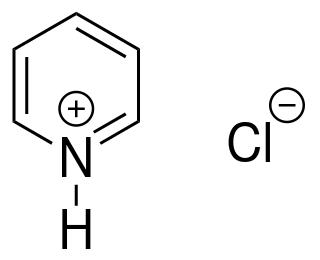
Pyridinium chloride is an organic chemical compound with a formula of C5H5NHCl.
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group. The general structure is R1R2R3Si−O−R4 where R4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group. Silyl ethers are usually used as protecting groups for alcohols in organic synthesis. Since R1R2R3 can be combinations of differing groups which can be varied in order to provide a number of silyl ethers, this group of chemical compounds provides a wide spectrum of selectivity for protecting group chemistry. Common silyl ethers are: trimethylsilyl (TMS), tert-butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS), tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS/TBDMS) and triisopropylsilyl (TIPS). They are particularly useful because they can be installed and removed very selectively under mild conditions.
Tetrahydropyran (THP) is the organic compound consisting of a saturated six-membered ring containing five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is named by reference to pyran, which contains two double bonds, and may be produced from it by adding four hydrogens. In 2013, its preferred IUPAC name was established as oxane. The compound is a colourless volatile liquid. Derivatives of tetrahydropyran are, however, more common. 2-Tetrahydropyranyl (THP-) ethers derived from the reaction of alcohols and 3,4-dihydropyran are commonly used as protecting groups in organic synthesis. Furthermore, a tetrahydropyran ring system, i.e., five carbon atoms and an oxygen, is the core of pyranose sugars, such as glucose.

Dimethoxymethane, also called methylal, is a colorless flammable liquid with a low boiling point, low viscosity and excellent dissolving power. It has a chloroform-like odor and a pungent taste. It is the dimethyl acetal of formaldehyde. Dimethoxymethane is soluble in three parts water and miscible with most common organic solvents.
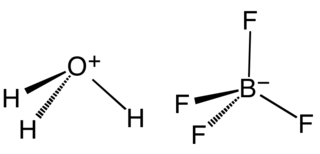
Fluoroboric acid or tetrafluoroboric acid is an inorganic compound with the simplified chemical formula H+[BF4]−. Solvent-free tetrafluoroboric acid has not been reported. The term "fluoroboric acid" usually refers to a range of compounds including hydronium tetrafluoroborate, which are available as solutions. The ethyl ether solvate is also commercially available, where the fluoroboric acid can be represented by the formula [H( 2O)n]+[BF4]−, where n is 2.
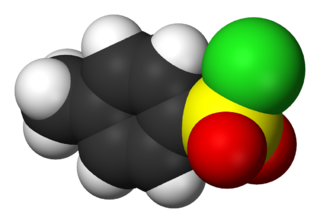
4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, toluene-p-sulfonyl chloride) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2Cl. This white, malodorous solid is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Abbreviated TsCl or TosCl, it is a derivative of toluene and contains a sulfonyl chloride (−SO2Cl) functional group.
Alcohol oxidation is a collection of oxidation reactions in organic chemistry that convert alcohols to aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters where the carbon carries a higher oxidation state. The reaction mainly applies to primary and secondary alcohols. Secondary alcohols form ketones, while primary alcohols form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.
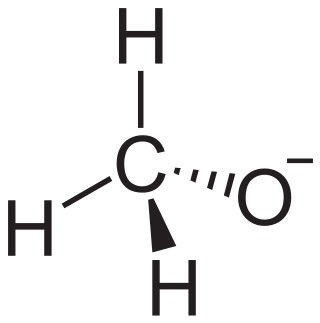
In chemistry, an alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as RO−, where R is the organyl substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts.











