Related Research Articles

The common sunflower is a large annual forb of the genus Helianthus grown as a crop for its edible oil and seeds. This sunflower species is also used as wild bird food, as livestock forage, in some industrial applications, and as an ornamental in domestic gardens. The plant was first domesticated in the Americas. Wild H. annuus is a widely branched annual plant with many flower heads. The domestic sunflower, however, often possesses only a single large inflorescence atop an unbranched stem.

The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
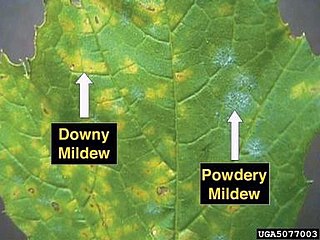
Downy mildew refers to any of several types of oomycete microbes that are obligate parasites of plants. Downy mildews exclusively belong to the Peronosporaceae family. In commercial agriculture, they are a particular problem for growers of crucifers, grapes and vegetables that grow on vines. The prime example is Peronospora farinosa featured in NCBI-Taxonomy and HYP3. This pathogen does not produce survival structures in the northern states of the United States, and overwinters as live mildew colonies in Gulf Coast states. It progresses northward with cucurbit production each spring. Yield loss associated with downy mildew is most likely related to soft rots that occur after plant canopies collapse and sunburn occurs on fruit. Cucurbit downy mildew only affects leaves of cucurbit plants.

Sunflower oil is the non-volatile oil pressed from the seeds of the sunflower. Sunflower oil is commonly used in food as a frying oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient.

Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. is a U.S.-based producer of seeds for agriculture. They are a major producer of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), including genetically modified crops with insect and herbicide resistance.
Dow AgroSciences LLC was a wholly owned subsidiary of the Dow Chemical Company specializing in not only agricultural chemicals such as pesticides, but also seeds and biotechnology solutions. The company was based in Indianapolis, Indiana, in the United States. On 31 January 2006, Dow AgroSciences announced that it had received regulatory approval for the world's first plant-cell-produced vaccine against Newcastle disease virus from USDA Center for Veterinary Biologics. Dow AgroSciences operates brand names such as Sentricon, Vikane, Mycogen®, SmartStax®, Enlist™, Pfister Seed®, PhytoGen®, Prairie Brand Seed®, Alforex Seeds®, Profume, Dairyland Seed®, and Brodbeck Seed®.

Tornquist Partido is a partido in the southwest of Buenos Aires Province in Argentina and is named after Ernesto Tornquist, founder of Tornquist, the partido's main city.
This is a list of articles that are lists of plant diseases.

Pycnopodia helianthoides, commonly known as the sunflower sea star, is a large sea star found in the northeast Pacific. The only species of its genus, it is among the largest sea stars in the world, with a maximum arm span of 1 m (3.3 ft). Adult sunflower sea stars usually have 16 to 24 limbs; their color can vary widely. They are predatory, feeding mostly on sea urchins, clams, snails, and other small invertebrates. Although the species had been widely distributed throughout the northeast Pacific, its population has rapidly declined since 2013.

Macrophomina phaseolina is a Botryosphaeriaceae plant pathogen fungus that causes damping off, seedling blight, collar rot, stem rot, charcoal rot, basal stem rot, and root rot on many plant species.

Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a plant pathogenic fungus and can cause a disease called white mold if conditions are conducive. S. sclerotiorum can also be known as cottony rot, watery soft rot, stem rot, drop, crown rot and blossom blight. A key characteristic of this pathogen is its ability to produce black resting structures known as sclerotia and white fuzzy growths of mycelium on the plant it infects. These sclerotia give rise to a fruiting body in the spring that produces spores in a sac which is why fungi in this class are called sac fungi (Ascomycetes). This pathogen can occur on many continents and has a wide host range of plants. When S. sclerotiorum is onset in the field by favorable environmental conditions, losses can be great and control measures should be considered.
Diaporthe phaseolorum var. phaseolorum is a plant pathogen infecting soybean, sweet potato and peanut.

Meloidogyne javanica is a species of plant-pathogenic nematodes. It is one of the tropical root-knot nematodes and a major agricultural pest in many countries. It has many hosts. Meloidogyne javanica reproduces by obligatory mitotic parthenogenesis (apomixis).

Tobacco streak virus (TSV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Bromoviridae, in the genus Ilarvirus. It has a wide host range, with at least 200 susceptible species. TSV is generally more problematic in the tropics or warmer climates. TSV does not generally lead to epidemics, with the exception of sunflowers in India and Australia, and peanuts in India.
Soybean chlorotic mottle virus (SbCMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Caulimoviridae, genus Soymovirus.

Aphis is a genus of insects in the family Aphididae containing at least 600 species of aphids. It includes many notorious agricultural pests, such as the soybean aphid Aphis glycines. Many species of Aphis, such as A. coreopsidis and A. fabae, are myrmecophiles, forming close associations with ants.
An oilseed press is a machine that lies at the center of vegetable oil extraction. This is due to the fact that this technology is designed to release oil from oilseeds. Multiple oilseed press layouts have been developed over time to complete this process, with each having its own distinct set of advantages and disadvantages. Moreover, the products that are created by oilseed presses, namely oil and oilseed meal, possess great nutritive benefits for humans and livestock respectively. The oilseed press, being at the center of the oil-extraction process, is joined with various other pieces of equipment and procedures that form a pre- and post-extraction system.

Cooking oil is plant, animal, or synthetic liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. It is also used in food preparation and flavoring not involving heat, such as salad dressings and bread dips, and may be called edible oil.