Contents
| Tylenchida | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Heterodera glycines , worm and egg | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Secernentea |
| Subclass: | Tylenchia |
| Order: | Tylenchida |
| Families | |
See text | |
| Tylenchida | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Heterodera glycines , worm and egg | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Secernentea |
| Subclass: | Tylenchia |
| Order: | Tylenchida |
| Families | |
See text | |

Secernentea was a class of nematodes in the Classical Phylogeny System and is no longer in use. This morphological-based classification system has been replaced by the Modern Phylogeny system, where taxonomy assignment is based on small subunit ribosomal DNA.
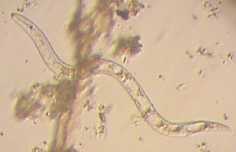
Dorylaimida (dorylaims) is a diverse order of nematodes with both soil and freshwater species.

Heterodera is a genus of nematodes in the family Heteroderidae. Members of the genus are obligate parasites and different species attack different crops, often causing great economic damage. The genus is unique among nematode genera because of the ability of the female to transform into a tough, brown, cyst which protects the eggs which have been formed within her body. The name heterodera "refers to the different 'skins' of female and cyst."
Anguina amsinckiae is a plant pathogenic nematode, which attacks the weed called fiddleneck.

Heteroderidae is a family of nematodes. The name comes from the Greek heteros = other and deras = skin (derm). This "refers to the different 'skins' of female and cyst."

Diplogasterida was an order of nematodes. It was sometimes placed in a monotypic subclass Diplogasteria, but molecular phylogenetic evidence has shown it to be embedded in the family Rhabditidae. The confusion of having a hierarchical nesting of groups that were formerly mutually exclusive has led to a profusion of names. Although completely revised taxonomy of nematodes that builds on recent classification systems as well as recent phylogenetic evidence is still necessary, most contemporary taxonomic studies now treat all groups listed under "Diplogasterina" below as a single family, Diplogastridae.
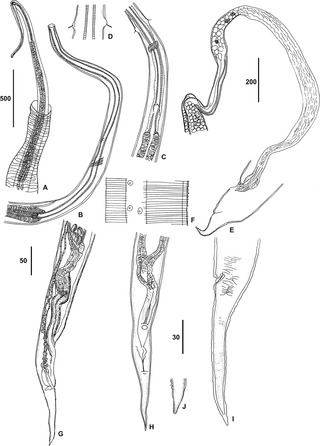
Thelazioidea is a superfamily of spirurian nematodes in the large order Spirurida. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.

Root-gall nematodes are plant-parasitic nematodes from the genus Subanguina that affect grasses, including cereals, and some other plants, such as mugwort. They are distinct from the Root-knot nematodes which are from the genus Meloidogyne. So far around twenty-five separate species of Subanguina have been identified, although the most well-known and type species is Subanguina radicicola.

Allantonematidae is a family of insect-parasitic nematodes from the order Tylenchida. Allantonematid nematodes infect a variety of insects including beetles, butterflies, flies, thrips, ants, and more. For instance, the nematode Howardula aoronymphium parasitizes mushroom-feeding fruit flies, Formicitylenchus oregonensis parasitizes carpenter ants, and Metaparasitylenchus hypothenemi parasitizes a pest of coffee beans, the coffee berry borer.

Fergusonina, the sole genus in the family of Fergusoninidae, are gall-forming flies. There are about 40 species in the genus, all of them producing galls on Eucalyptus, Melaleuca, Corymbia, and Metrosideros species in Australia and New Zealand.
Sphaerulariidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Parasitylenchidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Iotonchiidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Fergusobiidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Dolichodoridae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Belonolaimidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Tylenchulidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Criconematidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.
Neotylenchidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Tylenchida.