
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The NCBI is located in Bethesda, Maryland, and was founded in 1988 through legislation sponsored by US Congressman Claude Pepper.

Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization, clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures.

Caenogastropoda is a taxonomic subclass of molluscs in the class Gastropoda. It is a large diverse group which are mostly sea snails and other marine gastropod mollusks, but also includes some freshwater snails and some land snails. The subclass is the most diverse and ecologically successful of the gastropods.
The Thermotogota are a phylum of the domain Bacteria. The phylum Thermotogota is composed of Gram-negative staining, anaerobic, and mostly thermophilic and hyperthermophilic bacteria.

Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes Secernentea and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea.

Heterorhabditis is a genus of nematodes belonging to the order Rhabditida. All species of this genus are obligate parasites of insects, and some are used as biological control agents for the control of pest insects.
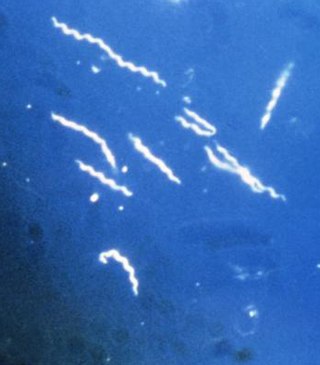
Borrelia is a genus of bacteria of the spirochete phylum. Several species cause Lyme disease, also called Lyme borreliosis, a zoonotic, vector-borne disease transmitted by ticks. Other species of Borrelia cause relapsing fever, and are transmitted by ticks or lice, depending on the species of bacteria. A few Borrelia species as Candidatus Borrelia mahuryensis harbor intermediate genetic features between Lyme disease and relapsing fever Borrelia. The genus is named after French biologist Amédée Borrel (1867–1936), who first documented the distinction between a species of Borrelia, B. anserina, and the other known type of spirochete at the time, Treponema pallidum. This bacterium must be viewed using dark-field microscopy, which make the cells appear white against a dark background. Borrelia species are grown in Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly medium. Of 52 known species of Borrelia, 20 are members of the Lyme disease group, 29 belong to the relapsing fever group, and two are members of a genetically distinct third group typically found in reptiles. A proposal has been made to split the Lyme disease group based on genetic diversity and move them to their own genus, Borelliella, but this change is not widely accepted. This bacterium uses hard and soft ticks and lice as vectors. Testing for the presence of the bacteria in a human includes two-tiered serological testing, including immunoassays and immunoblotting.
The Gemmatimonadota are a phylum of bacteria established in 2003. The phylum contains two classes Gemmatimonadetes and Longimicrobia.

Rotylenchulus reniformis, the reniform nematode, is a species of parasitic nematode of plants with a worldwide distribution in the tropical and subtropical regions.

Heterodera is a genus of nematodes in the family Heteroderidae. Members of the genus are obligate parasites and different species attack different crops, often causing great economic damage. The genus is unique among nematode genera because of the ability of the female to transform into a tough, brown, cyst which protects the eggs which have been formed within her body. The name heterodera "refers to the different 'skins' of female and cyst."

Anguina is a genus of plant pathogenic nematodes.
Aphelenchus avenae is a mycophagous nematode capable of feeding on plant tissue in culture. It is a nematode commonly found in the soil, known to primarily feed on fungi. However, there have been instances where Aphelenchus has been observed in healthy plant tissue, although there is currently no evidence suggesting that it causes harm to higher plants. Due to its ease of cultivation on fungi, Aphelenchus is considered a suitable organism for experimental purposes. Within the Aphelenchus genus, several species have been identified, but experts are uncertain whether these represent distinct species or if A. avenae is simply a morphologically variable species. In the Netherlands, only female specimens of Aphelenchus have been discovered, while in southern Europe, males are quite common. Interestingly, if we cultivate Dutch material at higher temperatures, males also appear in the population.

The Ascarididae are a family of the large intestinal roundworms. Members of the family are intestinal parasites, infecting all classes of vertebrates. It includes a number of genera, the most well known of which are:
Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli is the bacterium that causes ratoon stunting disease, a major worldwide disease of sugarcane. It is Gram positive and grows slowly in the laboratory.

The nematodesroundworms or eelworms, constitute the phylum Nematoda. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but there are many that are parasitic. The parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases.
Leifsonia is a Gram-positive genus of bacteria from the family Microbacteriaceae.
Globodera ellingtonae is one of the potato cyst nematodes and was recently recognized as a new species in the United States. This triggered a quarantine of the fields where it was isolated to prevent the spread of this nematode to other fields.
Paratrichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors. The females are didelphic, and are distributed worldwide.
Trichodoridae is a family of terrestrial root feeding nematodes, being one of two that constitute suborder Triplonchida. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.
Leifsonia xyli is a Gram-positive species of bacteria from the family Microbacteriaceae.











