| Heterodera | |
|---|---|
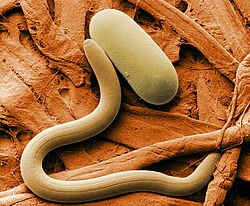 | |
| Heterodera glycines | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Nematoda |
| Class: | Secernentea |
| Order: | Tylenchida |
| Family: | Heteroderidae |
| Subfamily: | Heteroderinae |
| Genus: | Heterodera Schmidt, 1871 |
| Species | |
See § Diversity | |
| Synonyms | |
AfenestrataBaldwin & Bell, 1985 | |
Heterodera is a genus of nematodes in the family Heteroderidae. Members of the genus are obligate parasites and different species attack different crops, often causing great economic damage. The genus is unique among nematode genera because of the ability of the female to transform into a tough, brown, cyst which protects the eggs which have been formed within her body. [1] The name heterodera "refers to the different 'skins' of female and cyst." [2]