Function
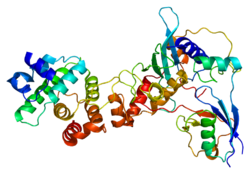
RanGAP1, is a homodimeric 65-kD polypeptide that specifically induces the GTPase activity of RAN, but not of RAS by over 1,000-fold. RanGAP1 is the immediate antagonist of RCC1, a regulator molecule that keeps RAN in the active, GTP-bound state. The RANGAP1 gene encodes a 587-amino acid polypeptide. The sequence is unrelated to that of GTPase activators for other RAS-related proteins, but is 88% identical to Rangap1 (Fug1), the murine homolog of yeast Rna1p. RanGAP1 and RCC1 control RAN-dependent transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm. RanGAP1 is a key regulator of the RAN GTP/GDP cycle. [6]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.