Related Research Articles

The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support.
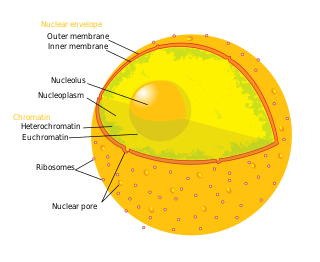
A nuclear pore is a channel as part of the nuclear pore complex (NPC), a large protein complex found in the nuclear envelope in eukaryotic cells, enveloping the cell nucleus containing DNA, which facilitates the selective membrane transport of various molecules across the membrane.
Small GTPases, also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases.

Telophase is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a nuclear envelope is re-assembled around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli reappear, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. The mitotic spindle is disassembled and remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized. Telophase accounts for approximately 2% of the cell cycle's duration.
A nuclear localization signalorsequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the cell's cytoplasm to the nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS).

Ran also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily.
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherins called importins to enter the nucleus and exportins to exit.

Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase.
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions.

Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membranes fuse, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nuclear pores enable the passive and facilitated transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. Nucleoporins, a family of around 30 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. Nucleoporin 62 is the most abundant member of this family. Nucleoporins are able to transport molecules across the nuclear envelope at a very high rate. A single NPC is able to transport 60,000 protein molecules across the nuclear envelope every minute.

Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNB1 gene.
Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP98 gene.

RAN binding protein 2 (RANBP2) is protein which in humans is encoded by the RANBP2 gene. It is also known as nucleoporin 358 (Nup358) since it is a member nucleoporin family that makes up the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 has a mass of 358 kDa.

Regulator of chromosome condensation 1, also known as RCC1, Ran guanine nucleotide exchange factor and RanGEF, is the name for a human gene and protein.

Nucleoporin 153 (Nup153) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NUP153 gene. It is an essential component of the basket of nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in vertebrates, and required for the anchoring of NPCs. It also acts as the docking site of an importing karyopherin. On the cytoplasmic side of the NPC, Nup358 fulfills an analogous role.

Ran GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANGAP1 gene.

Ran-specific binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANBP1 gene.

Importin 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO8 gene.

Mary C. Dasso is an American biochemist known for research on chromosome segregation and the discovery of Ran GTPase. She is the acting scientific director of the division of intramural research and a senior investigator in the section on cell cycle regulation at the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development.
References
- ↑ Matunis MJ, Wu J, Blobel G (February 1998). "SUMO-1 modification and its role in targeting the Ran GTPase-activating protein, RanGAP1, to the nuclear pore complex". The Journal of Cell Biology . 140 (3): 499–509. doi:10.1083/jcb.140.3.499. PMC 2140169 . PMID 9456312.
- ↑ Rose A, Meier I (December 2001). "A domain unique to plant RanGAP is responsible for its targeting to the plant nuclear rim". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 98 (26): 15377–82. Bibcode:2001PNAS...9815377R. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261459698 . PMC 65037 . PMID 11752475.
- ↑ Hopper AK, Traglia HM, Dunst RW (August 1990). "The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus". The Journal of Cell Biology . 111 (2): 309–21. doi:10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. PMC 2116204 . PMID 2116418.
- ↑ Cavalier-Smith T (2010). "Origin of the cell nucleus, mitosis and sex: roles of intracellular coevolution". Biology Direct . 5: 7. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-5-7 . PMC 2837639 . PMID 20132544.