RAN binding protein 2 (RANBP2) is protein which in humans is encoded by the RANBP2 gene. [3] It is also known as nucleoporin 358 (Nup358) since it is a member nucleoporin family that makes up the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 has a mass of 358 kDa.
RAN binding protein 2 (RANBP2) is protein which in humans is encoded by the RANBP2 gene. [3] It is also known as nucleoporin 358 (Nup358) since it is a member nucleoporin family that makes up the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 has a mass of 358 kDa.
RAN is a small GTP-binding protein of the RAS superfamily. Ran GTPase is a master regulatory switch, which among other functions, controls the shuttling of proteins between the nuclear and cytoplasm compartments of the cell. Ran GTPase controls a variety of cellular functions through its interactions with other proteins. The RanBP2 gene encodes a very large RAN-binding protein that localizes to cytoplasmic filaments emanating from the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2/Nup358 is a giant scaffold and mosaic cyclophilin-related nucleoporin implicated in controlling selective processes of the Ran-GTPase cycle. RanBP2 is composed of multiple domains. Each domain of RanBP2 selectively and directly interacts with distinct proteins such as Ran GTPase, importin-beta, exportin-1/CRM1, red opsin, subunits of the proteasome, cox11 and the kinesin-1 isoforms, KIF5B and KIF5C. Another partner of RanBP2 is the E2 enzyme UBC9. RanBP2 strongly enhances SUMO1 transfer from UBC9 to the SUMO1 target SP100. Another target for SUMOylation is RanGAP which is the GTPase activating protein for Ran. SUMO-RanGAP interacts with a domain near the carboxyl terminus of RanBP2. These findings place sumoylation at the cytoplasmic filaments of the nuclear pore complex and suggest that, for some substrates, modification and nuclear import are linked events. The pleiotropic (multifunctional) role of RanBP2 reflects its interaction with multiple partners, each presenting distinct cellular or molecular functions. This gene is partially duplicated in a gene cluster that lies in a hot spot for recombination on human chromosome 2q.
Insufficiency of RanBP2 is directly linked to carcinogenesis, aneuploidy, and neuroprotection of photoreceptor neurons to light-elicited stress and aging. Human missense mutations in RanBP2 were identified in its leucine-rich domain and they cause autosomal dominant necrotizing encephalopathy (ADNE). [4]
RANBP2 has been shown to interact with KPNB1 [5] [6] [7] and UBE2I. [8] [9]
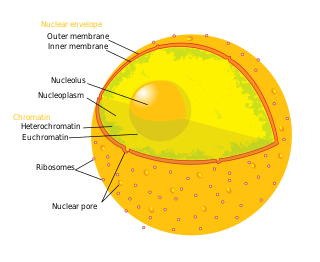
A nuclear pore is a channel as part of the nuclear pore complex (NPC), a large protein complex found in the nuclear envelope in eukaryotic cells, enveloping the cell nucleus containing DNA, which facilitates the selective membrane transport of various molecules across the membrane.
A nuclear localization signalorsequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the cell's cytoplasm to the nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS).

Ran also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily.
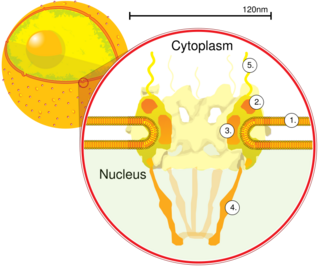
Nuclear pore glycoprotein p62 is a protein complex associated with the nuclear envelope. The p62 protein remains associated with the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. p62 is synthesized as a soluble cytoplasmic precursor of 61 kDa followed by modification that involve addition of N-acetylglucosamine residues, followed by association with other complex proteins. In humans it is encoded by the NUP62 gene.

Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membranes fuse, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nuclear pores enable the passive and facilitated transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. Nucleoporins, a family of around 30 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. Nucleoporin 62 is the most abundant member of this family. Nucleoporins are able to transport molecules across the nuclear envelope at a very high rate. A single NPC is able to transport 60,000 protein molecules across the nuclear envelope every minute.
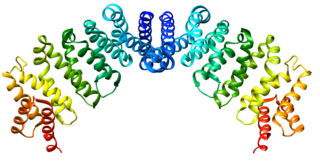
Exportin 1 (XPO1), also known as chromosomal region maintenance 1 (CRM1), is a eukaryotic protein that mediates the nuclear export of various proteins and RNAs.

Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNB1 gene.
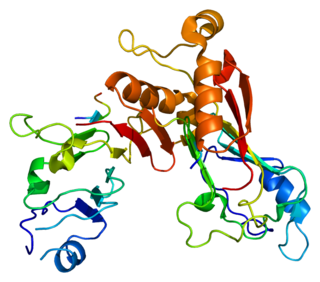
Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP98 gene.
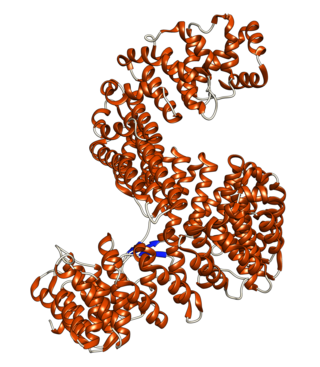
Importin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO5 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the importin beta family. Structurally, the protein adopts the shape of a right hand solenoid and is composed of 24 HEAT repeats.

Regulator of chromosome condensation 1, also known as RCC1, Ran guanine nucleotide exchange factor and RanGEF, is the name for a human gene and protein.

Nucleoporin 153 (Nup153) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NUP153 gene. It is an essential component of the basket of nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in vertebrates, and required for the anchoring of NPCs. It also acts as the docking site of an importing karyopherin. On the cytoplasmic side of the NPC, Nup358 fulfills an analogous role.

Transportin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNPO1 gene.

Nucleoporin 214 (Nup2014) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP214 gene.

Ran GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANGAP1 gene.

Ran-specific binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANBP1 gene.
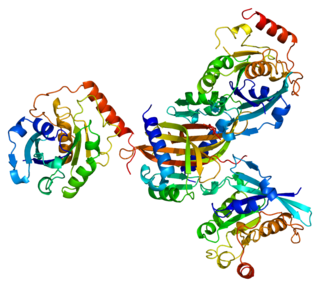
Nuclear transport factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUTF2 gene.

Nucleoporin 54 (Nup54) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUP54 gene.
RanGAP is a protein involved in the transport of other proteins from the cytosol to the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.

Importin 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO8 gene.