Function
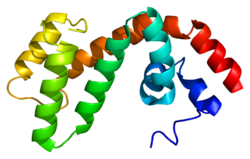
This gene encodes a member of the regulator of G-protein signaling family. This protein contains a conserved, 120 amino acid motif called the RGS domain and a cysteine-rich region. The protein attenuates the signaling activity of G-proteins by binding to activated, GTP-bound G alpha subunits and acting as a GTPase activating protein (GAP), increasing the rate of conversion of the GTP to GDP. This hydrolysis allows the G alpha subunits to bind G beta/gamma subunit heterodimers, forming inactive G-protein heterotrimers, thereby terminating the signal. [6] Along with RGS4, RGS9 and RGS14, [7] [8] RGS17 plays an important role in termination of signalling by mu opioid receptors and development of tolerance to opioid analgesic drugs. [9] [10]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.