Related Research Articles

BNSF Railway is the largest freight railroad network in North America. One of nine North American Class I railroads, BNSF has 41,000 employees, 32,500 miles (52,300 km) of track in 28 states, and more than 8,000 locomotives. It has three transcontinental routes that provide rail connections between the western and eastern United States. BNSF trains traveled over 169 million miles in 2010, more than any other North American railroad.

The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States. With headquarters in Atlanta, Georgia, the company operates 19,420 route miles in 22 eastern states, the District of Columbia, and has rights in Canada over the Albany to Montréal route of the Canadian Pacific Railway, and previously on CN from Buffalo to St. Thomas. NS is responsible for maintaining 28,400 miles (45,700 km), with the remainder being operated under trackage rights from other parties responsible for maintenance. The most common commodity hauled on the railway is coal from mines in Indiana, Kentucky, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, and West Virginia. The railway also offers the largest intermodal network in eastern North America. Norfolk Southern was formed in 1982, following the Norfolk and Western railroad being merged into the Southern railroad.

Kansas City Southern (KCS) is a Delaware-registered pure transportation holding company with railroad investments in the United States, Mexico, and Panama.

Conrail, formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway.

The San Diego and Arizona Eastern Railway Company is a short-line American railroad founded in 1906 as the San Diego and Arizona Railway (SD&A) by sugar magnate, developer, and entrepreneur John D. Spreckels. Dubbed "The Impossible Railroad" by many engineers of its day due to the immense logistical challenges involved, the line was established in part to provide San Diego with a direct rail link to the east by connecting with the Southern Pacific Railroad lines in El Centro, California.

Pan Am Railways, Inc. (PAR), known before March 2006 as Guilford Rail System, is an American holding company that owns and operates Class II regional railroads covering northern New England from Mattawamkeag, Maine, to Rotterdam Junction, New York. The primary subsidiaries of Pan Am Railways are Boston and Maine Corporation, Maine Central Railroad Company, Portland Terminal Company, and Springfield Terminal Railway Company.

The San Diego and Imperial Valley Railroad (SD&IV) is a class III railroad operating freight rail service in the San Diego area, providing service to customers in the region and moving railcars between the end of the BNSF Railway in Downtown San Diego and the Mexico–United States border in San Ysidro. The railroad has exclusive trackage rights to operates over tracks by the San Diego and Arizona Eastern Railway, a subsidiary of the Metropolitan Transit System, the regional public transit service provider. Tracks are shared with the San Diego Trolley, another subsidiary of the Metropolitan Transit System, and freight trains are only operated at nights when passenger service is not in operation. The San Diego & Imperial Valley Railroad was established in October 1984 and is owned and operated by Genesee & Wyoming, a holding company that operates more than 100 shortline railroads like the SD&IV.

The Texas Mexican Railway was a railroad that operated as a subsidiary of the Kansas City Southern Railway in Texas. It is often referred to as the Tex-Mex, or TexMex Railway.

Genesee & Wyoming Inc. (G&W) is an American short line railroad holding company, that owns or maintains an interest in 122 railroads in the United States, Canada, Belgium, Netherlands, Poland, United Kingdom and formerly Australia. It operates more than 13,000 miles (21,000 km) of owned and leased track. G&W owns or leases 116 freight railroads organized in locally managed operating regions with 7,300 employees serving 3,000 customers. The company had its roots in the Class III Genesee and Wyoming Railroad, which began in 1899.

The Connecticut Southern Railroad is a 90-mile (140 km) long short-line railroad operating in Connecticut and Massachusetts on lines originally operated by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, later operated by Penn Central and Conrail. It is a subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming. The line is headquartered in Hartford, Connecticut. Pan Am Railways exercises trackage rights to access its line in Berlin, Connecticut connecting to Waterbury, Connecticut.

The Toledo, Peoria and Western Railway is a short line railroad that operates 247 miles (398 km) of track from Mapleton, Illinois, through Peoria across Illinois to Logansport, Indiana. TP&W has trackage rights between Galesburg, Illinois, and Peoria, between Logansport and Kokomo, Indiana, and between Reynolds, Indiana, and Lafayette, Indiana. TPW has connections with UP, BNSF, NS, CSXT, CN, CP, CERA, CIM, KBSR and T&P. The railroad is now owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc. The railroad's traffic comes largely from agricultural products, including both raw and processed grain products, as well as chemicals and completed tractors. The TPW hauled around 26,000 carloads in 2008.

The San Pedro Valley Railroad, formerly the San Pedro & Southwestern Railroad, is an Arizona shortline railroad, currently operating from a connection with the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) at Benson, Arizona, seven miles to Curtiss, Arizona west of St. David. The SPSR formerly ran a total of 76.2 miles (122.6 km), with main track from Benson to Paul Spur, a location about 10 miles (16 km) west of Douglas, as well as the Bisbee Branch which ran 5.6 miles (9.0 km) to Bisbee, Arizona. The SPSR is owned by Ironhorse Resources.
The Texas Transportation Company was an electrified, Class III, short-line railroad in San Antonio, Texas, that operated from 1897 until 2001. It served the Pearl Brewery and several other businesses, moving carloads between those businesses and the Southern Pacific yard. Service ended on June 30, 2000, shortly before the Pabst Brewing Company closed the Pearl Brewery, in early 2001.

The Southern Railroad of New Jersey is a small short-line railroad company based in Winslow Township, New Jersey. The railroad operates freight trains in two areas in Southern New Jersey. In the Winslow area, trains operate between Winslow Junction and Pleasantville, and between Winslow Junction and the Winslow Hot Mix asphalt plant in Winslow Township. In Salem County and Gloucester County, the company operates on the Salem Branch between Salem and Woodbury.

The Indiana Northeastern Railroad is a Class III short line freight railroad operating on nearly 130 miles (210 km) in southern lower Michigan, northeast Indiana and northwest Ohio. The Indiana Northeastern Railroad Company began operations in December 1992 and is an independent privately owned company. As of 2017 the railroad hauled more than 7,000 carloads per year. Commodities moved by the railroad include corn, soybeans, wheat and flour. It also handles plastics, fiberboard, aluminum, copper, coal, perlite, stone, lumber, glass, rendering products, as well as agricultural fertilizers and chemicals.

The Carolina Piedmont Railroad is a class III railroad and subsidiary of Genesee & Wyoming Inc. operating in the Upstate region of South Carolina. From an interchange with CSX Transportation at Laurens the railroad runs 34 miles (55 km) to the northwest, terminating at East Greenville.

The Ohio Central Railroad System is a network of ten short line railroads operating in Ohio and western Pennsylvania. It is owned by Genesee & Wyoming Inc.
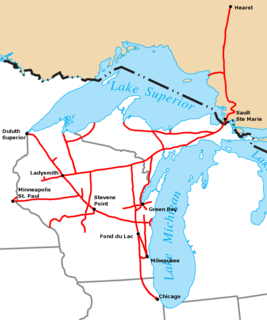
Wisconsin Central Ltd. is a railroad subsidiary of Canadian National. At one time, its parent Wisconsin Central Transportation Corporation owned or operated railroads in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, New Zealand, and Australia.

The South Carolina Central Railroad is a class III railroad that operates 42 miles (68 km) of former CSX Transportation trackage in South Carolina. Originally a RailTex subsidiary upon its start in 1987, the railroad passed to RailAmerica following their acquisition of RailTex in 2000 and passed to the Genesee & Wyoming Railroad upon its acquisition of RailAmerica.
The Delmarva Central Railroad is an American short-line railroad owned by Carload Express that operates 188 miles (303 km) of track on the Delmarva Peninsula in the states of Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia. The railroad operates lines from Porter, Delaware to Hallwood, Virginia and from Harrington, Delaware to Frankford, Delaware along with several smaller branches. The DCR interchanges with the Norfolk Southern Railway and the Maryland and Delaware Railroad. The railroad was created in 2016 to take over the Norfolk Southern Railway lines on the Delmarva Peninsula. The DCR expanded by taking over part of the Bay Coast Railroad in 2018 and the Delaware Coast Line Railroad in 2019.
References
- ↑ Who is RailTex? RailTex
- ↑ RailTex starts up 17th short line Railway Age May 1991 page 19
- ↑ RailTex: Cloning Success Railway Age September 1991 pages 59-73
- ↑ RailTex group wins Brazilian concession Railway Age July 1996 page 24
- ↑ RailTex expanding its role in Brazil Railway Age January 1997 page 27
- ↑ RailTex pulls out of Brazil Railway Age December 1999 page 18
- ↑ RailAmerica to Acquire RailTex, Creating World'sLargest Short Line/Regional Freight RailroadOperator Business Wire October 14, 1999