
The Bengal Nagpur Railway was one of the companies which pioneered development of the railways in eastern and central India. It was succeeded first by Eastern Railway and subsequently by South Eastern Railway.

The Asansol–Gaya section is a railway line connecting Asansol and Gaya in India. This 267-kilometre long (166 mi) track is part of the Grand Chord, Howrah–Gaya–Delhi line and Howrah–Allahabad–Mumbai line. This section includes the NSC Bose Gomoh–Barkakana line. It is under the jurisdiction of Eastern Railway and East Central Railway. The section links to South Eastern Railway through Bokaro Steel City and Adra.

The Howrah–Prayagraj–Mumbai line, is a railway line connecting Kolkata and Mumbai via Prayagraj. The 2,160-kilometre long (1,340 mi) railway line was opened to traffic in 1870. This railway line was 2,146-kilometre long (1,333 mi) until 2004. In 2004 the construction of Indira Sagar Dam submerged the old alignment near Khandwa & a new alignment of 14-kilometre long (8.7 mi) was relaid.

The Asansol–Adra–Tatanagar–Kharagpur line is part of Howrah and eastern India's links with Mumbai and Chennai. It is also a major freight line for transporting iron ore, coal and steel products. This page includes the Adra–Bokaro Steel City branch line, the Adra-Gomoh branch line, the Adra-Dhanbad branch line and Tatanagar–Badampahar branch lines.

The Howrah–Chennai main line is a railway line connecting Chennai and Kolkata cutting across Eastern Coastal Plains of India. It covers a distance of 1,661 kilometres (1,032 mi) across, West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
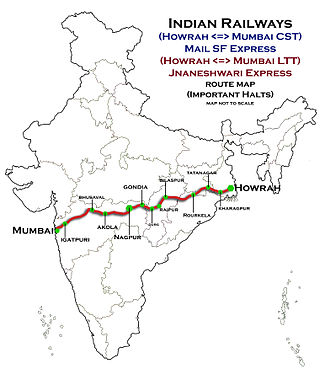
The Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line is a railway line in India connecting Kolkata and Mumbai via Nagpur. The 1,968-kilometre-long (1,223 mi) railway line was opened to traffic in 1900.

The Tatanagar–Bilaspur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Tatanagar in the Indian state of Jharkhand and Bilaspur in Chhattisgarh. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through an industrial-mining area and handles high volumes of freight, particularly coal and iron ore.

Bilaspur Junction Railway Station, located in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh, serves Bilaspur in Bilaspur district.

The Bilaspur–Nagpur section is part of the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line and connects Bilaspur in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and Nagpur in Maharashtra. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through a forested plateau region interspersed with fertile valleys.
Gondia Junction serves Gondia in Gondia district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is one of the important railway stations in India of South East central railways zone railways. This station is India's third and first in Vidarbha to get mist cooling system.Its falls under nagpur division

Raipur Junction is the main railway station serving the city of Raipur. It is only few of the railway stations in India which has been given the grade 'A-1' by the Indian Railways and is one of the highest-revenue-earning railway stations in India. This station is one of the prominent stations on the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line. It is also the originating point of the Raipur–Vizianagarm branch line route. Raipur is the busiest railway station in South Eastern Central Railway zone.
Chakraharpur Railway Station serves Chakradharpur in West Singhbhum district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.
Chandil Railway Station serves Chandil in Seraikela Kharsawan district in the Indian state of Jharkhand.

Purulia railway station serves Purulia City the headquarters of Purulia district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is situated at the eastern side of the city with railway owned colonies which is home for working staffs. The station is under NSG4 category.

Adra Junction railway station serves Adra town, and also serves the industrial towns of Raghunathpur and Kashipur in Purulia district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a gateway to the famous tourist spots of Purulia district. It also servers as the divisional headquarters of the Adra Division of the South Eastern Railway zone of Indian Railways. Adra (ADRA) station is categorized as NSG 4 on the basis of yearly window sale. The station has also been declared as 'Model' as well as 'Adarsh' station. The station serves the Divisional Head Quarters.

Durg Junction Railway Station, is a junction station located in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It serves Durg, Bhilai city and the adjoining areas of it. Durg Junction is the part of South East Central Railway. It is one of the largest railway junctions of Chhattisgarh in terms of network. It is also one of the most prominent and important station in Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line. It is an 'A' grade station of Indian Railways in terms of passenger services.

Joychandi Pahar Junction railway station serves Adra town and Raghunathpur in Purulia district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It was named after the hill called Joychandi Pahar which is located between these two towns. Joychandipahar rail station is situated on the Asansol–Purulia–Sini main line section. In the year of 2014 it was redeveloped and made as an alternative station of Adra Junction to decongest Adra station from a huge passenger and freight traffic.

Damodar is a railway station on the Asansol–Tatanagar–Kharagpur line, just east of the Damodar River. It is located in Asansol, Paschim Bardhaman district in the Indian state of West Bengal.

The Howrah–Gaya–Delhi is a railway line connecting Howrah and Delhi cutting across Indo-Gangetic Plain and a comparatively small stretch of the line crossing over the Chota Nagpur Plateau. It covers a distance of 1,452 kilometres (902 mi) across, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi. The Grand Chord is a part of this line and as such is referred to by many as Howrah–Delhi line.

The Barkakana–Muri–Chandil line is an Indian railway line connecting Barkakana and Muri with Chandil on the Asansol–Tatanagar–Kharagpur line. This 126-kilometre (78 mi) track is under the jurisdiction of South Eastern Railway.


















