Related Research Articles

An antibody (Ab) is the secreted form of a B cell receptor; the term immunoglobulin (Ig) can refer to either the membrane-bound form or the secreted form of the B cell receptor, but they are, broadly speaking, the same protein, and so the terms are often treated as synonymous. Antibodies are large, Y-shaped proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which are used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that cause disease. Antibodies can recognize virtually any size antigen with diverse chemical compositions from molecules. Each antibody recognizes one or more specific antigens. Antigen literally means "antibody generator", as it is the presence of an antigen that drives the formation of an antigen-specific antibody. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that specifically binds to one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing the two molecules to bind together with precision. Using this mechanism, antibodies can effectively "tag" a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.

A monoclonal antibody is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.

Phage display is a laboratory technique for the study of protein–protein, protein–peptide, and protein–DNA interactions that uses bacteriophages to connect proteins with the genetic information that encodes them. In this technique, a gene encoding a protein of interest is inserted into a phage coat protein gene, causing the phage to "display" the protein on its outside while containing the gene for the protein on its inside, resulting in a connection between genotype and phenotype. The proteins that the phages are displaying can then be screened against other proteins, peptides or DNA sequences, in order to detect interaction between the displayed protein and those of other molecules. In this way, large libraries of proteins can be screened and amplified in a process called in vitro selection, which is analogous to natural selection.
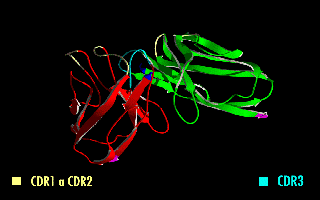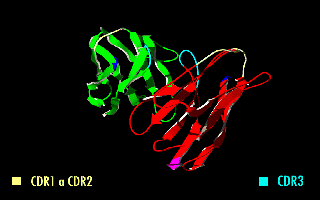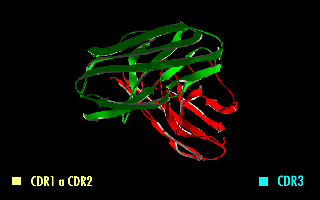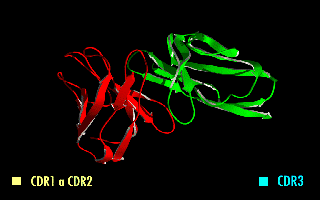
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or vice versa. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered.

A single-domain antibody (sdAb), also known as a Nanobody, is an antibody fragment consisting of a single monomeric variable antibody domain. Like a whole antibody, it is able to bind selectively to a specific antigen. With a molecular weight of only 12–15 kDa, single-domain antibodies are much smaller than common antibodies which are composed of two heavy protein chains and two light chains, and even smaller than Fab fragments and single-chain variable fragments.
Humanized antibodies are antibodies from non-human species whose protein sequences have been modified to increase their similarity to antibody variants produced naturally in humans. The process of "humanization" is usually applied to monoclonal antibodies developed for administration to humans. Humanization can be necessary when the process of developing a specific antibody involves generation in a non-human immune system. The protein sequences of antibodies produced in this way are partially distinct from homologous antibodies occurring naturally in humans, and are therefore potentially immunogenic when administered to human patients. The International Nonproprietary Names of humanized antibodies end in -zumab, as in omalizumab.

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.

Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have varied therapeutic uses. It is possible to create a mAb that binds specifically to almost any extracellular target, such as cell surface proteins and cytokines. They can be used to render their target ineffective, to induce a specific cell signal, to cause the immune system to attack specific cells, or to bring a drug to a specific cell type.
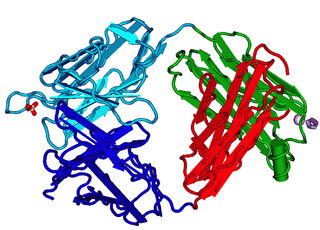
The fragment antigen-binding region is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope, comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
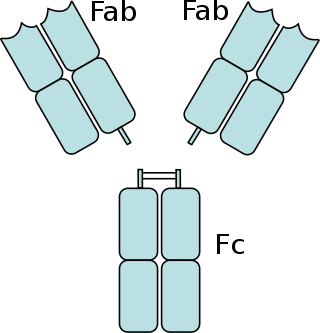
The fragment crystallizable region is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This region allows antibodies to activate the immune system, for example, through binding to Fc receptors. In IgG, IgA and IgD antibody isotypes, the Fc region is composed of two identical protein fragments, derived from the second and third constant domains of the antibody's two heavy chains; IgM and IgE Fc regions contain three heavy chain constant domains in each polypeptide chain. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core-fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,6 linked sialic acid residues.
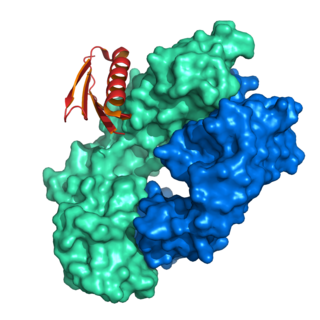
Protein L was first isolated from the surface of bacterial species Peptostreptococcus magnus and was found to bind immunoglobulins through L chain interaction, from which the name was suggested. It consists of 719 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of protein L purified from the cell walls of Peptostreptoccus magnus was first estimated as 95kD by SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent 2-mercaptoethanol, while the molecular weight was determined to 76kD by gel chromatography in the presence of 6 M guanidine HCl. Protein L does not contain any interchain disulfide loops, nor does it consist of disulfide-linked subunits. It is an acidic molecule with a pI of 4.0. Unlike protein A and protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins (antibodies), protein L binds antibodies through light chain interactions. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to protein L.
Small modular immunopharmaceuticals, or SMIPs for short, are artificial proteins that are intended for use as pharmaceutical drugs. They are largely built from parts of antibodies (immunoglobulins), and like them have a binding site for antigens that could be used for monoclonal antibody therapy. SMIPs have similar biological half-life and, being smaller than antibodies, are reasoned to have better tissue penetration properties. They were invented by Trubion and are now being developed by Emergent BioSolutions, which acquired Trubion in 2010.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzheimer's disease.
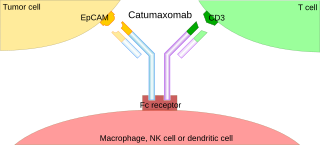
A trifunctional antibody is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an Fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.

Two chemically linked fragments antigen-binding form an artificial antibody that binds to two different antigens, making it a type of bispecific antibody. They are fragments antigen-binding of two different monoclonal antibodies and are linked by chemical means like a thioether. Typically, one of the Fabs binds to a tumour antigen and the other to a protein on the surface of an immune cell, for example an Fc receptor on a macrophage. In this way, tumour cells are attached to immune cells, which destroy them.
A rabbit hybridoma is a hybrid cell line formed by the fusion of an antibody producing rabbit B cell with a cancerous B-cell (myeloma).

ImmTACs are a class of bispecific biological drug being investigated for the treatment of cancer and viral infections which combines engineered cancer-recognizing TCRs with immune activating complexes. ImmTACs target cancerous or virally infected cells through binding human leukocyte antigen (HLA) presented peptide antigens and redirect the host's cytotoxic T cells to recognise and kill them.
Synthetic antibodies are affinity reagents generated entirely in vitro, thus completely eliminating animals from the production process. Synthetic antibodies include recombinant antibodies, nucleic acid aptamers and non-immunoglobulin protein scaffolds. As a consequence of their in vitro manufacturing method the antigen recognition site of synthetic antibodies can be engineered to any desired target and may extend beyond the typical immune repertoire offered by natural antibodies. Synthetic antibodies are being developed for use in research, diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Synthetic antibodies can be used in all applications where traditional monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies are used and offer many inherent advantages over animal-derived antibodies, including comparatively low production costs, reagent reproducibility and increased affinity, specificity and stability across a range of experimental conditions.
Creative Biolabs, Inc. is a life-science company which produces and supplies biotech products and services for early drug discovery and development, including various phage display libraries such as pre-made libraries, phage display services, antibody sequencing, and antibody humanization. Customers include pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, government agencies, clinical research organizations and biotechnology companies.

Pretargeting (imaging) is a tool for nuclear medicine and radiotherapy. Imaging studies require a high contrast of target to background. This can be provided by using a biomarker which has a high affinity and specificity for its target.
References
- 1 2 3 Creative Biolabs (2017-04-28), Introduction of Recombinant Antibody , retrieved 2017-08-18
- 1 2 3 Ahmad, Zuhaida Asra; Yeap, Swee Keong; Ali, Abdul Manaf; Ho, Wan Yong; Alitheen, Noorjahan Banu Mohamed; Hamid, Muhajir (2012). "scFv Antibody: Principles and Clinical Application". Clinical and Developmental Immunology. 2012: 980250. doi: 10.1155/2012/980250 . ISSN 1740-2522. PMC 3312285 . PMID 22474489.
- 1 2 3 Kunert R, Reinhart D (April 2016). "Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing". Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100 (8): 3451–61. doi:10.1007/s00253-016-7388-9. ISSN 0175-7598. PMC 4803805 . PMID 26936774.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Miltenyi Biotec (2017-03-22), Webinar: Recombinant Antibodies for Improved Flow Cytometry , retrieved 2017-08-20
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Kriangkum, Jitra; Xu, Biwen; Nagata, Les P.; Fulton, R.Elaine; Suresh, Mavanur R. (2001). "Bispecific and bifunctional single chain recombinant antibodies". Biomolecular Engineering. 18 (2): 31–40. doi:10.1016/s1389-0344(01)00083-1. PMID 11535414.
- ↑ Ma, Julian K.-C.; Hikmat, Ban Y.; Wycoff, Keith; Vine, Nicholas D.; Chargelegue, Daniel; Yu, Lloyd; Hein, Mich B.; Lehner, Thomas (May 1998). "Characterization of a recombinant plant monoclonal secretory antibody and preventive immunotherapy in humans". Nature Medicine. 4 (5): 601–606. doi:10.1038/nm0598-601. PMID 9585235. S2CID 10499678.
- 1 2 3 Bio-Rad Laboratories (2013-12-03), Developing Recombinant Anti Idiotypic Antibodies for PK/PD and Immunogenicity Assays , retrieved 2017-08-20
- 1 2 Glockshuber, Rudi; Malia, Mark; Pfitzinger, Ilse; Plueckthun, Andreas (1990-02-13). "A comparison of strategies to stabilize immunoglobulin Fv-fragments". Biochemistry. 29 (6): 1362–1367. doi:10.1021/bi00458a002. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 2110478.
- 1 2 3 4 Neri, D.; Petrul, H.; Roncucci, G. (August 1995). "Engineering recombinant antibodies for immunotherapy". Cell Biophysics. 27 (1): 47–61. doi:10.1007/BF02822526. ISSN 0163-4992. PMID 7493398. S2CID 8421714.
- 1 2 3 4 Frenzel, André; Hust, Michael; Schirrmann, Thomas (2013). "Expression of Recombinant Antibodies". Frontiers in Immunology. 4: 217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00217 . ISSN 1664-3224. PMC 3725456 . PMID 23908655.
- 1 2 Jørgensen, Mathias Lindh; Friis, Niels Anton; Just, Jesper; Madsen, Peder; Petersen, Steen Vang; Kristensen, Peter (2014-01-15). "Expression of single-chain variable fragments fused with the Fc-region of rabbit IgG in Leishmania tarentolae". Microbial Cell Factories. 13: 9. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-9 . ISSN 1475-2859. PMC 3917567 . PMID 24428896.
- ↑ Zhong, Nan; Loppnau, Peter; Seitova, Alma; Ravichandran, Mani; Fenner, Maria; Jain, Harshika; Bhattacharya, Anandi; Hutchinson, Ashley; Paduch, Marcin (2015-10-05). "Optimizing Production of Antigens and Fabs in the Context of Generating Recombinant Antibodies to Human Proteins". PLOS ONE. 10 (10): e0139695. Bibcode:2015PLoSO..1039695Z. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139695 . ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 4593582 . PMID 26437229.
- ↑ Arndt, M. A.; Krauss, J.; Kipriyanov, S. M.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Little, M. (1999-10-15). "A bispecific diabody that mediates natural killer cell cytotoxicity against xenotransplantated human Hodgkin's tumors". Blood. 94 (8): 2562–2568. doi:10.1182/blood.V94.8.2562.420k20_2562_2568. ISSN 0006-4971. PMID 10515858.
- ↑ Wu, Chengbin; Ying, Hua; Grinnell, Christine; Bryant, Shaughn; Miller, Renee; Clabbers, Anca; Bose, Sahana; McCarthy, Donna; Zhu, Rong-Rong (November 2007). "Simultaneous targeting of multiple disease mediators by a dual-variable-domain immunoglobulin". Nature Biotechnology. 25 (11): 1290–1297. doi:10.1038/nbt1345. ISSN 1087-0156. PMID 17934452. S2CID 35102991.
- ↑ Frenzel, André; Hust, Michael; Schirrmann, Thomas (2013). "Expression of Recombinant Antibodies". Frontiers in Immunology. 4: 217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00217 . ISSN 1664-3224. PMC 3725456 . PMID 23908655.
- ↑ Skerra, A.; Pluckthun, A. (1988-05-20). "Assembly of a functional immunoglobulin Fv fragment in Escherichia coli". Science. 240 (4855): 1038–1041. Bibcode:1988Sci...240.1038S. doi:10.1126/science.3285470. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 3285470.
- ↑ Boss, M A; Kenten, J H; Wood, C R; Emtage, J S (1984-05-11). "Assembly of functional antibodies from immunoglobulin heavy and light chains synthesised in E. coli". Nucleic Acids Research. 12 (9): 3791–3806. doi:10.1093/nar/12.9.3791. ISSN 0305-1048. PMC 318790 . PMID 6328437.
- ↑ "Recombinant antibodies: next level antibody technology". evitria. 2021-11-18.
- ↑ Köhler, G.; Milstein, C. (1975-08-07). "Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity". Nature. 256 (5517): 495–497. Bibcode:1975Natur.256..495K. doi:10.1038/256495a0. PMID 1172191. S2CID 4161444.
- 1 2 3 4 Yuan, Ruosen; Chen, Xiaoxu; Chen, Yan; Gu, Tiejun; Xi, Hualong; Duan, Ye; Sun, Bo; Yu, Xianghui; Jiang, Chunlai (2014-02-01). "Preparation and diagnostic use of a novel recombinant single-chain antibody against rabies virus glycoprotein". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 98 (4): 1547–1555. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5351-6. ISSN 0175-7598. PMID 24241896. S2CID 3207602.
- 1 2 Pietersz, Geoffrey A.; Wang, Xiaowei; Yap, May Lin; Lim, Bock; Peter, Karlheinz (2017-07-13). "Therapeutic targeting in nanomedicine: the future lies in recombinant antibodies". Nanomedicine. 12 (15): 1873–1889. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0043 . ISSN 1743-5889. PMID 28703636.
- 1 2 3 Bagheri, Vahid; Nejatollahi, Foroogh; Esmaeili, Seyed Alireza; Momtazi, Amir Abbas; Motamedifar, Mohamad; Sahebkar, Amirhossein (2017). "Neutralizing human recombinant antibodies against herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins B from a phage-displayed scFv antibody library". Life Sciences. 169: 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.018. PMC 7094719 . PMID 27888111.
- 1 2 Cartellieri, M.; Feldmann, A.; Koristka, S.; Arndt, C.; Loff, S.; Ehninger, A.; von Bonin, M.; Bejestani, E. P.; Ehninger, G. (2016-08-12). "Switching CAR T cells on and off: a novel modular platform for retargeting of T cells to AML blasts". Blood Cancer Journal. 6 (8): e458. doi:10.1038/bcj.2016.61. PMC 5022178 . PMID 27518241.
- 1 2 Burton, D. R.; Pyati, J.; Koduri, R.; Sharp, S. J.; Thornton, G. B.; Parren, P. W.; Sawyer, L. S.; Hendry, R. M.; Dunlop, N. (1994-11-11). "Efficient neutralization of primary isolates of HIV-1 by a recombinant human monoclonal antibody". Science. 266 (5187): 1024–1027. Bibcode:1994Sci...266.1024B. doi:10.1126/science.7973652. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 7973652.
- ↑ Golubovskaya, Vita; Wu, Lijun (2016-03-15). "Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy". Cancers. 8 (3): 36. doi: 10.3390/cancers8030036 . PMC 4810120 . PMID 26999211.
- ↑ Albert, Susann; Arndt, Claudia; Feldmann, Anja; Bergmann, Ralf; Bachmann, Dominik; Koristka, Stefanie; Ludwig, Florian; Ziller-Walter, Pauline; Kegler, Alexandra (2017-04-03). "A novel nanobody-based target module for retargeting of T lymphocytes to EGFR-expressing cancer cells via the modular UniCAR platform". OncoImmunology. 6 (4): e1287246. doi:10.1080/2162402x.2017.1287246. PMC 5414885 . PMID 28507794.
- ↑ Wang, Ding-ding; Su, Man-man; Sun, Yan; Huang, Shu-lin; Wang, Ju; Yan, Wei-qun (2012). "Expression, purification and characterization of a human single-chain Fv antibody fragment fused with the Fc of an IgG1 targeting a rabies antigen in Pichia pastoris". Protein Expression and Purification. 86 (1): 75–81. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2012.08.015. PMID 22982755.
- 1 2 Blanco E, Shen H, Ferrari M (September 2015). "Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery". Nat. Biotechnol. 33 (9): 941–51. doi:10.1038/nbt.3330. PMC 4978509 . PMID 26348965.
- 1 2 Longmire, Michelle; Choyke, Peter L.; Kobayashi, Hisataka (2008-09-25). "Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: considerations and caveats". Nanomedicine. 3 (5): 703–717. doi:10.2217/17435889.3.5.703. ISSN 1743-5889. PMC 3407669 . PMID 18817471.
- ↑ Yokota, T.; Milenic, D. E.; Whitlow, M.; Wood, J. F.; Hubert, S. L.; Schlom, J. (1993-08-15). "Microautoradiographic analysis of the normal organ distribution of radioiodinated single-chain Fv and other immunoglobulin forms". Cancer Research. 53 (16): 3776–3783. ISSN 0008-5472. PMID 8339291.
- ↑ "What's the difference between afucosylated antibodies and recombinant antibodies? - evitria". 2021-03-29. Retrieved 2021-04-28.
- ↑ EURL ECVAM Recommendation on Non-Animal-Derived Antibodies. Publications Office of the European Union. 2020. ISBN 978-92-76-18346-4.
- ↑ Baker, Monya (May 2015). "Reproducibility crisis: Blame it on the antibodies". Nature. 521 (7552): 274–276. Bibcode:2015Natur.521..274B. doi: 10.1038/521274a . PMID 25993940.
- ↑ Goodman, Simon. L. (October 2018). "The antibody horror show: an introductory guide for the perplexed". New Biotechnology. 45: 9–13. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2018.01.006. PMID 29355666. S2CID 29628410.