In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.

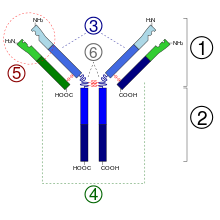
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.

The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions.

B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed.

The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules.

Immunoglobulin G is a type of antibody. Representing approximately 75% of serum antibodies in humans, IgG is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation. IgG molecules are created and released by plasma B cells. Each IgG antibody has two paratopes.
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The part of an antibody that binds to the epitope is called a paratope. Although epitopes are usually non-self proteins, sequences derived from the host that can be recognized are also epitopes.
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed by phagocytes. Different types of things ("targets") can be tagged by opsonins for phagocytosis, including: pathogens, cancer cells, aged cells, dead or dying cells, excess synapses, or protein aggregates. Opsonins help clear pathogens, as well as dead, dying and diseased cells.

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates.
Antigen processing, or the cytosolic pathway, is an immunological process that prepares antigens for presentation to special cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes. It is considered to be a stage of antigen presentation pathways. This process involves two distinct pathways for processing of antigens from an organism's own (self) proteins or intracellular pathogens, or from phagocytosed pathogens ; subsequent presentation of these antigens on class I or class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules is dependent on which pathway is used. Both MHC class I and II are required to bind antigens before they are stably expressed on a cell surface. MHC I antigen presentation typically involves the endogenous pathway of antigen processing, and MHC II antigen presentation involves the exogenous pathway of antigen processing. Cross-presentation involves parts of the exogenous and the endogenous pathways but ultimately involves the latter portion of the endogenous pathway.

MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on platelets, but not on red blood cells. Their function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to cytotoxic T cells; this will trigger an immediate response from the immune system against a particular non-self antigen displayed with the help of an MHC class I protein. Because MHC class I molecules present peptides derived from cytosolic proteins, the pathway of MHC class I presentation is often called cytosolic or endogenous pathway.
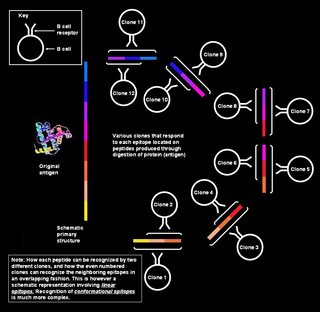
In immunology, a linear epitope is an epitope—a binding site on an antigen—that is recognized by antibodies by its linear sequence of amino acids. In contrast, most antibodies recognize a conformational epitope that has a specific three-dimensional shape.
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted:

An immune complex, sometimes called an antigen-antibody complex or antigen-bound antibody, is a molecule formed from the binding of multiple antigens to antibodies. The bound antigen and antibody act as a unitary object, effectively an antigen of its own with a specific epitope. After an antigen-antibody reaction, the immune complexes can be subject to any of a number of responses, including complement deposition, opsonization, phagocytosis, or processing by proteases. Red blood cells carrying CR1-receptors on their surface may bind C3b-coated immune complexes and transport them to phagocytes, mostly in liver and spleen, and return to the general circulation.

The B cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule and a signal transduction moiety. The former forms a type 1 transmembrane receptor protein, and is typically located on the outer surface of these lymphocyte cells. Through biochemical signaling and by physically acquiring antigens from the immune synapses, the BCR controls the activation of the B cell. B cells are able to gather and grab antigens by engaging biochemical modules for receptor clustering, cell spreading, generation of pulling forces, and receptor transport, which eventually culminates in endocytosis and antigen presentation. B cells' mechanical activity adheres to a pattern of negative and positive feedbacks that regulate the quantity of removed antigen by manipulating the dynamic of BCR–antigen bonds directly. Particularly, grouping and spreading increase the relation of antigen with BCR, thereby proving sensitivity and amplification. On the other hand, pulling forces delinks the antigen from the BCR, thus testing the quality of antigen binding.
Antigenic variation or antigenic alteration refers to the mechanism by which an infectious agent such as a protozoan, bacterium or virus alters the proteins or carbohydrates on its surface and thus avoids a host immune response, making it one of the mechanisms of antigenic escape. It is related to phase variation. Antigenic variation not only enables the pathogen to avoid the immune response in its current host, but also allows re-infection of previously infected hosts. Immunity to re-infection is based on recognition of the antigens carried by the pathogen, which are "remembered" by the acquired immune response. If the pathogen's dominant antigen can be altered, the pathogen can then evade the host's acquired immune system. Antigenic variation can occur by altering a variety of surface molecules including proteins and carbohydrates. Antigenic variation can result from gene conversion, site-specific DNA inversions, hypermutation, or recombination of sequence cassettes. The result is that even a clonal population of pathogens expresses a heterogeneous phenotype. Many of the proteins known to show antigenic or phase variation are related to virulence.

Complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) are part of the variable chains in immunoglobulins (antibodies) and T cell receptors, generated by B-cells and T-cells respectively, where these molecules bind to their specific antigen. A set of CDRs constitutes a paratope. As the most variable parts of the molecules, CDRs are crucial to the diversity of antigen specificities generated by lymphocytes.

Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.

In immunology, an idiotype is a shared characteristic between a group of immunoglobulin or T-cell receptor (TCR) molecules based upon the antigen binding specificity and therefore structure of their variable region. The variable region of antigen receptors of T cells (TCRs) and B cells (immunoglobulins) contain complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) with unique amino acid sequences. They define the surface and properties of the variable region, determining the antigen specificity and therefore the idiotope of the molecule. Immunoglobulins or TCRs with a shared idiotope are the same idiotype. Antibody idiotype is determined by:
Antigen-antibody interaction, or antigen-antibody reaction, is a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B cells of the white blood cells and antigens during immune reaction. The antigens and antibodies combine by a process called agglutination. It is the fundamental reaction in the body by which the body is protected from complex foreign molecules, such as pathogens and their chemical toxins. In the blood, the antigens are specifically and with high affinity bound by antibodies to form an antigen-antibody complex. The immune complex is then transported to cellular systems where it can be destroyed or deactivated.