
Bonaparte's gull is a member of the gull family Laridae found mainly in northern North America. At 28 to 38 cm in length, it is one of the smallest species of gull. Its plumage is mainly white with grey upperparts. During breeding season, Bonaparte's gull gains a slate-grey hood. The sexes are similar in appearance.

Maxillopoda is a diverse class of crustaceans including barnacles, copepods and a number of related animals. It does not appear to be a monophyletic group, and no single character unites all the members.

The Pentastomida are an enigmatic group of parasitic arthropods commonly known as tongue worms due to the resemblance of the species of the genus Linguatula to a vertebrate tongue. They are traditionally seen as crustaceans, even if that position has been questioned.

Karl (Carl) Moriz (Moritz) Diesing was an Austrian naturalist and zoologist, specializing in the study of helminthology.

Pancrustacea is the clade that comprises all crustaceans and hexapods. This grouping is contrary to the Atelocerata hypothesis, in which Myriapoda and Hexapoda are sister taxa, and Crustacea are only more distantly related. As of 2010, the Pancrustacea taxon is considered well accepted, with most studies recovering Hexapoda within Crustacea. The clade has also been called Tetraconata, referring to having four cone cells in the ommatidia. This name is preferred by some scientists as a means of avoiding confusion with the use of "pan-" to indicate a clade that includes a crown group and all of its stem group representatives.
Richard Heymons was a German zoologist and entomologist.

Dichomeris is a genus of moths in the family Gelechiidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1818.

Gigantorhynchus is a genus of Acanthocephala that parasitize marsupials, anteaters, and possibly baboons by attaching themselves to the intestines using their hook-covered proboscis. Their life cycle includes an egg stage found in host feces, a cystacanth (larval) stage in an intermediate host such as termites, and an adult stage where cystacanths mature in the intestines of the host. This genus is characterized by a cylindrical proboscis with a crown of robust hooks at the apex followed by numerous small hooks on the rest of the proboscis, a long body with pseudosegmentation, filiform lemnisci, and ellipsoid testes. The largest known specimen is the female G. ortizi with a length of around 240 millimetres (9.4 in) and a width of 2 millimetres (0.08 in). Genetic analysis on one species of Gigantorhynchus places it with the related genus Mediorhynchus in the family Gigantorhynchidae. Six species in this genus are distributed across Central and South America and possibly Zimbabwe. Infestation by a Gigantorhynchus species may cause partial obstructions of the intestines, severe lesions of the intestinal wall, and may lead to death.

Gonyaulax is a genus of dinoflagellates with the type species Gonyaulax spinifera Diesing. Gonyaulax belongs to red dinoflagellates and commonly causes red tides. It secretes a poisonous toxin known as "saxitoxin" which causes paralysis in humans.
Dipteropeltis hirundo is a little-known species of fish louse. It is an ectoparasite of fish in South America, including piranhas and Pseudoplatystoma fasciatum.

Armillifer is a genus of Pentastomida, containing the following species:

Armillifer armillatus is a species of the genus Armillifer occurring in tropical Africa. Its typical definitive hosts are pythons, such as the African rock python, while rodents are presumed to act as intermediate hosts. Humans may become accidentally infected by the eggs particularly if consuming infected snakes. Ingested eggs develop into nymphs that invade different visceral organs causing a disease called porocephalosis. Most human infections are asymptomatic, some are debilitating, or rarely even lethal.

Branchiura is a group of crustaceans ranked as a subclass of Maxillopoda. Branchiurans are commonly known as fish louse or fish lice if plural.
Mazocraeidae is a flatworm family in the order Mazocraeidea.

The Capsalidae is a family of monopisthocotylean monogeneans, which includes about 200 species.
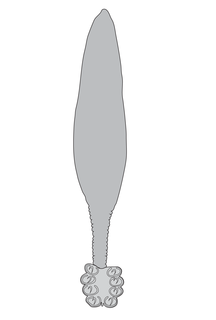
Chimaericola leptogaster is a species of polyopisthocotylean monogenean in the family Chimaericolidae. It is ectoparasitic on the gills of the chimaera Chimaera monstrosa.
Raillietiella teagueselfi is a species of parasitic crustacean. They are found in tropical and sub-tropical regions and affects the lungs of reptiles. The species was named after Dr. John Teague Self, a zoologist from the University of Oklahoma, for his contributions on Pentastomida.

Günter Krings is a German lawyer and politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU) who has been serving as a member of the Bundestag from the state of North Rhine-Westphalia since 2002. From 2013 until 2021, he also served as Parliamentary State Secretary at the Federal Ministry of the Interior in the government of Chancellor Angela Merkel.
"Tage wie diese", is a song by the German punk-rock band Die Toten Hosen. It was released on 23 March 2012 as a single, being a teaser for the album Ballast der Republik that was released afterwards on 4 May 2012.
"Segne, Vater, diese Gaben" is a Christian hymn. The authors of text and melody are unknown. It is meant to be sung as a round. The song, which is often used for a prayer before a meal, has appeared in German hymnals and songbooks. It is regarded as a song of the genre Neues Geistliches Lied (NGL), and has been used in schools and events for young people.












