
Linaria is a genus of almost 200 species of flowering plants, one of several related groups commonly called toadflax. They are annuals and herbaceous perennials, and the largest genus in the Antirrhineae tribe of the plantain family Plantaginaceae.

Anthonomus is a genus of weevils. This genus includes major agricultural pests such as the boll weevil, strawberry blossom weevil, and pepper weevil, as well as promising biological pest control agents such as Anthonomus santacruzi.

Centaurea solstitialis, the yellow star-thistle, is a species of thorny plant in the genus Centaurea, which is part of the family Asteraceae. A winter annual, it is native to the Mediterranean Basin region and invasive in many other places. It is also known as golden starthistle, yellow cockspur and St. Barnaby's thistle.

Linaria vulgaris, the common toadflax, yellow toadflax or butter-and-eggs, is a species of flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae, native to Europe, Siberia and Central Asia. It has also been introduced and is now common in North America.

Cymbalaria muralis, commonly called ivy-leaved toadflax, is a low, spreading, trailing plant with small purple flowers, native to rocky habitats in southern Europe. It belongs to the plantain family (Plantaginaceae), and is introduced and naturalised in many other temperate locations. The flower stalk is unusual for seeking light until it is fertilized, after which it grows away from the light. Other names include coliseum ivy, Kenilworth ivy, mother of thousands, Oxford ivy, and wandering sailor.

Calophasia lunula is a Palearctic species of noctuid moth known by the common names toadflax moth and toadflax brocade moth.

Glyptapanteles is a genus of endoparasitoid wasps found in all continents, except Antarctica. The larvae of Glyptapanteles species are able to manipulate their hosts into serving as bodyguards.

The Entiminae are a large subfamily in the weevil family Curculionidae, containing most of the short-nosed weevils, including such genera as Entimus, Otiorhynchus, Phyllobius, Sitona, and Pachyrrhynchus. In comparison with their stunning diversity, only a few of these weevils are notorious pests of major economic importance. Entimines are commonly encountered in the field, including urban environments, and abundant in entomological collections.

Aceria anthocoptes, also known as the russet mite, rust mite, thistle mite or the Canada thistle mite, is a species of mite that belongs to the family Eriophyidae. It was first described by Alfred Nalepa in 1892.

Linaria dalmatica is a herbaceous, short-lived perennial plant native to western Asia and southeastern Europe that has become a weed in other areas. The family this plant now belongs to is the Plantaginaceae Family. Previously, it belonged to the Scrophulariaceae (Figwort) family. Its common names include Balkan toadflax, broadleaf toadflax, and Dalmatian toadflax. Linaria dalmatica has unique yellow flowers with an orange center that draw individuals to purchase them to display in their gardens. The distribution of L. dalmatica to North America can be attributed to use as a fabric dye, folk remedies and as an ornamental plant. However, it is now classified as a weed in both Canada and the U.S.A.

Hylobius transversovittatus is a species of weevil in the family Curculionidae. It is native to the Old World where both adults and larvae feed on purple loosestrife. This plant is regarded as an invasive species in North America and the weevil has been introduced into both the United States and Canada in an effort to control the plant.

Mirabilis macfarlanei is a rare species of flowering plant in the four o'clock family known by the common name MacFarlane's four o'clock. It is native to Idaho and Oregon in the United States, where it is only known from three river canyons. It faces a number of threats and is federally listed as a threatened species of the United States.

The Antirrhineae are one of the 12 tribes of the family Plantaginaceae. It contains the toadflax relatives, such as snapdragons.

Rhinusa antirrhini, known generally as toadflax seedhead weevil, is a species of true weevil in the family of beetles known as Curculionidae. Other common names include the toadflax capsule weevil and seed-gall weevil.

Rhinusa is a genus of true weevils in the family of beetles known as Curculionidae. There are at least 20 described species in Rhinusa.

Dictyophara europaea, is the type species of planthoppers belonging to the subgenus Dictyophara (Dictyophara): in the family Dictyopharidae, and tribe Dictyopharini.

Trigonopterus asterix is a species of flightless weevil in the genus Trigonopterus from Indonesia.
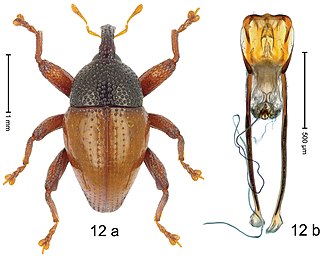
Trigonopterus bonthainensis is a species of flightless weevil in the genus Trigonopterus from Indonesia.
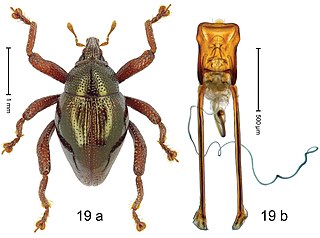
Trigonopterus curvipes is a species of flightless weevil in the genus Trigonopterus from Indonesia.

Trigonopterus seticnemis is a species of flightless weevil in the genus Trigonopterus from Indonesia.


















