| Ribes marshallii | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Saxifragales |
| Family: | Grossulariaceae |
| Genus: | Ribes |
| Species: | R. marshallii |
| Binomial name | |
| Ribes marshallii Greene 1887 | |
| Synonyms [1] | |
| |
Ribes marshallii is a North American species of currant known by the common names Hupa gooseberry and Marshall's gooseberry. It is endemic to the Klamath Mountains of southern Oregon and northern California. [2] [3]

Ribes is a genus of about 150 known species of flowering plants native throughout the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. It is usually treated as the only genus in the family Grossulariaceae, but a few taxonomists place the gooseberry species in a separate genus of Grossularia. Sometimes Ribes is instead included in the family Saxifragaceae.

Endemism is the ecological state of a species being unique to a defined geographic location, such as an island, nation, country or other defined zone, or habitat type; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. The extreme opposite of endemism is cosmopolitan distribution. An alternative term for a species that is endemic is precinctive, which applies to species that are restricted to a defined geographical area.

The Klamath Mountains are a rugged and lightly populated mountain range in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon in the western United States. They have a varied geology, with substantial areas of serpentinite and marble, and a climate characterized by moderately cold winters with very heavy snowfall and warm, very dry summers with limited rainfall, especially in the south. As a consequence of the geology and soil types, the mountains harbor several endemic or near-endemic trees, forming one of the largest collections of conifers in the world. The mountains are also home to a diverse array of fish and animal species, including black bears, large cats, owls, eagles, and several species of Pacific salmon. Millions of acres in the mountains are managed by the United States Forest Service. The northernmost and largest sub-range of the Klamath Mountains are the Siskiyou Mountains.
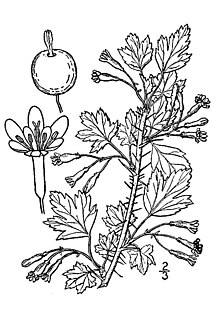
Ribes marshallii grows in mountain coniferous forests. It is a shrub producing arching stems 1 to 2 meters (40-80 inches) long which may root at the tip when it reaches moist substrate. Nodes on the stem bear three spines each up to a centimeter (0.4 inch) long. The lightly hairy leaves are roughly three centimeters (1.2 inches) long and are divided into a few widely toothed lobes. Glandular hairs occur on veins and leaf margins. The inflorescence is a solitary flower or raceme of up to three flowers which hang pendent from the branches from leaf axils. The small, showy flower has five pointed purple-red sepals which are reflexed upward. At the center is a tubular corolla of bright yellow petals from which emerge five stamens and two thin, mostly fused styles. The fruit is a prickly oblong berry up to 2 centimeters (0.8 inch) long which ripens to dark red. The fruits are edible and reputedly palatable. [4]

Temperate coniferous forest is a terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Temperate coniferous forests are found predominantly in areas with warm summers and cool winters, and vary in their kinds of plant life. In some, needleleaf trees dominate, while others are home primarily to broadleaf evergreen trees or a mix of both tree types. A separate habitat type, the tropical coniferous forests, occurs in more tropical climates.

A shrub or bush is a small- to medium-sized woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, and are usually under 6 m (20 ft) tall. Plants of many species may grow either into shrubs or trees, depending on their growing conditions. Small, low shrubs, generally less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall, such as lavender, periwinkle and most small garden varieties of rose, are often termed "subshrubs".

An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. Inflorescence can also be defined as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern.