
The mineral petzite, Ag3AuTe2, is a soft, steel-gray telluride mineral generally deposited by hydrothermal activity. It forms isometric crystals, and is usually associated with rare tellurium and gold minerals, often with silver, mercury, and copper.

Sylvanite or silver gold telluride, chemical formula (Ag,Au)Te2, is the most common telluride of gold.

Tellurite is a rare oxide mineral composed of tellurium dioxide (TeO2).
Weissite is a telluride mineral, a copper telluride. Its chemical formula is Cu
2−xTe. Weissite has hexagonal crystal structure. Its specific gravity is 6 and its Mohs hardness is 3. Occurrence is in Gunnison County, Colorado, Arizona and New Mexico in the United States. It is also reported from Kalgoorlie, Western Australia and Dalarna and Värmland, Sweden.

Tellurobismuthite, or tellurbismuth, is a telluride mineral: bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3). It crystallizes in the trigonal system. There are natural cleavage planes in the (0001) direction as the crystal is effectively lamellar (layered) in that plane. The Mohs hardness is 1.5 – 2 and the specific gravity is 7.815. It is a dull grey color, which exhibits a splendent luster on fresh cleavage planes.

A native metal is any metal that is found pure in its metallic form in nature. Metals that can be found as native deposits singly or in alloys include antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, indium, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, rhenium, tantalum, tellurium, tin, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zinc, as well as the gold group and the platinum group. Among the alloys found in native state have been brass, bronze, pewter, German silver, osmiridium, electrum, white gold, silver-mercury amalgam, and gold-mercury amalgam.

Nagyágite is a rare sulfide mineral with known occurrence associated with gold ores. Nagyágite crystals are opaque, monoclinic and dark grey to black coloured.

Roscoelite is a green mineral from the mica group that contains vanadium.

Vulcanite is a rare copper telluride mineral. The mineral has a metallic luster, and has a green or bronze-yellow tint. It has a hardness between 1 and 2 on the Mohs scale. Its crystal structure is orthorhombic.

Xocomecatlite is a rare tellurate mineral with formula: Cu3(TeO4)(OH)4. It is an orthorhombic mineral which occurs as aggregates or spherules of green needlelike crystals.

Coloradoite, also known as mercury telluride (HgTe), is a rare telluride ore associated with metallic deposit. Gold usually occurs within tellurides, such as coloradoite, as a high-finess native metal.

Zemannite is a very rare oxide mineral with the chemical formula Mg0.5ZnFe3+[TeO3]3·4.5H2O. It crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system and forms small prismatic brown crystals. Because of the rarity and small crystal size, zemannite has no applications and serves as a collector's item.

Walfordite is a very rare tellurite mineral that was discovered in Chile in 1999. The mineral is described as orange with orange-yellow streak, and is determined to have a chemical formula of Fe3+,Te6+Te4+3O8 with minor titanium and magnesium substitution resulting in an approximate empirical formula of (Fe3+,Te6+,Ti4+,Mg)(Te4+)3O8.

Emmonsite, also known as durdenite, is an iron tellurite mineral with the formula: Fe2(TeO3)3·2(H2O). Emmonsite forms triclinic crystals. It is of a yellowish-green color, with a vitreous luster, and a hardness of 5 on the Moh scale.

Tlapallite is a rare and complex tellurate mineral with the chemical formula (Ca,Pb)3CaCu6[Te4+3Te6+O12]2(Te4+O3)2(SO4)2·3H2O. It has a Moh's hardness of 3 and it is green in colour. It was named after the Nahua word "Tlalpalli", which translates to paint, referring to the paint-like habit of the mineral. Its formula and crystal structure were redefined in 2019, showing it contained a mixed-valence phyllotellurate layer [Te4+3Te6+O12]12−.

Carlfriesite is a rare tellurium mineral with the formula CaTe4+2Te6+O8, or more simplified: CaTe3O8. It has a Moh's hardness of 3.5 and it occurs in various shades of yellow, ranging from bright yellow to a light buttery color. It was named after Carl Fries Jr. (1910–1965) from the U.S. Geological Survey and the Geological Institute of the National University, Mexico City, Mexico. It was previously thought to have the formula H4Ca(TeO3)3, but this was proven to be incorrect. It has no uses beyond being a collector's item.

Tlalocite is a rare and complex tellurate mineral with the formula Cu10Zn6(TeO4)2(TeO3)(OH)25Cl · 27 H2O. It has a Mohs hardness of 1, and a cyan color. It was named after Tlaloc, the Aztec god of rain, in allusion to the high amount of water contained within the crystal structure. It is not to be confused with quetzalcoatlite, which often looks similar in color and habit.
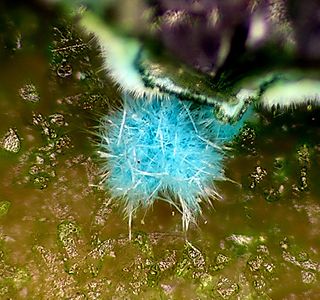
Quetzalcoatlite is a rare tellurium oxysalt mineral with the formula Zn6Cu3(TeO6)2(OH)6 · AgxPbyClx+2y. It also contains large amounts of silver- and lead(II)chloride with the formula AgxPbyClx+2y (x+y≤2). It has a Mohs hardness of 3 and it crystallizes in the trigonal system. It has a deep blue color. It was named after Quetzalcoatl, the Aztec and Toltec god of the sea, alluding to its color. It is not to be confused with tlalocite, which has a similar color and habit.

Teineite is a tellurite mineral with the formula Cu(TeO3). 2 H2O. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 and it comes in many different shades of blue, ranging from cerulean blue to bluish-gray. The mineral millsite has the same chemical composition, but crystallizes in the monoclinic system, while teineite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system.

Frohbergite (German: Frohbergit, title by proper name: Max Hans Frohberg), also iron telluride is a rare hydrothermal mineral from the sulfide class, in composition — iron telluride with the ideal formula FeTe2 (contains 82.05% tellurium and 17.95% iron).




















