
Basidiomycota is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: agarics, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and Cryptococcus, the human pathogenic yeast.

In molecular biology and genetics, transformation is the genetic alteration of a cell resulting from the direct uptake and incorporation of exogenous genetic material from its surroundings through the cell membrane(s). For transformation to take place, the recipient bacterium must be in a state of competence, which might occur in nature as a time-limited response to environmental conditions such as starvation and cell density, and may also be induced in a laboratory.

Saccharomycotina is a subdivision (subphylum) of the division (phylum) Ascomycota in the kingdom Fungi. It comprises most of the ascomycete yeasts. The members of Saccharomycotina reproduce by budding and they do not produce ascocarps.

Dothideomycetes is the largest and most diverse class of ascomycete fungi. It comprises 11 orders 90 families, 1,300 genera and over 19,000 known species. Wijayawardene et al. in 2020 added more orders to the class.
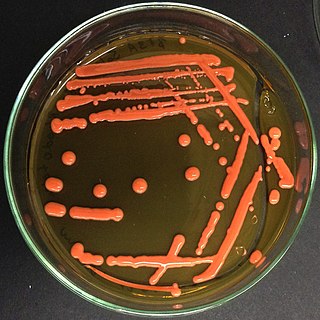
Rhodotorula is a genus of fungi in the class Microbotryomycetes. Most species are known in their yeast states which produce orange to red colonies when grown on Sabouraud's dextrose agar (SDA). The colour is the result of pigments that the yeast creates to block out certain wavelengths of light (620–750 nm) that would otherwise be damaging to the cell. Hyphal states, formerly placed in the genus Rhodosporidium, give rise to teliospores from which laterally septate basidia emerge, producing sessile basidiospores. Species occur worldwide and can be isolated from air, water, soil, and other substrates.

Mycoviruses, also known as mycophages, are viruses that infect fungi. The majority of mycoviruses have double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) genomes and isometric particles, but approximately 30% have positive-sense, single-stranded RNA (+ssRNA) genomes.

Pucciniomycotina is a subdivision of fungus within the division Basidiomycota. The subdivision contains 10 classes, 21 orders, and 38 families. Over 8400 species of Pucciniomycotina have been described - more than 8% of all described fungi. The subdivision is considered a sister group to Ustilaginomycotina and Agaricomycotina, which may share the basal lineage of Basidiomycota, although this is uncertain due to low support for placement between the three groups. The group was known as Urediniomycetes until 2006, when it was elevated from a class to a subdivision and named after the largest order in the group, Pucciniales.

A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista.

The Agaricostilbomycetes are a class of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. The class consists of a single order, six families, and 15 genera. Its type genus, Agaricostilbum was originally placed in Ascomycota, and later, Agaricomycotina, before being placed in Pucinniomycotina.
The Agaricostilbales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricostilbomycetes. The order consists of six families and 15 genera.
The Chionosphaeraceae are a family of fungi in the order Agaricostilbales. The family contains six genera. Some species form small, stilboid (pin-shaped) fruitbodies. Others are known only from their yeast states.

Colacogloea is a genus of fungi belonging to the class Microbotryomycetes. Most species in the genus are known only from their yeast states. Where known, basidiocarps have auricularioid basidia and occur as parasites on or in the fruit bodies of other fungi.
Solicoccozyma is a genus of fungi in the family Piskurozymaceae. Species have only been isolated in their yeast states, several of which were formerly referred to the genus Cryptococcus, but can produce filamentous states with basidia in culture. Nine species have been described worldwide.
Jianyuniaceae is a family of fungi in the order Agaricostilbales. The family contains three genera. Species are known only from their yeast states.

The Doassansiaceae are a family of fungi in the division Basidiomycota and order of Doassansiales. The family contains 11 genera and about 58 species. They have a widespread distribution. Doassansiaceae is also known and classified as a smut fungi.
The Spiculogloeomycetes are a class of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. The class consists of a single order, the Spiculogloeales, together with an additional, unassigned genus, Meniscomyces. Many species are currently known only from their yeast states. Species in the genus Spiculogloea form hyphal states that produce auricularioid basidia and are parasitic on other fungi.
The Spiculogloeales are an order of fungi in the subdivision Pucciniomycotina of the Basidiomycota. The order is currently monotypic, consisting of a single family, the Spiculogloeaceae. Species in the genus Phyllozyma are currently known only from their yeast states. Species in the genus Spiculogloea form hyphal states that produce auricularioid basidia and are parasitic on other fungi.
The Cystobasidiales are an order of fungi in the class Cystobasidiomycetes. The order currently consists of a single family (Cystobasidiaceae) and two genera as yet unassigned to a family.
Cystobasidium is a genus of fungi in the order Cystobasidiales. The type species is a fungal parasite forming small gelatinous basidiocarps on various ascomycetous fungi on dung. Microscopically, it has auricularioid basidia producing basidiospores that germinate by budding off yeast cells. Other species are known only from their yeast states. The yeasts Cystobasidium minutum and C. calyptogenae are rare but known human pathogens.

Cystobasidium fimetarium is a species of fungus in the order Cystobasidiales. It is a fungal parasite forming small gelatinous basidiocarps on various ascomycetous fungi on dung. Microscopically, it has auricularioid basidia producing basidiospores that germinate by budding off yeast cells. The species is known from Europe and North America.











