
The Gettysburg Battlefield is the area of the July 1–3, 1863, military engagements of the Battle of Gettysburg within and around the borough of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Locations of military engagements extend from the 4-acre (1.6 ha) site of the first shot at Knoxlyn Ridge on the west of the borough, to East Cavalry Field on the east. A military engagement prior to the battle was conducted at the Gettysburg Railroad trestle over Rock Creek, which was burned on June 27.

Rock Creek is an 18.9-mile-long (30.4 km) tributary of the Monocacy River in south-central Pennsylvania and serves as the border between Cumberland and Mount Joy townships. Rock Creek was used by the Underground Railroad and flows near several Gettysburg Battlefield sites, including Culp's Hill, the Benner Hill artillery location, and Barlow Knoll.
Harney is an unincorporated community in Carroll County, Maryland, United States. Harney is also the home of the 'World's Best Carnival'. It has been the home of the Harney Volunteer Fire Company since 1951.

The Gettysburg Railroad was a railway line in Pennsylvania that operated from 1858 to 1870 over the 17-mile (27 km) main line from the terminus in Gettysburg to the 1849 Hanover Junction. After becoming the Susquehanna, Gettysburg & Potomac Railway line in 1870, the tracks between Gettysburg and Hanover Junction became part of the Hanover Junction, Hanover and Gettysburg Railroad in 1874, the Baltimore and Harrisburg Railway in 1886, and the Western Maryland Railway in 1917.

Round Top is a populated place in Adams County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, near Little Round Top. It is notable for two Battle of Gettysburg hospitals, the 1884 Round Top Station, and several battlefield commemorative era attractions such as Round Top Park and the Round Top Museum. The unincorporated community lies on an elevated area of the north-south Taneytown Road with three intersections: at Blacksmith Shop Road to the northeast, Wheatfield Road, and Sachs Road.

The Gettysburg Electric Railway was a borough trolley that provided summer access to Gettysburg Battlefield visitor attractions such as military engagement areas, monuments, postbellum camps, and recreation areas. Despite the 1896 Supreme Court ruling under the Takings Clause against the railway, battlefield operations continued until 1916. The trolley generating plant was leased by the Electric Light, Heat, and Power Company of Gettysburg to supply streetlights and homes until electricity was imported from Hanover.

The Round Top Branch was an extension of the Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad from the Gettysburg borough across the Gettysburg Battlefield to Round Top, Pennsylvania. The branch ran southward from the terminus of the railroad's main line, west of the school and St. Francis Xavier Cemetery, across the field of Pickett's Charge, south of Cemetery Ridge, east of Weikert Hill and Munshower Knoll, and through Round Top to a point between Little Round Top's east base and Taneytown Road. In addition to battlefield tourists, the line carried stone monoliths and statues for monuments during the battlefield's memorial association and commemorative eras and equipment, supplies and participants for Gettysburg Battlefield camps after the American Civil War.
United States v. Gettysburg Electric Ry. Co., 160 U.S. 668 (1896), was a case to prevent trolley operations on the Gettysburg Battlefield. The dispute began in August 1891 when the Gettysburg Battlefield Memorial Association's board approved attorney Samuel Swope's motion to deny trolley right-of-way along GBMA roads. Despite the 1896 US Supreme Court ruling that the railway could be seized for historic preservation, as well as earlier legislative efforts to appropriate federal acquisition funds, create a War Department commission, and form the Gettysburg National Military Park; the trolley continued operations until obsolete in 1916.

Barlow is a populated place between the Gettysburg Battlefield and the Mason–Dixon line in Adams County, Pennsylvania, United States, situated at the intersection of Rock Creek and Pennsylvania Route 134. North of the creek on the road summit is the principal facility of the rural community: the 1939 community hall at the Barlow Volunteer Fire Company fire station. The hall is a Cumberland Township polling place and was used by Mamie and Dwight D. Eisenhower after purchasing their nearby farm. Horner's Mill was the site of an 1861 Union Civil War encampment, and the covered bridge was used by the II Corps and General George G. Meade en route to the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg.

The Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad was a railway line of Pennsylvania from Hunter's Run southward to Gettysburg in the 19th century. The north junction was with the South Mountain RR, and a crossing with the Hanover Junction, Hanover and Gettysburg Railroad's westward extension was at Gettysburg. The crossing also served as a junction for westbound trains to transfer southward across the Gettysburg Battlefield via the G. & H. R. R.'s Round Top Branch to the company's Little Round Top Park.

The South Mountain Railroad was a southcentral Pennsylvania railway line for "connecting the Pine Grove works to the Cumberland Valley R. R." and which provided mining and passenger services via a southwest section from Hunter's Run, Pennsylvania, and a northern section from Hunter's Run to the CVRR junction northeast of Carlisle. The northern section merged with the Gettysburg & Harrisburg Railroad line south from Hunter's Run to the Gettysburg Battlefield in 1891 to create the Gettysburg & Harrisburg Railway line, while the branch southwest from Hunter's Run became the Hunter's Run and Slate Belt Railroad line.

The Wheatfield Road is a Gettysburg Battlefield crossroad from the Peach Orchard east-southeastward along the north side of The Wheatfield, north of the Valley of Death, and over the north foot of Little Round Top. In addition to modern tourist use, the road is notable for Battle of Gettysburg use and postbellum trolley use associated with the 1892-1896 US v. Gettysburg Electric Ry. case of the US Supreme Court.

Tipton Station was a Gettysburg Battlefield trolley stop of the Gettysburg Electric Railway for passenger access to Crawford's Glen to the north, Devil's Den (west), and Tipton Park (east). The station was established during the 1894 construction of the end of the trolley line and was near the Devil's Den trolley siding, south of the trolley's Warren Avenue crossing, and northeast of the Plum Run trolley bridge. An uphill trail led southwest to Big Round Top with its 1895 Observation Tower, and the "Slaughter Pen Path and Steps" were built to Devil's Den.

The Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railway was a Pennsylvania line from near Carlisle southward to Gettysburg operated by a subsidiary of the Reading Company. The line also included the Round Top Branch over the Gettysburg Battlefield to Round Top, Pennsylvania until c. 1942.

The Tapeworm Railroad was a railway line planned by Congressman Thaddeus Stevens and nicknamed by opponents ridiculing a lengthy serpentine section around the Green Ridge of South Mountain after an orator compared the path to a tapeworm depiction on a product's packaging. Switchbacks were planned on the west slope at Hughs Forge along the E Br Antietam Creek and on the east slope at Stevens' 1822 Maria Furnace along Toms Creek, with 3 east slope tunnels through spurs of Jacks Mountain.
Bendersville was a Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad (G&H) stop east of Bendersville, Pennsylvania, with facilities of Frederick A. Asper that included a 3-story brick flour mill, grain elevator, and warehouse built in 1883. The depot was opposite the mill over the tracks.
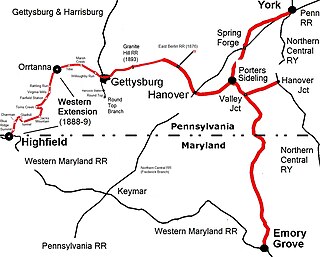
The Western Extension is a Western Maryland section of railway line between Highfield-Cascade, Maryland, and Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The extension of the Hanover Junction, Hanover and Gettysburg Railroad westward from the Gettysburg Battlefield to Marsh Creek was completed in 1884, crossing the north-south Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad and its 1884 Round Top Branch in the borough The line was completed to Orr Station by June 30, 1885, then after an 1886 merger formed the Baltimore and Harrisburg Railway, the 15 mi (24 km) to the mainline at Highland near the Mason–Dixon line was completed in 1888-1889. The B&H leased their line to the Western Maryland Railway until the WM purchased it in 1917. The Western Extension used portions of the 1830s Tapeworm Railroad bed and required construction of the Jacks Mountain Tunnel south of Maria Furnace.
Round Top Park was a Gettysburg Battlefield excursion park of 15 acres (6.1 ha) east of Little Round Top near the end of the Round Top Branch and owned by the Gettysburg & Harrisburg Railroad. In addition to amusements, the park provided services during the memorial association era for steamtrain and trolley tourists visiting nearby military sites of the Battle of Gettysburg.
The Round Top hospitals during the Battle of Gettysburg were located at the Little Round Top side of the Gettysburg Battlefield at 2 houses now in the community of Round Top, Pennsylvania.
Pine Grove Park was a South Mountain Railroad excursion park "in a grove of magnificent trees" established by Colonel Jackson C. Fuller c. 1881 It was located east of the Pine Grove Iron Works near Toland in Cumberland County, south-central Pennsylvania It was in the South Mountain Range of the northern Blue Ridge Mountains System.










