
Gettysburg National Cemetery is a United States national cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania created for Union casualties from the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. The Battle of Gettysburg, which was fought between July 1 to 3, 1863, resulted in the largest number of casualties of any Civil War battle but also was considered the war's turning point, leading ultimately to the Union victory.

The Gettysburg Battlefield is the area of the July 1–3, 1863, military engagements of the Battle of Gettysburg within and around the borough of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. Locations of military engagements extend from the 4-acre (1.6 ha) site of the first shot at Knoxlyn Ridge on the west of the borough, to East Cavalry Field on the east. A military engagement prior to the battle was conducted at the Gettysburg Railroad trestle over Rock Creek, which was burned on June 27.

The 1913 Gettysburg reunion was a Gettysburg Battlefield encampment of American Civil War veterans for the Battle of Gettysburg's 50th anniversary. The June 29–July 4 gathering of 53,407 veterans was the largest ever Civil War veteran reunion. All honorably discharged veterans in the Grand Army of the Republic and the United Confederate Veterans were invited, and veterans from 46 of the 48 states attended, all but Nevada and Wyoming.

Round Top is a populated place in Adams County in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, near Little Round Top. It is notable for two Battle of Gettysburg hospitals, the 1884 Round Top Station, and several battlefield commemorative era attractions such as Round Top Park and the Round Top Museum. The unincorporated community lies on an elevated area of the north-south Taneytown Road with three intersections: at Blacksmith Shop Road to the northeast, Wheatfield Road, and Sachs Road.

The Round Top Branch was an extension of the Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad from the Gettysburg borough across the Gettysburg Battlefield to Round Top, Pennsylvania. The branch ran southward from the terminus of the railroad's main line, west of the school and St. Francis Xavier Cemetery, across the field of Pickett's Charge, south of Cemetery Ridge, east of Weikert Hill and Munshower Knoll, and through Round Top to a point between Little Round Top's east base and Taneytown Road. In addition to battlefield tourists, the line carried stone monoliths and statues for monuments during the battlefield's memorial association and commemorative eras and equipment, supplies and participants for Gettysburg Battlefield camps after the American Civil War.

The Angle is a Gettysburg Battlefield area which includes the 1863 Copse of Trees used as the target landmark for Pickett's Charge, the 1892 monument that marks the high-water mark of the Confederacy, a rock wall, and several other Battle of Gettysburg monuments.
United States v. Gettysburg Electric Ry. Co., 160 U.S. 668 (1896), was a case to prevent trolley operations on the Gettysburg Battlefield. The dispute began in August 1891 when the Gettysburg Battlefield Memorial Association's board approved attorney Samuel Swope's motion to deny trolley right-of-way along GBMA roads. Despite the 1896 US Supreme Court ruling that the railway could be seized for historic preservation, as well as earlier legislative efforts to appropriate federal acquisition funds, create a War Department commission, and form the Gettysburg National Military Park; the trolley continued operations until obsolete in 1916.

Barlow is a populated place between the Gettysburg Battlefield and the Mason–Dixon line in Adams County, Pennsylvania, United States, situated at the intersection of Rock Creek and Pennsylvania Route 134. North of the creek on the road summit is the principal facility of the rural community: the 1939 community hall at the Barlow Volunteer Fire Company fire station. The hall is a Cumberland Township polling place and was used by Mamie and Dwight D. Eisenhower after purchasing their nearby farm. Horner's Mill was the site of an 1861 Union Civil War encampment, and the covered bridge was used by the II Corps and General George G. Meade en route to the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg.

The 72nd Pennsylvania Infantry Monument is an 1891 statuary memorial on the Gettysburg Battlefield. It is located on Cemetery Ridge, by The Angle and the copse of trees, where Union forces – including the 72nd Pennsylvania Infantry – beat back Confederate forces engaged in Pickett's Charge.
Emmor Cope (1834-1927) was an American Civil War officer of the Union Army noted for the "Map of the Battlefield of Gettysburg from the original survey made August to October, 1863", which he researched by horseback as a sergeant after being ordered back to Gettysburg by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade. Cope is also noted for commemorative era battlefield administration and designs, including the layout of the 1913 Gettysburg reunion. Cope had enlisted as a Private of Company A,, temporarily detached to Battery C, 5th U.S. Artillery, and mustered out as a V Corps aide-de-camp of Maj Gen Gouverneur K. Warren.

The Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad was a railway line of Pennsylvania from Hunter's Run southward to Gettysburg in the 19th century. The north junction was with the South Mountain RR, and a crossing with the Hanover Junction, Hanover and Gettysburg Railroad's westward extension was at Gettysburg. The crossing also served as a junction for westbound trains to transfer southward across the Gettysburg Battlefield via the G. & H. R. R.'s Round Top Branch to the company's Little Round Top Park.

The Wheatfield Road is a Gettysburg Battlefield crossroad from the Peach Orchard east-southeastward along the north side of The Wheatfield, north of the Valley of Death, and over the north foot of Little Round Top. In addition to modern tourist use, the road is notable for Battle of Gettysburg use and postbellum trolley use associated with the 1892-1896 US v. Gettysburg Electric Ry. case of the US Supreme Court.

Tipton Station was a Gettysburg Battlefield trolley stop of the Gettysburg Electric Railway for passenger access to Crawford's Glen to the north, Devil's Den (west), and Tipton Park (east). The station was established during the 1894 construction of the end of the trolley line and was near the Devil's Den trolley siding, south of the trolley's Warren Avenue crossing, and northeast of the Plum Run trolley bridge. An uphill trail led southwest to Big Round Top with its 1895 Observation Tower, and the "Slaughter Pen Path and Steps" were built to Devil's Den.

The Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railway was a Pennsylvania line from near Carlisle southward to Gettysburg operated by a subsidiary of the Reading Company. The line also included the Round Top Branch over the Gettysburg Battlefield to Round Top, Pennsylvania until c. 1942.

The Gettysburg Battlefield Memorial Association (GBMA) was an historic preservation membership organization and is the eponym for the battlefield's memorial association era. The association was chartered by the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania on April 13, 1864, after attorney David McConaughy recommended on August 14, 1863, a preservation association to sell membership stock for battlefield fundraising. McConaughy transferred his land acquired in 1863 to the GBMA, and the association's boardmembers were initially local officials. The GBMA sold stock to raise money, hired a superintendent at $1000/yr, added to McConaughy's land holdings, and operated a wooden observation tower on East Cemetery Hill from 1878–95.
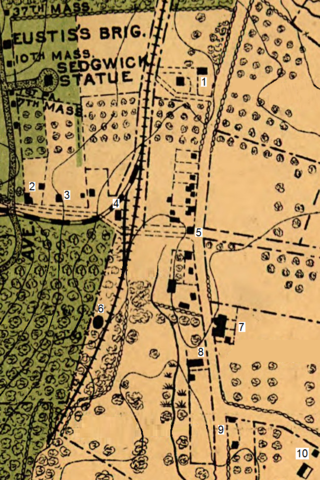
Round Top Station was the southernmost station of the Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad and was located west of a blacksmith shop along the Taneytown Road that was in operation in 1880.

Hancock was a Gettysburg Battlefield station of the Gettysburg and Harrisburg Railroad near the Tammany and Vermont monuments. The station was used at the end of the memorial association era and through the commemorative era for delivering tourists and materials such as for the 1910 Pennsylvania State Memorial and 1913 Gettysburg reunion. Before the G & H denied use of the steamtrain line, the Gettysburg Electric Railway considered placing a generator plant at the station for the electric trolley, but the trolley plant and its coal yard were instead built diagonal from the borough's G & H RR station.

Camp George G. Meade was one of the Gettysburg Battlefield camps after the American Civil War for Pennsylvania National Guard training of the Keystone Division. The military installation's structures on the Gettysburg Battlefield were subsequently used in the battlefield's commemorative and development eras, e.g., for a WWI recruiting and Tank Corps camp, the 1913 Gettysburg reunion, and the Third Corps camp during the 1938 Gettysburg reunion.
Round Top Park was a Gettysburg Battlefield excursion park of 15 acres (6.1 ha) east of Little Round Top near the end of the Round Top Branch and owned by the Gettysburg & Harrisburg Railroad. In addition to amusements, the park provided services during the memorial association era for steamtrain and trolley tourists visiting nearby military sites of the Battle of Gettysburg.













