
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift launch vehicle that is part of the Ariane rocket family, an expendable launch system designed by the Centre national d'études spatiales (CNES). It is used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) or low Earth orbit (LEO).

The Dnepr rocket is a space launch vehicle named after the Dnieper River. It is a converted ICBM used for launching artificial satellites into orbit, operated by launch service provider ISC Kosmotras. The first launch, on April 21, 1999, successfully placed UoSAT-12, a 350 kg demonstration mini-satellite, into a 650 km circular Low Earth orbit.
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is conducted by the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Air Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station, piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services.
This is a comparison of orbital launch systems. The following exposes the full list of conventional orbital launch systems. For the short simple list of conventional launcher families, see: Comparison of orbital launchers families. For the list of predominantly solid-fuelled orbital launch systems, see: Comparison of solid-fuelled orbital launch systems.

Gonets is a Russian civilian low Earth orbit communication satellite system. It consists of a number of satellites, derived from Strela military communication satellites. The first two satellites, which were used to test and validate the system, were launched by a Tsyklon-3 carrier rocket from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome on 13 July 1992, and were designated Gonets-D. The first operational satellites, designated Gonets-D1, were launched on 19 February 1996. After launch, the first three satellites were given military Kosmos designations, a practice which was not continued with the other satellites.

USA-200, also known as NRO Launch 28 or NROL-28, is an American signals intelligence satellite, operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. Launched in 2008, it has been identified as the second satellite in a series known as Improved Trumpet, Advanced Trumpet, or Trumpet follow-on; a replacement for the earlier Trumpet series of satellites.
Orbcomm is a family of low Earth orbit communications satellites, operated by the American satellite communications company Orbcomm. As of July 2014, 51 such satellites have orbited Earth, with 50 still continuing to do so.
AeroCube 3 is a single-unit CubeSat which was built and is being operated by The Aerospace Corporation. It is the third AeroCube satellite, following on from AeroCube 1, which was lost in a launch failure in 2006, and AeroCube 2 which was successfully launched in 2007 but failed immediately after launch. Compared to its predecessors it contains several improvements in its infrastructure, including a redesigned power system, replacing the older system which was responsible for the loss of AeroCube 2. Its development was funded by the United States Air Force Space and Missile Systems Center.

SwissCube-1 is a Swiss satellite operated by Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL). The spacecraft is a single unit CubeSat, which was designed to conduct research into nightglow within the Earth's atmosphere, and to develop technology for future spacecraft. It has also been used for amateur radio. It was the first Swiss satellite to be launched.

BeeSat-1 or Berlin Experimental and Educational Satellite 1, is a German satellite operated by the Technical University of Berlin. The spacecraft is a single unit CubeSat, which was designed to test systems intended for use on future spacecraft, including a new design of reaction wheel. It has also been used for amateur radio, and is equipped with a small camera.
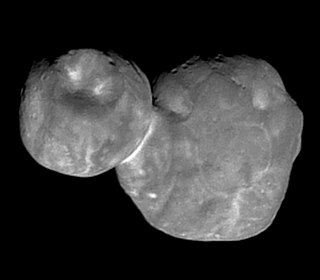
This article documents notable spaceflight events during the year 2019.
Notable spaceflight activities in 2017 included the maiden flight of India's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III on 5 June and the first suborbital test of Rocket Lab's Electron rocket, inaugurating the Mahia spaceport in New Zealand. The rocket is named for its innovative Rutherford engine which feeds propellants via battery-powered electric motors instead of the usual gas generator and turbopumps.

This article lists achieved and expected spaceflight events in 2018. For the first time since 1990, more than 100 orbital launches were performed globally.
Sapphire is a Canadian space surveillance satellite which was launched in 2013. Sapphire was constructed by MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates (MDA) based on an SSTL-150 bus produced by Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) and an optical payload produced by COM DEV International.
CUTE-1.7 + APD II, or CUTE-1.7+APD 2, is a Japanese nanosatellite which was launched in 2008 as a follow-up to the CUTE-1.7 + APD satellite. It was built and is operated by the Tokyo Institute of Technology.

Spire Global, Inc. is an American private company specializing in the design, build, launch, and management of a network of small satellites. It has successfully deployed more than eighty Earth observation CubeSats into low Earth orbit. The company has offices in San Francisco, Glasgow, Luxembourg, Singapore, and Boulder. Spire's constellation of cube satellites 'listen' to the planet in real-time, then apply machine learning and analytics to that data.
The JSAT constellation is a communication and broadcasting satellite constellation formerly operated by JSAT Corporation and currently by SKY Perfect JSAT Group. It has become the most important commercial constellation in Japan, and fifth in the world. It has practically amalgamated all private satellite operators in Japan, with only B-SAT left as a local competitor.

This article documents expected notable spaceflight events during the year 2020.












