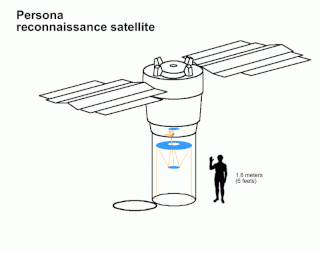
Persona is a class of Russian reconnaissance satellites, derived from the Resurs DK class of remote sensing satellite, in turn derived from the Soviet Yantar reconnaissance satellites. The satellites are built by TsSKB-Progress, and the optics by LOMO and the Vavilov State Optical Institute.
Meridian 2, also known as Meridian No.12L, was a Russian communications satellite. It was the second satellite of the Meridian system, which replaced the older Molniya series. It followed on from Meridian 1, which was launched in December 2006.
EKSKupol is a developing programme of Russian early warning satellites as a replacement for the US-KMO and US-K satellites of the Oko programme. The satellites are designed to identify any possible future ballistic missile launches, from outer space, and complement early warning radars such as the Voronezh. This gives advance notice of a nuclear attack and would provide information to the A-135 missile defence system which protects Moscow, as well as other Russian missile defense and counterattack resources. Six satellites are planned to be initially orbited. The first of these was launched on 17 November 2015 and as of November 2022, all six of them are in service.

Kosmos 2469 was a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2010 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.

Kosmos 2446 is a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2008 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite is designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.

Kosmos 2430 was a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2007 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Kosmos 2422 was a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2006 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Kosmos 2393 is a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2002 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite is designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Kosmos 2388 was a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 2002 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Kosmos 2312 is a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 1995 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite is designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Kosmos 2261 is a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 1993 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite is designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors. It was estimated in the west that it stopped functioning in March 1998, and reentered destructively on December 31, 2012.
Kosmos 2105 is a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 1990 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite is designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.
Kosmos 2084 is a Russian US-K missile early warning satellite which was launched in 1990 as part of the Russian Space Forces' Oko programme. The satellite was designed to identify missile launches using optical telescopes and infrared sensors.

Kosmos 2480 was a Russian Kobalt-M reconnaissance satellite which was launched in 2012 by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. It was the last launch of a Soyuz-U rocket launched from Plesetsk Cosmodrome.
Kosmos 2472 was a Russian Kobalt-M reconnaissance satellite which was launched in 2011 by the Russian Aerospace Defence Forces. It was launched in June 2011 and remained in orbit until October 2011.
Kosmos 2467 is one of a pair of Russian military communications satellites which were launched in 2010 by the Russian Space Forces. It was launched with Kosmos 2468 and a Gonets-M civilian communication satellite.
Kosmos 2468 is a Russian military communications satellite which was launched in 2010 by the Russian Space Forces. It was launched with Kosmos 2467 and a Gonets-M civilian communication satellite.
Kosmos 2478 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2011 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.
Kosmos 2474 is a Russian military satellite launched in 2011 as part of the GLONASS satellite navigation system.





