
EGF, latrophilin and seven transmembrane domain-containing protein 1 is a latrophilin-like orphan receptor of the adhesion G protein-coupled receptor family. In humans this protein is encoded by the ELTD1 gene. ELTD1 appears to have a role in angiogenesis, both physiological and pathological in cancer.

In enzymology, an ADP-specific glucokinase also known as ADP-dependent glucokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Synaptic Ras GTPase-activating protein 1, also known as synaptic Ras-GAP 1 or SYNGAP1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SYNGAP1 gene. SYNGAP1 is a ras GTPase-activating protein that is critical for the development of cognition and proper synapse function. Mutations in humans can cause intellectual disability, epilepsy, autism and sensory processing deficits.

Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YKT6 gene.

EF-hand domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFHC1 gene.

Lysine-specific demethylase 5C is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KDM5C gene. KDM5C belongs to the alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylase superfamily.

Chloride intracellular channel protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLIC5 gene.
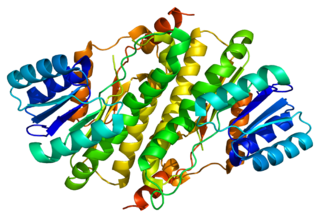
Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 11 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HSD17B11 gene.

Dixin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIXDC1 gene. When active it stops cancer metastasis due to extreme stickiness, both in vitro and in vivo.

Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC2A6 gene.
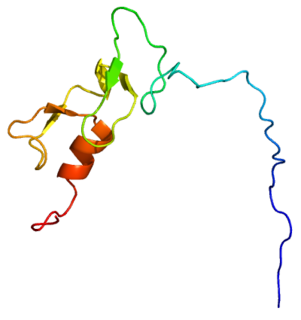
RUN and FYVE domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUFY1 gene. It is named after the RUN and FYVE domains it contains.

Sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC38A1 gene.

Seizure protein 6 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEZ6 gene.

Transmembrane protein 184B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMEM184B gene.

NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYB5R1 gene.

Protein wntless homolog, commonly known as Wntless, is encoded in humans by the WLS gene. Wntless is a receptor for Wnt proteins in Wnt-secreting cells.

L-asparaginase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ASRGL1 gene.

Redox-regulatory protein FAM213A also known as peroxiredoxin-like 2 activated in M-CSF stimulated monocytes (PAMM) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM213A gene.

ATP synthase subunit s-like protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATP5SL gene.

Inverted formin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the INF2 gene. It belongs to the protein family called the formins. It has two splice isoforms, CAAX which localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and non-CAAX which localizes to focal adhesions and the cytoplasm with enrichment at the Golgi. INF2 plays a role in mitochondrial fission and dorsal stress fiber formation. INF2 accelerates actin nucleation and elongation by interacting with barbed ends of actin filaments, but also accelerates disassembly of actin through encircling and severing filaments.



















