Related Research Articles

Bhopal is the capital city of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of both Bhopal district and Bhopal division. It is known as the City of Lakes, due to presence of various natural and artificial lakes. It is also one of the greenest cities in India. It is the 16th largest city in India and 131st in the world. After the formation of Madhya Pradesh, Bhopal was part of the Sehore district. It was bifurcated in 1972 and a new district, Bhopal, was formed. Flourishing around 1707, the city was the capital of the former Bhopal State, a princely state of the British ruled by the Nawabs of Bhopal until India's independence in 1947.

The Serpentine is a 40-acre (16 ha) recreational lake in Hyde Park, London, England, created in 1730 at the behest of Queen Caroline. Although it is common to refer to the entire body of water as the Serpentine, the name refers in the strict sense only to the eastern half of the lake. Serpentine Bridge, which marks the boundary between Hyde Park and Kensington Gardens, also marks the Serpentine's western boundary; the long and narrow western half of the lake is known as the Long Water. The Serpentine takes its name from its snakelike, curving shape, although it only has one bend.

Lake Quinsigamond is a body of water situated between the city of Worcester and the town of Shrewsbury in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. It is 4 miles (6.4 km) long, between 50 and 85 feet deep, and has a surface area of approximately 772 acres (3.12 km2). Lake Quinsigamond hosts 8 islands with the majority owned by private citizens. Two islands are connected to land via bridge. The largest island, Drake Island, is still state owned. Water from the lake empties into the Quinsigamond River in the Blackstone Valley.

Canopy walkways – also called canopy walks, treetop walks or treetop walkways – provide pedestrian access to a forest canopy. Early walkways consisted of bridges between trees in the canopy of a forest; mostly linked up with platforms inside or around the trees. They were originally intended as access to the upper regions of ancient forests for scientists conducting canopy research. Eventually, because they provided only limited, one-dimensional access to the trees, they were abandoned for canopy cranes. Today they serve as ecotourism attractions in places such as Dhlinza Forest, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, Taman Negara National Park, Malaysia, Sedim River, Kulim, Nyungwe National Park, Rwanda and Kakum National Park, Ghana.

The Cooum river, or simply Koovam, is one of the shortest classified rivers draining into the Bay of Bengal. This river is about 72 km (45 mi) in length, flowing 32 km (20 mi) in the city of Chennai and the rest in rural part. The river is highly polluted in the urban area (Chennai). Along with the Adyar River running parallel to the south and the Kosasthalaiyar River, the river trifurcates the city of Chennai and separates Northern Chennai from Central Chennai. It is also sometimes known as Thiruvallikenni river

Mukah Division is one of the twelve administrative divisions in Sarawak, Malaysia. It was established on 1 March 2002 and it has a total area of 6,997.61 square kilometres.

Sabarmati Riverfront is a waterfront being developed along the banks of Sabarmati river in Ahmedabad, India. Proposed in the 1960s, the construction began in 2005. Since 2012, under Phase 1, the waterfront is gradually opened to public as and when facilities are constructed and various facilities are actively under construction. The major objectives of project are environment improvement, social infrastructure and sustainable development. Phase 2 was approved in 2020.

Malampuzha Dam is the second largest dam and reservoirs in Kerala, located near Palakkad, in the state of Kerala in South India, built post independence by the then Madras state. Situated in the scenic hills of the Western Ghats in the background it is a combination of a masonry dam with a length of 1,849 metres and an earthen dam with a length of 220 metres making it the longest dam in the state. The dam is 355 feet high and crosses the Malampuzha River, a tributary of Bharathappuzha, Kerala's second longest river. There is a network of two canal systems that serve the dam's reservoir of 42,090 hectares.

Shikellamy State Park is a 132-acre (53 ha) Pennsylvania state park located at the confluence of the West Branch Susquehanna River and Susquehanna River in Pennsylvania. The park is divided into two sections. The older part, on a bluff on the western bank of the Susquehanna River, is the 78-acre (32 ha) Shikellamy overlook in Union Township, Union County. The newer part is the 54-acre (22 ha) marina on the southern end of Packer Island in Upper Augusta Township, Northumberland County. Packer's Island lies between the city of Sunbury and the borough of Northumberland at the confluence of the two branches of the river.
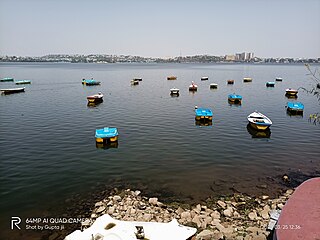
Bhojtal, formerly known as Upper Lake, is a large lake which lies on the western side of the capital city of Madhya Pradesh, Bhopal, India. It is a major source of drinking water for the residents of the city, serving around 40% of the residents with nearly 30 million imperial gallons (140,000 m3) of water per day. Bada talaab, along with the nearby Chhota Talaab, meaning small lake in Hindi, constitute Bhoj Wetland, which is now a Ramsar site.

Tholkappia Poonga or Adyar Eco Park is an ecological park set up by the Government of Tamil Nadu in the Adyar estuary area of Chennai, India. According to the government, the project, conceived based on the master plan for the restoration of the vegetation of the freshwater ecosystems of the Coromandel Coast, especially the fragile ecosystem of the Adyar estuary and creek, was expected to cost around ₹ 1,000 million which will include the beautification of 358 acres of land. The park's ecosystem consists of tropical dense evergreen forest, predominantly comprising trees and shrubs that have thick dark green foliage throughout the year, with over 160 woody species, and comprises six vegetative elements such as trees, shrubs, lianas, epiphytes, herbs and tuberous species. The park was opened to public by Chief Minister M. Karunanidhi on 22 January 2011 and named after the renowned Tamil scholar Tholkappiar. About 65 percent of the park is covered by water and artefacts and signages. In the first 2 months of its inauguration, nearly 4,000 children from several schools in the city and the nearby Kancheepuram and Tiruvallur districts have visited the park to learn about wetland conservation, eco-restoration and water management. While the first phase of the ecopark covered about 4.16 acres of CRZ-III area, the entire area covered under the second phase falls under this category.

Aliyar ( Reservoir is a 6.48 km2 reservoir located in Aliyar village near Pollachi town in Coimbatore District, Tamil Nadu, South India. The dam is located in the foothills of Valparai, in the Anaimalai Hills of the Western Ghats. It is about 65 kilometres from Coimbatore. The dam offers some ideal getaways including a park, garden, aquarium, play area and a mini Theme-Park maintained by Tamil Nadu Fisheries Corporation for visitors enjoyment. The scenery is beautiful, with mountains surrounding three quarters of the reservoir. Boating is also available.

The Adyar River, originating near the Chembarambakkam Lake in Kanchipuram district, is one of the three rivers which winds through Chennai (Madras), Tamil Nadu, India, and joins the Bay of Bengal at the Adyar estuary. The 42.5-kilometre (26.4 mi) long river contributes to the estuarine ecosystem of Chennai. Despite the high pollution levels, boating and fishing take place in this river. The river collects surplus water from about 200 tanks and lakes, small streams and the rainwater drains in the city, with a combined catchment area of 860 square kilometres (331 sq mi). Most of the waste from the city is drained into this river and the Cooum.

Durgam Cheruvu, also known as Raidurgam Cheruvu, is a freshwater lake located in Rangareddy district, Jagathgiri Gutta Telangana, India. The lake, which is spread over 83 acres (34 ha), is located near the city of Hyderabad. The lake is also known as Secret Lake because it is hidden between the localities of Jubilee Hills and Madhapur. The Durgam Cheruvu Bridge, which traverses the lake, was inaugurated in September 2020.

Hussain Sagar is a heart-shaped lake in Hyderabad, Telangana, built by Ibrahim Quli Qutb Shah in 1563. It is spread across an area of 5.7 square kilometres (2.2 sq mi) and is fed by the River Musi. A large monolithic statue of the Gautama Buddha, erected in 1992, stands on Gibraltar Rock in the middle of the lake. It also separates the city centre of Hyderabad from its neighbourhood Secunderabad. The maximum depth of the lake is 32 feet (9.8 m)

Tamil Nadu Government Multi-Super-Speciality Hospital is a 400-bed government-owned super-speciality hospital in Chennai, India. It is located at the Omandurar Government Estate on Anna Salai and was opened in February 2014. Originally built as Tamil Nadu legislative assembly and secretariat complex in 2010 to house the assembly hall, secretariat and offices of the chief minister and cabinet ministers, the complex was later converted into a super-speciality hospital. It was built in 1.93 million sq ft. at a total cost of ₹ 4,250 million in 2010.

Asramam Adventure Park is an urban park in the core Kollam city of Kerala state. It was opened after 1980, on 48 acres (19 ha) of city-owned land. Located beside the Kerala's pride, backwaters of Ashtamudi, this place popularly known as Asramam Picnic Village. It is the main centre of recreational activities in Kollam city. The Kollam District Tourism Promotion Council conducts regular backwater cruises in houseboats, luxury boats and speedboats from the Boat Club. The mangroves near this park is very famous in all over India. So many endangered species of trees are surviving in the park.
References
- ↑ "MP CM inaugurates tourist complex in Bhopal". IBN Live. 29 September 2011. Archived from the original on 1 October 2011. Retrieved 30 January 2013.
- 1 2 "Sair-Sapata to open today Tuesday,". Daily Pioneer. 27 September 2011. Retrieved 30 January 2013.