
The giant catfish, also known as the giant sea catfish, giant salmon catfish, giant marine-catfish, or the khagga, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Eduard Rüppell in 1837, originally under the genus Bagrus. It inhabits estuaries and occasionally freshwater bodies, in Japan, Australia, Polynesia, southern Vietnam in the Mekong Delta, the Red Sea and the northwestern Indian Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 10 to 195 m. It reaches a maximum total length of 185 cm (73 in), but usually reaches a TL of 70 cm (28 in).
The bronze catfish, also known as the giant catfish, the roundsnout sea catfish, or the two-line sea catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840, originally under the genus Bagrus. It inhabits marine, brackish and freshwaters throughout the Indo-western Pacific. It reaches a maximum standard length of 62 cm (24 in).

Nikolai Mikhailovich Knipovich was a Russian and Soviet ichthyologist, marine zoologist and oceanographer, notable as the founder of fisheries research in the Russian North.
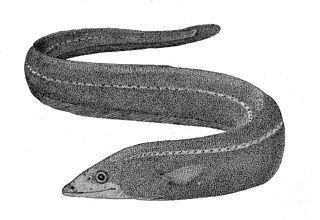
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).
The northern spearnose poacher, also known as the window-tailed sea-poacher or the windowtail poacher, is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1880, originally under the genus Agonus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the eastern Pacific Ocean, including southeastern Alaska to southern California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 163 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 20 centimetres (7.9 in).
The sturgeon poacher, also known as the sturgeon-like sea-poacher in Canada, is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Wilhelm Gottlieb Tilesius von Tilenau in 1813. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the western Bering Sea, Cape Navarin, the Commander Islands, the Sea of Okhotsk, the Aleutian Islands, and northern California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 2 to 710 metres, and inhabits soft benthic sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30.5 centimetres (12.0 in).
The sawback poacher is a species of fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896, originally under the genus Odontopyxis. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including Japan, the Gulf of Anadyr, the Bering Sea, the Aleutian chain, and British Columbia, Canada. It dwells at a depth range of 18 to 975 metres, and inhabits soft sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 27 centimetres (11 in).
The longnose poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896, originally under the genus Odontopyxis. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Bering Sea, southeastern Alaska, northern Japan, the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk. It dwells at a depth range of 20 to 460 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 25 centimetres (9.8 in).
the smooth alligatorfish, also known as the smooth poacher or the smooth sea-poacher,) is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1860. It is a marine fish which dwells in temperate waters, and is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including California, USA, and possibly Korea. It dwells at a depth range of 8–102 metres, usually around rocks. Males can reach a maximum total length of 15 centimetres.
The Arctic alligatorfish is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by C.F. Lütken in 1877. It is a marine and brackish-water dwelling fish which is known from the Arctic, the northwestern Atlantic and northwestern and northeastern Pacific Ocean, including Canada, Greenland, Siberia, the Barents Sea, the White Sea, the Kara Sea, the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, and the Anadyr Gulf. It dwells at a depth range of 7–520 metres, in salinities of 30–35 ppt, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting sand and mud bottoms. It mostly lives in temperatures below 0 °C, but on rare occasions has been found in temperatures of 2–3 °C. Males can reach a maximum total length of 8.6 centimetres.
The gray starsnout, also known as the gray starsnout poacher in the United States, is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the eastern Pacific Ocean, from the coast of the Bering Sea in Alaska, to the Oregon-California border. It dwells at a depth range of 18–252 metres, and inhabits rocky areas. Males can reach a maximum total length of 13 centimetres.

The bluespotted poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890, originally in the genus Xenochirus. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from British Columbia, Canada to northern central Baja California, Mexico, in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 73–373 metres, and inhabits soft benthic sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 18 centimetres.

The fourhorn poacher, also known as the four-horned sea-poacher, is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1829, originally under the genus Aspidophorus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan, the Bering Sea, the Kuril Islands, and Washington, USA. It is non-migratory, and dwells at a depth range of 0 to 452 metres, most often at around 100 to 150 metres. It inhabits sediments of sand and gravel. Males can reach a maximum total length of 12 centimetres (4.7 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 10 centimetres (3.9 in). The maximum recorded weight is 24 grams (0.053 lb), and the maximum recorded age is 7 years.

The dragon poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1769, originally under the genus Cottus. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Sea of Japan, the Sea of Okhotsk, and the Bering Sea. It dwells at a depth range of 19 to 750 metres, and inhabits gravel, sand and mud sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 42 centimetres (17 in).
The hard-palate catfish, also known as the hard-plate catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Albert William Herre in 1935, originally under the genus Arius. It is a tropical freshwater fish which is found in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. It reaches a maximum standard length of 60 cm (24 in), with both sexes more commonly reaching an SL of 35 cm (14 in). It reaches a maximum weight of 1.8 kg (4.0 lb).
The Guinean sea catfish, also known as the marine catfish, is a species of sea catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1864, originally under the genus Arius. It is a tropical fish which is found in the eastern Atlantic off Mauritania, Angola, Morocco and Western Sahara. A single record was reported in the eastern Mediterranean Sea in 1986. It inhabits coastal marine waters at a depth range of 50 to 80 m, also frequently entering estuaries and freshwater rivers. It reaches a maximum total length of 70 cm (28 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 40 cm (16 in).

The blacktip sea catfish, also known as Dussumier's catfish, giant marine cat fish, Shupanga sea catfish, and tropical seacatfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840, originally under the genus Arius. It inhabits rivers and marine waters ranging between Africa and India in the Indo-western Pacific. It dwells at a depth range of 20 to 50 m. It reaches a maximum standard length of 62 cm (24 in), and a maximum weight of 1.4 kg (3.1 lb).
The Couma sea catfish, also known as the Pemecou sea catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1840, originally under the genus Bagrus. It inhabits estuaries and rivers in Guyana, French Guiana, Suriname, Brazil, Trinidad and Tobago, and Venezuela. It reaches a maximum total length of 97 cm (38 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 50 cm (20 in). It reaches a maximum weight of 30 kg (66 lb). Its maximum known life expectancy is 5 years.
The flapnose sea catfish, also known as the brown sea catfish, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Theodore Gill in 1863, originally under the genus Leptarius. It inhabits rivers and estuaries in Ecuador, Colombia, Guatemala, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Panama, Honduras, Nicaragua, Mexico, and Peru. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 15 m. It reaches a maximum total length of 90 cm (35 in), more commonly reaching a TL of 50 cm (20 in).
The crucifix sea catfish — also known as the Christfish, the crucifix/crucifex catfish, the crucifixfish, or the gillbacker, — is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae.






