
Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, formerly Baroda College, is a public university in the city of Vadodara, Gujarat, India. Originally established as a college in 1881, it became a university in 1949 after India's independence. It was later renamed after its benefactor Maharaja Sayajirao Gaekwad III, the former ruler of Baroda State.

Banaras Hindu University (BHU) is a collegiate, central, and research university located in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India, and founded in 1916. The university incorporated the Central Hindu College, founded by Indian Home Rule-leaguer and Theosophist, Annie Besant in 1898. After Besant and her associates were marginalised, the university was established by Madan Mohan Malaviya with the support of the maharaja of Darbhanga Rameshwar Singh, the maharaja of Benares Prabhu Narayan Singh, and the lawyer Sunder Lal. With over 30,000 students, and 18,000 residing on campus, BHU is the largest residential university in Asia. The university is one of the eight public institutions declared as an Institute of Eminence by the Government of India. It is also one of the 12 institutions from India in BRICS Universities League, a consortium of leading research universities from BRICS countries.

Indian Institute of Technology Varanasi(IIT-BHU) is a public technical university located in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. Founded in 1919 as the Banaras Engineering College, it became the Institute of Technology, Banaras Hindu University in 1968. It was later designated an Indian Institute of Technology in 2012. IIT (BHU) Varanasi has 16 departments, 3 inter-disciplinary schools and a Humanities & Social Sciences Section. It is located inside the Banaras Hindu University Campus.

Sayajirao Gaekwad III was the Maharaja of Baroda State from 1875 to 1939, and is remembered for reforming much of his state during his rule. He belonged to the royal Gaekwad dynasty of the Marathas which ruled parts of present-day Gujarat.
Central Hindu School, located in Kamachha at the heart of the sacred city Varanasi, is one of India's largest educational institutions. The school is affiliated with the Central Board of Secondary Education and is overseen by Banaras Hindu University. The institution was formerly known as Central Hindu College, and its Senior High School program was previously called Pre University Course.
The state of Uttar Pradesh had a small tradition of learning, although it had remained mostly confined to the elite class and the religious establishment.

The National Mission for Manuscripts (NAMAMI) is an autonomous organisation under Ministry of Culture, Government of India, established to survey, locate and conserve Indian manuscripts, with an aim to create national resource base for manuscripts, for enhancing their access, awareness and use for educational purposes. The Mission was initiated in February 2003, by the Ministry of Tourism and Culture, Government of India and Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts is the nodal agency for the execution of this project. It creates bibliographic databases of Indian manuscripts and is involved in the conservation and preservation of the manuscripts.
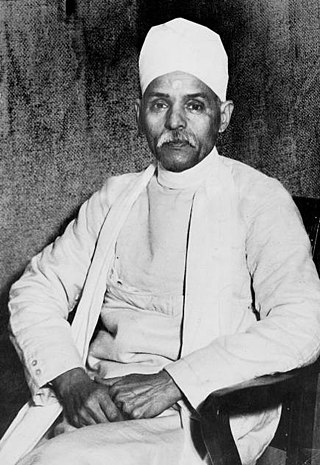
Madan Mohan Malaviya was an Indian scholar, educational reformer and politician notable for his role in the Indian independence movement. He was president of the Indian National Congress three times and the founder of Akhil Bharat Hindu Mahasabha. He was addressed as Pandit, a title of respect.

Faculty of Arts, Banaras Hindu University is a faculty in the Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India which offers courses in Humanities along with various professional and vocational courses except social sciences. It was founded in 1898 and is the oldest and largest faculty in the University. Faculty of Arts was formerly known as the Central Hindu College (1898–1916). In 1916, the Banaras Hindu University grew around the nucleus of the Faculty of Arts.

Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Banaras Hindu University is one of India's premier agricultural colleges located in Varanasi in Uttar Pradesh state. It is one of the three institutes of the Banaras Hindu University.

Shri Vishwanath Mandir also known as Vishwanath Mandir, Vishwanath Temple, New Vishwanath Temple and Birla Temple is another prominent Hindu temple in the holy city of Varanasi. Hindus across India and abroad visit this particular Lord Shiva temple to offer prayer to the Lord Vishwanath for the well-being of their families, and eternal peace. Every Hindu must perform a specific ritualistic homage for the departed souls of their ancestors this requires them to undertake pilgrimage to the holy city of Varanasi. The temple is situated near the Banaras Hindu University. Therefore, the temple site and the neighbourhood is a major attraction among Hindu students and visitors touring Varanasi. Shri Vishwanath Mandir has the tallest temple tower in the world with the Shikhara's height being around 250 feet. The temple is colloquially called VT, an acronym of Vishwanath Temple. The temple is under direct administration of the BHU.
Prithvi Nath Kaula (1924-2009) was an Indian librarian, Library and Information Sciences specialist and author who worked with the Banaras Hindu University in Varanasi, India. Kaula authored sixty books and monographs, six professional journals (founder-editor), over 400 scholarly journal, over 400 peer review, 43 bibliographies and 6000 notes. Kaula was also the recipient of the Padma Shri award in the year 2004.
RajBali Pandey was an Indian writer and author who authored several books on Socio-Religious study of the Hindu sacraments and Vedas.

Bharat Kala Bhavan is a university museum located in Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. It has been instrumental in the dissemination of knowledge on Indian art and culture. It is one of the important touristic attractions in the Banaras Hindu University and in the city of Varanasi.

Faculty of Law, Banaras Hindu University also known as the Law School, BHU is a faculty in the Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India which offers undergraduate, postgraduate and doctorate courses in legal education. It was founded in 1924.

Central Hindu Boys School aka C.H.B.S is a boys secondary school in Kamachha, Bhelupur, Varanasi. It was established in 1898 by Annie Besant. It is associated with Banaras Hindu University.

Faculty of Sanskrit Vidya Dharma Vijnan is a faculty of Banaras Hindu University (BHU) in the city of Varanasi in India. The Faculty of Sanskrit Vidya Dharma Vijnan, also called SVDV, or the Faculty of SVDV, offers bachelor's, master's and doctoral degrees in the studies of ancient Indian Shastra, Sanskrit language and Sanskrit literature. It was founded by Mahamana Pandit Madan Mohan Malviya in 1918.

Pandit Govind Malaviya was an Indian freedom fighter, educationist and politician.

The Banaras Hindu University Act,1915, is an act of Parliament of India, passed on 1 October 1915 and assented by the Viceroy and Governor-General of India on the same day to establish Banaras Hindu University. It was the act number 16 of 1915, and came into force from 1 April 1916 on being published in the Gazette of India on 23 March 1916.

Giridhar Malaviya is the chancellor of Banaras Hindu University and a retired judge of Allahabad High Court.

















