The Potez XV was a French single-engine, two-seat observation biplane designed as a private venture by Louis Coroller and built by Potez and under licence by Podlaska Wytwórnia Samolotów and Plage i Laśkiewicz in Poland.

The Lioré et Olivier LeO 12 was a large biplane designed and produced by the French aircraft manufacturer Lioré et Olivier. Designed for use as a night bomber, it was adapted to other roles, including that of a civilian airliner, following a lack of interest from the French Air Force.

The Wibault Wib 210 C.1 was a single engine, single seat low wing monoplane fighter aircraft, designed and built in France in the late 1920s. Flight tests revealed vibration problems and development was quickly abandoned.
The Wibault 313, Wibault Wib 313 or Penhoët Wibault Wib 313 was a single engine, single seat low wing monoplane fighter aircraft, designed and built in France in the early 1930s. It was entered into a government competitive tender programme but was not ordered.
The Lioré et Olivier LeO 8, Lioré et Olivier LeO 8-Cau 2 or Lioré et Olivier LeO 8 CAN 2 was a French two seat, parasol wing monoplane night fighter and reconnaissance aircraft, built in 1923.

The Potez VIII was a French training aircraft which first flew in 1920. Originally it had a very unusual vertical inline engine and a four-wheeled undercarriage, though the production version was more conventional.
The Potez 27 was a French reconnaissance biplane first flown in 1924. 175 were operated by the Polish Air Force, most built in Poland by PWS under licence. Others went to Romania, where they were also used as light bombers.
The Caudron C.91 was a French single engine biplane with an enclosed passenger cabin seating four. It first flew in 1923.

The Descamps 17 A.2 was a two-seat reconnaissance fighter built under a French government programme of 1923. Two versions, with different engines, were tested and six examples were built under licence by Caudron as the Caudron C.17 A.2.

The Villiers IV or Villiers 4 was a French two seat naval floatplane. Two were built, the first with twin floats and the second with one. The first was short-lived but the second set several world and national records; it later became the Villiers XI.
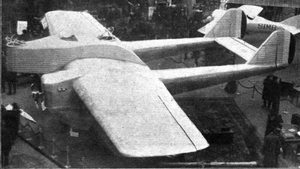
The Buscaylet-de Monge 7-4 was a small, French, twin-boom aircraft without a fuselage, built in the mid-1920s to explore the characteristics of a proposed larger machine.

The Buscaylet-de Monge 7-5 was a twin engine, twin-boom aircraft without a fuselage but with pilot, passenger and fuel accommodated in a thickened wing centre-section. It was designed by Belgian pioneer Louis de Monge and built in France in the mid-1920s.

The Rohrbach Ro VII Robbe was an all-metal, twin engine flying boat built in Germany in the 1920s. It could be adapted to commercial or military rôles.

The Dyle and Bacalan DB-20 was a heavily armoured, all-metal, French ground attack aircraft built in the late 1920s.

The Weymann-Lepère WEL-80 R.2 was a French two seat reconnaissance aircraft built to compete for a 1928 government contract. It was not successful and did not enter production.

The Wibault 260 R.2 was a contender for a French government contract for a long range, two seat reconnaissance aircraft, issued in 1928. There were eight prototypes in the 1931-2 contest and the Wibault was not selected for production.

The Nieuport-Delage NiD 580 R.2 was a contender for a French government contract for a long range, two seat reconnaissance aircraft, issued in 1928. There were eight prototypes in the 1931-2 contest and the NiD 580 was not selected for production.

The SECM-Amiot 130 R.2 was a contender for a French government contract for a long range, two seat reconnaissance aircraft, issued in 1928. There were eight prototypes in the 1931–32 contest and the Amiot 130 was not selected for production.
The Blériot 117 or B-117 was a large, twin-engined French aircraft from the mid-1920s. Heavily armed with three gun positions, it was designed to defend bomber formations against fighter attack. It did not reach production but was developed into the more successful Blériot 127.

The Aviméta 92 was a French, all-metal, five seat monoplane built in the late 1920s. Three different engines were fitted, and one example flew the first non-stop Paris-Algiers flight in preparation for an abandoned trans-Atlantic attempt.