Neuengamme was a network of Nazi concentration camps in northern Germany that consisted of the main camp, Neuengamme, and more than 85 satellite camps. Established in 1938 near the village of Neuengamme in the Bergedorf district of Hamburg, the Neuengamme camp became the largest concentration camp in Northwest Germany. Over 100,000 prisoners came through Neuengamme and its subcamps, 24 of which were for women. The verified death toll is 42,900: 14,000 in the main camp, 12,800 in the subcamps, and 16,100 in the death marches and bombings during the final weeks of World War II. Following Germany's defeat in 1945, the British Army used the site as an internment camp for SS and other Nazi officials. In 1948, the British transferred the land to the Free Hanseatic City of Hamburg, which summarily demolished the camp's wooden barracks and built in its stead a prison cell block, converting the former concentration camp site into two state prisons operated by the Hamburg authorities from 1950 to 2004. Following protests by various groups of survivors and allies, the site now serves as a memorial. It is situated 15 km southeast of the centre of Hamburg.

Kaltenkirchen is a town located 35 km north of Hamburg in Germany. It is part of the Segeberg district, in Schleswig-Holstein. It has about 20,000 inhabitants.

Wandsbek is the second-largest of seven boroughs that make up the city and state of Hamburg, Germany. The name of the district is derived from the river Wandse which passes through here. Wandsbek, which was formerly an independent city, is urban and, along with Eilbek and Marienthal, part of the city's economic and cultural core. In 2020 the population was 442,702, making it the most populous borough in Hamburg.

Breitenfelde is a village in the district of Lauenburg, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated near the Elbe-Lübeck Canal, approx. 5 km southwest of Mölln, and 30 km south of Lübeck.

Neustadt in Holstein is a town in the district of Ostholstein, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, on the Bay of Lübeck 30 km northeast of Lübeck, and 50 km southeast of Kiel.

Wedel is a town in the district of Pinneberg, in Schleswig-Holstein, in northern Germany. It is situated on the right bank of the Elbe, approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Elmshorn, and 17 kilometres (11 mi) west of Hamburg.

Finkenwerder is a quarter of Hamburg, Germany in the borough Hamburg-Mitte. It is the location of the Hamburg Airbus plant and its airport. In 2016 the population was 11,668.

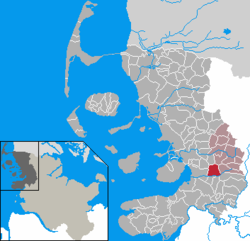
Ladelund is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, in northern Germany.

Glasau is a municipality in the district of Segeberg, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is named after the estate and the manor house of the same name. Sarau is the largest village in the municipality; about half of the population lives there.

[] is a quarter of Hamburg, Germany, and belongs to the borough Harburg. The quarter consists of the old settlements Neugraben and Fischbek, and the more recently constructed area Neuwiedenthal.
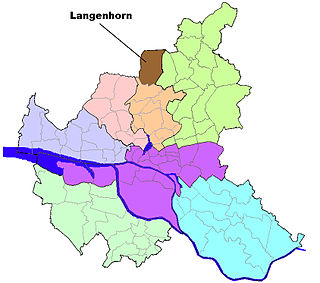
is a quarter in the borough Hamburg-Nord of Hamburg, Germany. In 2020 the population was 46,272.

Poppenbüttel is a quarter in the borough Wandsbek of Hamburg, Germany. In 2020 the population was 24,135.

Kleiner Grasbrook is a quarter of Hamburg, Germany within the borough of Hamburg-Mitte. It is situated on the eponymous island between the Northern and Southern branches of the Elbe river, together with the other quarters of Steinwerder, Veddel and Wilhelmsburg. It almost exclusively consists of facilities of the port of Hamburg. The four quarters are technically all islands of their own, as they are all separated by their own dams. In 2020 the population was 1,120.

Neuengamme is a quarter of Hamburg, Germany, located in the Bergedorf borough, near the river Dove Elbe. In this rural quarter, part of the Vierlande, the population in 2020 was 3,711.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Hamburg, Germany.

Bruus, formerly Brausebart or Brusbart, is a north German card game for four players in two teams of two. It was once highly popular but has since died out except for a few pockets in the state of Schleswig-Holstein. As Brusbart, it was the ancestor of a family of similar games in northern Europe, including Swedish Bräus and Danish Brus which are still played today. Bruus features 'daring and tormenting' which has been said to give the game a certain charm. Once considered the national game of Hamburg, Bruus is a descendant of Karnöffel, the oldest identifiable European card game in the history of playing cards with a continuous tradition of play down to the present day. The game is named after the Bruus or Brusbart, once its top card, but now its second-highest trump.
The Husum-Schwesing subcamp in the Schwesing district of Engelsburg, about five kilometres northeast of Husum, became a satellite of Neuengamme concentration camp on 26 September 1944 and was occupied by prisoners in connection with the construction of the so-called Frisian Wall (Friesenwall). Some 2,500 people from 14 countries were incarcerated here in autumn 1944; 297 prisoners died as a result of forced labour, malnutrition and abuse. The camp was closed on 29 December 1944.
Like other areas under Nazi Germany, Jews were persecuted in the northernmost German state Schleswig-Holstein. Before the Nazis came to power in 1933, an estimated 1,900 Jews lived in Schleswig-Holstein, mostly in Lübeck and Kiel. By the time of Nazi Germany's defeat in 1945, many of Schleswig-Holstein's Jews had been murdered in the Holocaust.
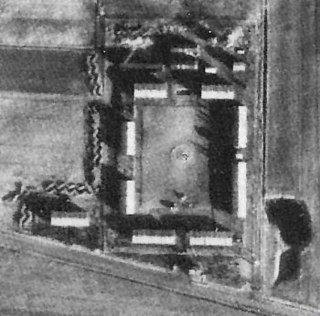
The Ladelund concentration camp, located 20 km north-east of Niebüll on the German-Danish border, was set up as a satellite camp of Neuengamme concentration camp on November 1, 1944, as part of the construction of the so-called Friesenwall. The Friesenwall was a planned but only partially completed fortification that was to be built on the German North Sea coast towards the end of World War II. The concentration camp near Ladelund was responsible for the construction of trenches and gun emplacements for a militarily pointless "blocking position" south of the Danish border. The camp was disbanded on December the 16th, 1944. Within the month and a half that it existed, 300 out of over 2,000 prisoners died.