
Sordariomycetes is a class of fungi in the subdivision Pezizomycotina (Ascomycota). It is the second-largest class of Ascomycota, with a worldwide distribution that mostly accommodates terrestrial based taxa, although several can also be found in aquatic habitats. Some are phytopathogens that can cause leaf, stem, and root diseases in a wide variety of hosts, while other genera can cause diseases in arthropods and mammals.

Cuphophyllus is a genus of agaric fungi in the family Hygrophoraceae. Cuphophyllus species belong to a group known as waxcaps in English, sometimes also waxy caps in North America or waxgills in New Zealand. In Europe, Cuphophyllus species are typical of waxcap grasslands, a declining habitat due to changing agricultural practices. As a result, four species, Cuphophyllus atlanticus, C. colemannianus, C. lacmus, and C. lepidopus are of global conservation concern and are listed as "vulnerable" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.

The Dacrymycetaceae are a family of fungi in the order Dacrymycetales. Species are saprotrophs and occur on dead wood. Their distribution is worldwide. Basidiocarps are ceraceous (waxy) to gelatinous, often yellow to orange, and variously clavarioid, disc-shaped, cushion-shaped, spathulate (spoon-shaped), or corticioid (effused).

Pleosporaceae is a family of sac fungi. They are pathogenic to humans or saprobic on woody and dead herbaceous stems or leaves.

The Fomitopsidaceae are a family of fungi in the order Polyporales. Most species are parasitic on woody plants, and tend to cause brown rots. The name comes from Fomitopsis + -aceae.

The Auriculariaceae are a family of fungi in the order Auriculariales. Species within the family were formerly referred to the "heterobasidiomycetes" or "jelly fungi", since many have gelatinous basidiocarps that produce spores on septate basidia. Around 100 species are known worldwide. All are believed to be saprotrophic, most growing on dead wood. Fruit bodies of several Auricularia species are cultivated for food on a commercial scale, especially in China.
Lanspora is a genus of marine fungi in the family Phomatosporaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1986 by mycologists Kevin D. Hyde and E.B. Gareth Jones with L. coronata as the type, and at that time, only species. Lanspora cylindrospora was added to the genus in 2020.
Hydnomerulius pinastri is a fungal species of the monotypic genus Hydnomerulius within the Paxillaceae family. H. pinastri is a saprophyte whose nutritional mode creates a brown rot through H2O2 decay of cellulose and hemi-cellulose. This species has not been thoroughly studied outside of taxonomic attempts to place it within the fungal tree. As such, its ecological role beyond as a wood decaying agent is unclear at this time. H. pinastri may be referred to colloquially as "spiny dry rot" or "spiny dry rot fungus".
Eichleriella is a genus of fungi in the order Auriculariales. Species produce effused or cupulate, waxy to leathery basidiocarps on wood, with a smooth to spiny surface. The genus contains some twelve species.
Heterochaete is a genus of fungi in the order Auriculariales. Species produce effused, gelatinous, waxy, or leathery basidiocarps on wood, partly or wholly covered in small sterile spines or pegs. The presence of these sterile spines distinguishes the genus from Exidiopsis, species of which are microscopically similar but have smooth basidiocarps.

Heteroradulum is a genus of fungi in the order Auriculariales. Species produce effused, leathery basidiocarps on wood, often pinkish red and partly or wholly covered in small sterile spines. The genus was originally published in 1917 by American mycologist Curtis Gates Lloyd under the facetious pseudonym "McGinty", rendering the name invalid. It was validated a century later to accommodate a group of species formerly placed in the genera Eichleriella or Heterochaete, but not closely related to either.

Gliophorus is a genus of agaric fungi in the family Hygrophoraceae. Gliophorus species belong to a group known as waxcaps in English, sometimes also waxy caps in North America or waxgills in New Zealand. In Europe, Gliophorus species are typical of waxcap grasslands, a declining habitat due to changing agricultural practices. As a result, two species, Gliophorus europerplexus and Gliophorus reginae, are of global conservation concern and are listed as "vulnerable" on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
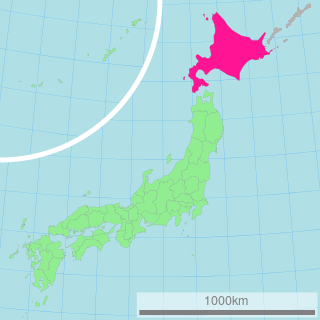
Volvopluteus asiaticus is a species of mushroom in the Pluteaceae family. The cap of this mushroom is about 70–90 mm (2.8–3.5 in) in diameter, greyish brown to brown. The gills start out white but they soon turn pink. The stipe is white and has a volva at the base. Microscopical features and DNA sequence data are of great importance for separating this taxon from related species. V. asiaticus is a saprotrophic fungus that was originally described as growing on the ground, in the humus layer. It is only known from Hokkaido (Japan).
Paralecia is a monotypic fungal genus in the family Cladoniaceae. It contains a single species, the lichenicolous fungus Paralecia pratorum, found in Europe.

Myriostoma calongei is a fungal species in the family Geastraceae. Basidiocarps resemble earthstars, but the spore sac is supported by multiple columns and has multiple ostioles instead of a single, apical ostiole. The fungus was described from Brazil in 2017 as a result of molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences. Previously, it had been identified as Myriostoma coliforme, now known to be restricted to northern, temperate regions. Myriostoma calongei can be distinguished by the conspicuously verrucose endoperidium. The species has also been confirmed from Argentina, Mexico, and the United States.
Adustochaete is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. Species produce effused basidiocarps on wood, typically covered in small sterile spines or pegs. The genus was created as a result of molecular research, based on cladistic analysis of DNA sequences, to accommodate two species from Brazil and Mexico that are not closely related to the older and superficially similar genus Heterochaete. Two additional species, from Brazil and China, have since been described.

Tremellochaete is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. Species produce pustular or lobed, effused, gelatinous basidiocarps on wood, typically covered in small sterile spines or pegs.
Amphistereum is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. Species produce cupulate to effused, leathery basidiocarps on wood. Microscopically, fruit bodies have a dimitic hyphal system. The genus is currently only known from North and South America.
Proterochaete is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. The type and only species, Proterochaete adusta, produces thin, effused, corticioid basidiocarps with a smooth or spiny surface on wood. The species was originally described from North America and is also known from northern Europe and Asia.

Protodaedalea is a genus of fungi in the family Auriculariaceae. Species produce bracket-like basidiocarps on wood with a lamellate (gilled) undersurface. The genus currently comprises two species, both known from Asia.











