
The X Window System is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.

In computing, Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop-sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It transmits the keyboard and mouse input from one computer to another, relaying the graphical-screen updates, over a network.
In computing, TightVNC is a free and open-source remote desktop software server and client application for Linux and Windows. A server for macOS is available under a commercial source code license only, without SDK or binary version provided. Constantin Kaplinsky developed TightVNC, using and extending the RFB protocol of Virtual Network Computing (VNC) to allow end-users to control another computer's screen remotely.
RealVNC is a company that provides remote access software. The software consists of a server and client application for the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) protocol to control another computer's screen remotely.
x11vnc is a Virtual Network Computing (VNC) server program. It allows remote access from a remote client to a computer hosting an X Window session and the x11vnc software, continuously polling the X server's frame buffer for changes. This allows the user to control their X11 desktop from a remote computer either on the user's own network, or from over the Internet as if the user were sitting in front of it. x11vnc can also poll non-X11 frame buffer devices, such as webcams or TV tuner cards, iPAQ, Neuros OSD, the Linux console, and the Mac OS X graphics display. x11vnc is part of the LibVNCServer project and is free software available under the GNU General Public License. x11vnc was written by Karl Runge.
Remote administration refers to any method of controlling a computer from a remote location. Software that allows remote administration is becoming increasingly common and is often used when it is difficult or impractical to be physically near a system in order to use it. A remote location may refer to a computer in the next room or one on the other side of the world. It may also refer to both legal and illegal remote administration.

Apple Remote Desktop (ARD) is a Macintosh application produced by Apple Inc., first released on March 14, 2002, that replaced a similar product called Apple Network Assistant. Aimed at computer administrators responsible for large numbers of computers and teachers who need to assist individuals or perform group demonstrations, Apple Remote Desktop allows users to remotely control or monitor other computers over a network. Mac Pro (2019) and Mac mini with 10Gbps Ethernet have Lights Out Management function are able to power-on by Apple Remote Desktop.
Multiplicity is a computer program that enables one keyboard and mouse to access two or more client computers from a host computer. It was developed for Stardock as part of their ThinkDesk subscription service, but is available separately.
Xvfb or X virtual framebuffer is a display server implementing the X11 display server protocol. In contrast to other display servers, Xvfb performs all graphical operations in virtual memory without showing any screen output. From the point of view of the client, it acts exactly like any other X display server, serving requests and sending events and errors as appropriate. However, no output is shown. This virtual server does not require the computer it is running on to have any kind of graphics adapter, a screen or any input device. Only a network layer is necessary.
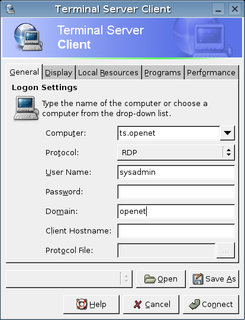
tsclient is a discontinued frontend for rdesktop and other remote desktop tools, which allow remotely controlling one computer from another. It is a GNOME application. Notable visual options include color depth, screen size, and motion blocking.

UltraVNC is an open-source remote-administration/remote-desktop-software utility. The client supports Microsoft Windows and Linux but the server only supports Windows. It uses the VNC protocol to control/access another computer remotely over a network connection.
Desktop sharing is a common name for technologies and products that allow remote access and remote collaboration on a person's computer desktop through a graphical terminal emulator.
In systems management, out-of-band management involves the use of management interfaces for managing and networking equipment. Out-of-band (OOB) is a networking term which refers to having a separate channel of communication which does not travel over the usual data stream.
A home server is a computing server located in a private computing residence providing services to other devices inside or outside the household through a home network or the Internet. Such services may include file and printer serving, media center serving, home automation control, web serving, web caching, file sharing and synchronization, video surveillance and digital video recorder, calendar and contact sharing and synchronization, account authentication, and backup services.

In computing, the term remote desktop refers to a software- or operating system feature that allows a personal computer's desktop environment to be run remotely on one system, while being displayed on a separate client device. Remote desktop applications have varying features. Some allow attaching to an existing user's session and "remote controlling", either displaying the remote control session or blanking the screen. Taking over a desktop remotely is a form of remote administration.
This page is a comparison of notable remote desktop software available for various platforms.

ThinLinc is a cross-platform remote desktop server developed by Cendio AB. The server software and the users' main desktops run on Linux. Clients are available for Linux, Windows, macOS, and a number of thin clients. A browser client using HTML5 technologies is also available.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier, is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to take control of a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS is Microsoft's implementation of thin client architecture, where Windows software, and the entire desktop of the computer running RDS, are made accessible to any remote client machine that supports Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). User interfaces are displayed from the server onto the client system and input from the client system is transmitted to the server - where software execution takes place. This is in contrast to application streaming systems, like Microsoft App-V, in which computer programs are streamed to the client on-demand and executed on the client machine.
CrossLoop was a remote desktop service from CrossLoop Inc., which allowed users to share their computer screens and collaborate with others over the Internet.

Splashtop is a family of remote-desktop software and remote support software, developed by Splashtop Inc. Splashtop enables users to remotely access or remotely support computers from desktop and mobile devices. Splashtop enables remote computer access for businesses, IT support and help desks, MSPs, and educational institutions.







