
Canada has a vast geography that occupies much of the continent of North America, sharing a land border with the contiguous United States to the south and the U.S. state of Alaska to the northwest. Canada stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west; to the north lies the Arctic Ocean. Greenland is to the northeast with a shared border on Hans Island. To the southeast Canada shares a maritime boundary with France's overseas collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the last vestige of New France. By total area, Canada is the second-largest country in the world, after Russia. By land area alone, however, Canada ranks fourth, the difference being due to it having the world's largest proportion of fresh water lakes. Of Canada's thirteen provinces and territories, only two are landlocked while the other eleven all directly border one of three oceans.

The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch 3,000 miles in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Canada, to New Mexico in the Southwestern United States. Depending on differing definitions between Canada and the U.S., its northern terminus is located either in northern British Columbia's Terminal Range south of the Liard River and east of the Trench, or in the northeastern foothills of the Brooks Range/British Mountains that face the Beaufort Sea coasts between the Canning River and the Firth River across the Alaska-Yukon border. Its southernmost point is near the Albuquerque area adjacent to the Rio Grande rift and north of the Sandia–Manzano Mountain Range. Being the easternmost portion of the North American Cordillera, the Rockies are distinct from the tectonically younger Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada, which both lie farther to its west.

The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia south to the Fraser River. The mountain range's name derives from its proximity to the sea coast, and it is often referred to as the Coast Range. The range includes volcanic and non-volcanic mountains and the extensive ice fields of the Pacific and Boundary Ranges, and the northern end of the volcanic system known as the Cascade Volcanoes. The Coast Mountains are part of a larger mountain system called the Pacific Coast Ranges or the Pacific Mountain System, which includes the Cascade Range, the Insular Mountains, the Olympic Mountains, the Oregon Coast Range, the California Coast Ranges, the Saint Elias Mountains and the Chugach Mountains. The Coast Mountains are also part of the American Cordillera—a Spanish term for an extensive chain of mountain ranges—that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western backbone of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica.

The Pacific Coast Ranges are the series of mountain ranges that stretch along the West Coast of North America from Alaska south to Northern and Central Mexico. Although they are commonly thought to be the westernmost mountain range of the continental United States and Canada, the geologically distinct Insular Mountains of Vancouver Island lie farther west.

The Alaska Range is a relatively narrow, 600-mile-long (950 km) mountain range in the southcentral region of the U.S. state of Alaska, from Lake Clark at its southwest end to the White River in Canada's Yukon Territory in the southeast. Denali, the highest mountain in North America, is in the Alaska Range. The range is part of the American Cordillera.

The Canadian Rockies or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera, which is the northern segment of the North American Cordillera, the expansive system of interconnected mountain ranges between the Interior Plains and the Pacific Coast that runs northwest–southeast from central Alaska to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in Mexico.

The Liard River of the North American boreal forest flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows 1,115 km (693 mi) southeast through British Columbia, marking the northern end of the Rocky Mountains and then curving northeast back into Yukon and Northwest Territories, draining into the Mackenzie River at Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The river drains approximately 277,100 km2 (107,000 sq mi) of boreal forest and muskeg.

Alfred Richard Cecil Selwyn, CMG, LL.D, FRS, FGS was a British geologist and public servant, director of the Geological Survey of Victoria from 1852 to 1869, director of the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC) from 1869 to 1894, and President of the Royal Society of Canada from 1895 to 1896.

The Mackenzie Mountains are a Canadian mountain range forming part of the Yukon–Northwest Territories boundary between the Liard and Peel rivers. The range is named in honour of Canada's second prime minister, Alexander Mackenzie. Nahanni National Park Reserve and Nááts'ihch'oh National Park Reserve are in the Mackenzie Mountains.
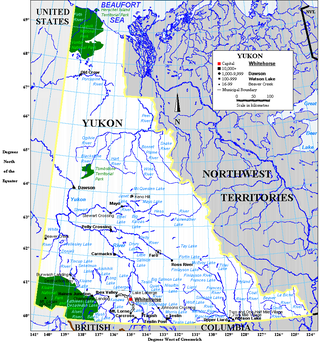
Yukon is in the northwestern corner of Canada and is bordered by Alaska, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories. The sparsely populated territory abounds with natural scenery, snowmelt lakes and perennial white-capped mountains, including many of Canada's highest mountains. The territory's climate is Arctic in territory north of Old Crow, subarctic in the region, between Whitehorse and Old Crow, and humid continental climate south of Whitehorse and in areas close to the British Columbia border. Most of the territory is boreal forest with tundra being the main vegetation zone only in the extreme north and at high elevations.
The Pacific Cordillera, also known as the Western Cordillera or simply The Cordillera, is a top-level physiographic region of Canada, referring mainly to the extensive cordillera system in Western and Northwestern Canada that constitutes the northern part of the North American Cordillera. The mountain ranges in this region were covered during the Pleistocene by the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, the extent of which gives perspective on the geographic extent of this region. The cordillera extends from the Alaska's Brooks and Alaska Ranges, southeast through most of the Yukon and British Columbia as well as the southwestern fringe of Northwest Territories and Alberta, to stretch its margin beyond the Canada–United States border with five extensive lobes reaching into the mountain valleys of Montana and Washington.

The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera, or the Pacific Cordillera, is the North American portion of the American Cordillera, the mountain chain system along the Pacific coast of the Americas. The North American Cordillera covers an extensive area of mountain ranges, intermontane basins, and plateaus in Western and Northwestern Canada, Western United States, and Mexico, including much of the territory west of the Great Plains.

The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province (NCVP), formerly known as the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is a geologic province defined by the occurrence of Miocene to Holocene volcanoes in the Pacific Northwest of North America. This belt of volcanoes extends roughly north-northwest from northwestern British Columbia and the Alaska Panhandle through Yukon to the Southeast Fairbanks Census Area of far eastern Alaska, in a corridor hundreds of kilometres wide. It is the most recently defined volcanic province in the Western Cordillera. It has formed due to extensional cracking of the North American continent—similar to other on-land extensional volcanic zones, including the Basin and Range Province and the East African Rift. Although taking its name from the Western Cordillera, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one. The southmost part of the NCVP has more, and larger, volcanoes than does the rest of the NCVP; further north it is less clearly delineated, describing a large arch that sways westward through central Yukon.

The South Nahanni River is a major tributary of the Liard River, located roughly 500 km (310 mi) west of Yellowknife in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the centerpiece of Nahanni National Park Reserve. It flows from the Mackenzie Mountains in the west, through the Selwyn Mountains, growing as it heads east over the majestic Virginia Falls, and finally empties into the Liard River. The Nahanni has a unique geological history. It was formed when the area was a broad flat plain, forming a winding course typical of flatland rivers. As the mountains lifted, the river cut four deep canyons into the rock, maintaining its eccentric course.
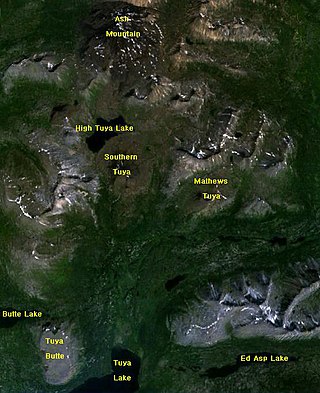
The Tuya Range is a mountain range in the Stikine Ranges of the Cassiar Mountains in the far north of the Canadian province of British Columbia, near its border with the Yukon Territory and to the southwest of Watson Lake, Yukon, which is the nearest major settlement.
The Horseranch Range is a 40 km (25 mi) long north–south trending mountain range in northern British Columbia, Canada, located at the head of the Red River to the northwest of Deadwood Lake. Part of the Dease Plateau of either the Yukon Plateau or Cassiar Mountains system, it contains no glaciers and lies completely above tree line.
The Kotaneelee River is a river in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is a tributary of the Liard River.
The geology of Yukon includes sections of ancient Precambrian Proterozoic rock from the western edge of the proto-North American continent Laurentia, with several different island arc terranes added through the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic, driving volcanism, pluton formation and sedimentation.
















