| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name N-[2-(Diethylamino)ethyl]-4-(methanesulfonamido)benzamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Sematilide |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H23N3O3S | |
| Molar mass | 313.42 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
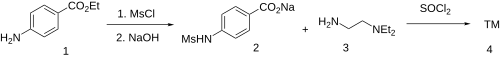
Sematilide is an antiarrhythmic agent. It is the same structure as for procainamide, differing only by the placement of a mesyl sulfonamide moiety to the anilino nitrogen.