
A pilus is a hair-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria and archaea. The terms pilus and fimbria can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term pilus for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All pili in the latter sense are primarily composed of pilin proteins, which are oligomeric.

Escherichia coli, also known as E. coli, is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes (EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. The harmless strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, and can benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2, and preventing colonisation of the intestine with pathogenic bacteria, having a mutualistic relationship. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for 3 days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.

A spirochaete or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetes, which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled cells. Spirochaetes are chemoheterotrophic in nature, with lengths between 3 and 500 μm and diameters around 0.09 to at least 3 μm.

Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 validly described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture in vitro and availability of an increasing number of Pseudomonas strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include P. aeruginosa in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen P. syringae, the soil bacterium P. putida, and the plant growth-promoting P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae, and P. graminis.

Serratia is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria of the family Yersiniaceae. According to the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing Nomenclature (LPSN), there are currently 19 species of Serratia that are credibly published with accurate names as of 2020: S. aquatilis, S. entomophila, S. ficaria, S. fonticola, S. grimesii, S. liquefaciens, S. marcescens, S. microhaemolytica, S. myotis, S. nematodiphila, S. odoriferae, S. oryzae, S. plymuthica, S. proteamaculans, S. quinivorans corrig, S. rubidaea, S. symbiotica, S. ureilytica, S. vespertilionis. They are typically 1–5 μm in length, do not produce spores, and can be found in water, soil, plants, and animals. Some members of this genus produce a characteristic red pigment, prodigiosin, and can be distinguished from other members of the order Enterobacterales by their unique production of three enzymes: DNase (nucA), lipase, and gelatinase (serralysin). Serratia was thought to be a harmless environmental bacteria until it was discovered that the most common species in the genus, S. marcescens, is an opportunistic pathogen of many animals, including humans. In humans, S. marcescens is mostly associated with nosocomial, or hospital-acquired, infections, but can also cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis. S. marcescens is frequently found in showers, toilet bowls, and around wetted tiles as a pinkish to red biofilm but only causes disease in immunocompromised individuals. Aside from S marcescens, some rare strains of the Serratia species S. plymuthica, S. liquefaciens, S. rubidaea, and S. odoriferae have been shown to cause infection such as osteomyelitis and endocarditis.

Serratia marcescens is a species of rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacteria in the family Yersiniaceae. It is a facultative anaerobe and an opportunistic pathogen. It was discovered in 1819 by Bartolomeo Bizio in Padua, Italy. S. marcescens is commonly involved in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), particularly catheter-associated bacteremia, urinary tract infections, and wound infections, and is responsible for 1.4% of HAI cases in the United States. It is commonly found in the respiratory and urinary tracts of hospitalized adults and in the gastrointestinal systems of children.

Proteus is a genus of Gram-negative Proteobacteria. Proteus bacilli are widely distributed in nature as saprophytes, being found in decomposing animal matter, sewage, manure soil, the mammalian intestine, and human and animal feces. They are opportunistic pathogens, commonly responsible for urinary and septic infections, often nosocomial.
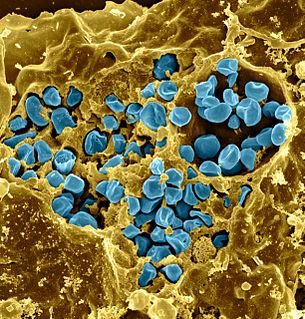
Francisella tularensis is a pathogenic species of Gram-negative coccobacillus, an aerobic bacterium. It is nonspore-forming, nonmotile, and the causative agent of tularemia, the pneumonic form of which is often lethal without treatment. It is a fastidious, facultative intracellular bacterium, which requires cysteine for growth. Due to its low infectious dose, ease of spread by aerosol, and high virulence, F. tularensis is classified as a Tier 1 Select Agent by the U.S. government, along with other potential agents of bioterrorism such as Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, and Ebola virus. When found in nature, Francisella tularensis can survive for several weeks at low temperatures in animal carcasses, soil, and water. In the laboratory, F. tularensis appears as small rods, and is grown best at 35–37 °C.
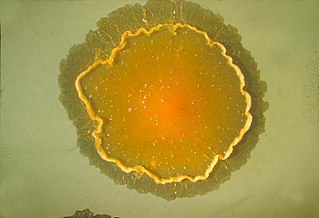
Mycobacterium marinum is a slow growing mycobacterium (SGM) belonging to the genus Mycobacterium and the phylum Actinobacteria. The strain marinum was first identified by Aronson in 1926 and it is observed as a pathogenic mycobacterium. For example, tuberculosis like infections in fish (mycobacteriosis) and skin lesions in humans.

Aeromonas hydrophila is a heterotrophic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium mainly found in areas with a warm climate. This bacterium can be found in fresh or brackish water. It can survive in aerobic and anaerobic environments, and can digest materials such as gelatin and hemoglobin. A. hydrophila was isolated from humans and animals in the 1950s. It is the best known of the species of Aeromonas. It is resistant to most common antibiotics and cold temperatures and is oxidase- and indole-positive. Aeromonas hydrophila also has a symbiotic relationship as gut flora inside of certain leeches, such as Hirudo medicinalis.
Mycobacterium heckeshornense is a species of the phylum Actinobacteria, belonging to the genus Mycobacterium.

Enterobacter cloacae is a clinically significant Gram-negative, facultatively-anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium.
Streptococcus uberis is a species of Streptococcus.
Cedecea is a genus of extremely rare bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The name of this genus was derived from CDC, the abbreviation for the Centers for Disease Control where the initial members of this genus were discovered. This genus resembles no other group of Enterobacteriaceae. Cedecea bacteria are Gram-negative, bacillus in shape, motile, nonencapsulated, and non-spore-forming. The strains of Cedecea appear to be similar to those of Serratia. Both Cedecea and Serratia are lipase positive and resistant to colistin and cephalothin; however, Cedecea is unable to hydrolyze gelatin or DNA.
Hamiltonella defensa is a species of bacteria. It is maternally or sexually transmitted and lives as an endosymbiont of whiteflies and aphids, meaning that it lives within a host, protecting its host from attack. It does this through bypassing the host's immune responses by protecting its host against parasitoid wasps. However, H. defensa is only defensive if infected by a virus. H. defensa shows a relationship with Photorhabdus species, together with Regiella insecticola. Together with other endosymbionts, it provides aphids protection against parasitoids. It is known to habitate Bemisia tabaci.
Streptomyces reticuliscabiei is a streptomycete bacterium species that is associated with netted scab in potatoes. Its type strain is CFBP 4517T. It is considered to be part of a cluster together with S. turgidiscabies, however they cause different diseases, the former involved in common scab.
Vibrio tapetis is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium, the causative agent of the brown ring disease that affects cultured clams. B1090 is the type strain.

Costelytra giveni, commonly known as New Zealandgrass grub, is a scarab beetle that is endemic to New Zealand and is a prevalent pasture pest.
Yersinia entomophaga is a species of bacteria that was originally isolated from the diseased larvae of the New Zealand grass grub, Costelytra zealandica. The type strain is MH96. It is currently being studied for biological pest control of insect pests like the porina moth, Wiseana cervinata.

Costelytra zealandica is a species of scarab beetle found in forested areas of greater Wellington. It was originally described in 1846 by the British entomologist Adam White as Rhisotrogus zealandicus from a specimen obtained during the Ross expedition. The species is known to feed on roots of plants and trees, so is considered a pest for many farm pastures.












