Related Research Articles

A chordate is an animal of the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess 5 synapomorphies, or primary characteristics, at some point during their larval or adulthood stages that distinguish them from all other taxa. These 5 synapomorphies include a notochord, dorsal hollow nerve cord, endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. Chordates get their name from their characteristic “notochord”, which plays a significant role in chordate structure and movement. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation.

The Cambrian Period was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 55.6 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 541 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 485.4 mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. Sedgwick identified the layer as part of his task, along with Roderick Murchison, to subdivide the large "Transition Series", although the two geologists disagreed for a while on the appropriate categorization. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of lagerstätte sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biology surpasses that of some later periods.
Hallucigenia is a genus of Cambrian animal known from articulated fossils in Burgess Shale-type deposits in Canada and China, and from isolated spines around the world. The generic name reflects the type species' unusual appearance and eccentric history of study; when it was erected as a genus, H. sparsa was reconstructed as an enigmatic animal upside down and back to front. Hallucigenia is later recognized as part of lobopodians, a grade of paleozoic panarthropods where the velvet worms, water bears and arthropods arose.

A sclerite is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates.

Microdictyon is an extinct armoured worm-like animal coated with net-like scleritic plates, known from the Early Cambrian Maotianshan shale of Yunnan China and other parts of the world. Microdictyon is part of the ill-defined taxon – Lobopodia – that includes several other odd worm-like animals that resembling worm with legs, such as Hallucigenia, Onychodictyon, Cardiodictyon, Luolishania, and Paucipodia. The isolated sclerites of Microdictyon are known from other Lower Cambrian deposits. Microdictyon sclerites appear to have moulted; one sclerite seems to have been preserved during ecdysis.

Panarthropoda is a proposed animal clade containing the extant phyla Arthropoda, Tardigrada and Onychophora. Panarthropods also including extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians ("Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members (stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum though to be arose. Although the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well. Common characteristics of the Panarthropoda include a segmented body, paired ladder-like ventral nervous system and the presence of paired appendages correlated with body segments.

Ottoia is a stem-group archaeopriapulid worm known from Cambrian fossils. Although priapulid-like worms from various Cambrian deposits are often referred to Ottoia on spurious grounds, the only clear Ottoia macrofossils come from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia, which was deposited 508 million years ago. Microfossils extend the record of Ottoia throughout the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin, from the mid- to late- Cambrian. A few fossil finds are also known from China.

The Kaili Formation is a stratigraphic formation which was deposited during the Lower and Middle Cambrian. The formation is approximately 200 metres (660 ft) thick and was named after the city Kaili in the Guizhou province of southwest China.

Parapeytoia was a prehistoric animal that lived over 530 million years ago in the Maotianshan shales of prehistoric China. It was interpreted as an anomalocaridid (radiodont) with legs, but later studies reveal it was a megacheiran, a group of arthropods which are no longer thought to be closely related to the radiodonts.
The Pioche Shale is an Early to Middle Cambrian Burgess shale-type Lagerstätte in Nevada. It spans the Early–Middle Cambrian boundary; fossils from the Early Cambrian are preserved in botryoidal hematite, whereas those from the Middle Cambrian are preserved in the more familiar carbon films, and very reminiscent of the Chengjiang County preservation.
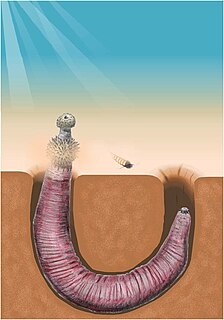
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid-like worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte. The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids. It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic. Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins, they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous. They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.

The palaeoscolecids are a group of extinct ecdysozoan worms resembling armoured priapulids. They are known from the Lower Cambrian to the late Silurian; they are mainly found as disarticulated sclerites, but are also preserved in many of the Cambrian lagerstätten. They take their name from the typifying genus Palaeoscolex.

Louisella is a genus of worm known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale. It was originally described by Charles Walcott in 1911 as a holothurian echinoderm, and represents a senior synonym of Miskoia, which was originally described as an annelid. 48 specimens of Louisella are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise < 0.1% of the community. It has been stated to have palaeoscolecid-like sclerites, though this is not in fact the case.
Hyolithellus is a conical tubular fossil from the Cambrian, originally considered a hyolith but since reinterpreted tentatively as an annelid worm.

Paleontology in Wisconsin refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Wisconsin. The state has fossils from the Precambrian, much of the Paleozoic, and the later part of the Cenozoic. Most of the Paleozoic rocks are marine in origin. Because of the thick blanket of Pleistocene glacial sediment that covers the rock strata in most of the state, Wisconsin’s fossil record is relatively sparse. In spite of this, certain Wisconsin paleontological occurrences provide exceptional insights concerning the history and diversity of life on Earth.
Eximipriapulus is a genus of priapulid-like organisms, perhaps belonging to the crown group, known from the Chengjiang biota.
Gapparodus is an extinct genus of conodonts in the family Furnishinidae. Gapparodus gapparites is a species of the Early Cambrian of Shuijingtuo Formation in China.
Protoconodonts are an extinct taxonomic group of conodonts or, possibly, Chaetognaths.
Protohertzina is a genus of conodonts or, possibly, Chaetognaths, found at the beginning of the Cambrian explosion.
References
- ↑ Yuning Yang; Xingliang Zhang; Yuanlong Zhao; Yiru Qi; Linhao Cui (2018). "New paleoscolecid worms from the early Cambrian north margin of the Yangtze Platform, South China". Journal of Paleontology. 92: 49–58. doi:10.1017/jpa.2017.50. S2CID 134657064.